Abstract
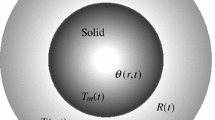
In this paper we study the melting of a spherical nanoparticle. To match with experimental data, the model includes several new features such as size-dependent latent heat and a cooling boundary condition at the boundary. Melt temperature variation and density change are also included. A novel form of Stefan condition is used to determine the position of the melt front. Results show that melting times can be significantly faster than those predicted by previous theoretical models, primarily due to the latent heat variation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexiades, V., Solomon, A.D.: Mathematical Modeling of Melting and Freezing Processes. Hemisphere, Washington, DC (1992)
Bachels, T., Güntherodt, H.-J., Schäfer, R.: Melting of isolated tin nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 1250–1253 (2000)
Back, J.M.: Stefan problems for melting nanoscaled particles. Ph.D. thesis, U. Queensland (2014). http://eprints.qut.edu.au/79905/1/Julian_Back_Thesis.pdf
Buffat, P., Borel, J.-P.: Size effect on the melting temperature of gold particles. Phys. Rev. A 13, 2287–2298 (1976)
Ercolessi, F., Andreoni, W., Tosatti, E.: Melting of small gold particles: mechanism and size effects. Phys. Rev. Lett. 66, 911–914 (1991)
Font, F., Myers, T.G., Mitchell, S.L.: A mathematical model for nanoparticle melting with density change. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 18, 233–243 (2014)
Jiang, H., Moon, K.-S., Dong, H., Hua, F., Wong, C.: Size-dependent melting properties of tin nanoparticles. Chem. Phys. Lett. 429, 492–496 (2006)
Lai, S., Guo, J., Petrova, V., Ramanath, G., Allen, L.: Size-dependent melting properties of small tin particles: nanocalorimetric measurements. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 99–102 (1996)
Myers, T.G.: Mathematical modelling of phase change at the nanoscale. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 76, 59–62 (2016)
Ribera, H., Myers, T.G.: A mathematical model for nanoparticle melting with size-dependent latent heat and melt temperature. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 20(11), 147 (2016)
Shin, J.-H., Deinert, M.R.: A model for the latent heat of melting in free standing metal nanoparticles. J. Chem. Phys. 140, 164707 (2014)
Sun, J., Simon, S.: The melting behavior of aluminum nanoparticles. Thermochim. Acta 463, 32–40 (2007)
Tolman, R.C.: The effect of droplet size on surface tension. J. Chem. Phys. 17, 333 (1949)
Xiong, S., Qi, W., Cheng, Y., Huang, B., Wang, M., Li, Y.: Universal relation for size dependent thermodynamic properties of metallic nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 13, 10652–10660 (2011)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge that the research leading to these results has received funding from “la Caixa” Foundation. TM acknowledges financial support from the Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación grant MTM2014-56218.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ribera, H., Myers, T.G. (2017). A Model for Nanoparticle Melting with a Newton Cooling Condition and Size-Dependent Latent Heat. In: Quintela, P., et al. Progress in Industrial Mathematics at ECMI 2016. ECMI 2016. Mathematics in Industry(), vol 26. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-63082-3_47
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-63082-3_47
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-63081-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-63082-3
eBook Packages: Mathematics and StatisticsMathematics and Statistics (R0)