Abstract
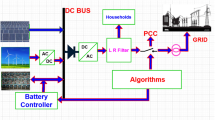
With the emergence of smart grid (SG), the residents have the opportunity to integrate renewable energy sources (RESs) and take part in demand side management (DSM). In this regard, we design energy management control unit (EMCU) based on genetic algorithm (GA), binary particle swarm optimization (BPSO), and wind driven optimization (WDO) to schedule appliances in presence of objective function, constraints, control parameters, and comparatively evaluate the performance. For energy pricing, real time pricing (RTP) plus inclined block rate (IBR) is used. RESs integration to SG is a challenge due stochastic nature of RE. In this paper, two techniques are addressed to handle the stochastic nature of RE. First one is energy storage system (ESS) which smooths out variation in RE generation. Second one is the trading/cooperation of excess generation to neighboring consumers. The simulation results show that WDO perform more efficiently than unscheduled in terms of reduction in: electricity cost, the tradeoff between electricity cost and waiting time, and peak to average ratio (PAR). Moreover, incorporation of RESs into SG design increase the revenue and reduce carbon emission.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saad, W., et al.: Game-theoretic methods for the smart grid: An overview of microgrid systems, demand-side management, and smart grid communications. IEEE Sig. Process. Mag. 29(5), 86–105 (2012)
Logenthiran, T., Srinivasan, D., Shun, T.Z.: Demand side management in smart grid using heuristic optimization. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 3(3), 1244–1252 (2012)
Roselund, C., Bernhardt, J.: Lessons learned along Europes road to renewables. IEEE Spect., 4 May 2015
Liang, X., Bagen, B.: Probabilistic planning and risk analysis for renewable power generation system. In: Proceedings of CIGRE Canada Conference, Winnipeg, Manitoba, 31 August–2 September 2015
Hart, E.K., Jacobson, M.Z.: A Monte Carlo approach to generator portfolio planning and carbon emissions assessments of systems with large penetrations of variable renewables. Renew. Energy 36(8), 22782286 (2011)
Khalid, A., et al.: Optimized home load management with reduced cost and peak to average ratio in smart grid with demand side management. Energies 10(1), 1–28 (2016)
Lakshminarayana, S., Quek, T.Q.S., VincentPoor, H.: Cooperation and storage tradeoffs in power grids with renewable energy resources. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 32(7), 1386–1397 (2014)
Member Sr, X.L.: Emerging power quality challenges due to integration of renewable energy sources. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 9994(c) (2016)
Li, T., Member, S., Dong, M., Member, S.: Real-time residential-side joint energy storage management and load scheduling with renewable integration. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 3053(c), 115 (2016)
Zhao, Z., Lee, W.C., Shin, Y., Member, S., Song, K.: An optimal power scheduling method for demand response in home energy management system. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 4(3), 13911400 (2013)
Rahim, S., et al.: Exploiting heuristic algorithms to efficiently utilize energy management controllers with renewable energy sources. Energy Build. 129, 452–470 (2016)
Ullah, I., et al.: An incentive-based optimal energy consumption scheduling algorithm for residential users. Procedia Comput. Sci. 52, 851–857 (2015)
Arun, S.L., Selvan, M.P.: Intelligent residential energy management system for dynamic demand response in smart buildings. IEEE Syst. J. 19379234, 112 (2017)
Wang, L., Wang, Z., Yang, R.: Intelligent multiagent control system for energy and comfort management in smart and sustainable buildings. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 3(2), 605–617 (2012)
Ramchurn, S.D., Vytelingum, P., Rogers, A., Jennings, N.: Agent-based control for decentralised demand side management in the smart grid, p. 512 (2011)
Awais, M., et al.: An efficient genetic algorithm based demand side management scheme for smart grid. In: 2015 18th International Conference on Network-Based Information Systems (NBiS). IEEE (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Hafeez, G., Javaid, N., Zahoor, S., Fatima, I., Ali Khan, Z., Safeerullah (2018). Energy Efficient Integration of Renewable Energy Sources in Smart Grid. In: Barolli, L., Zhang, M., Wang, X. (eds) Advances in Internetworking, Data & Web Technologies. EIDWT 2017. Lecture Notes on Data Engineering and Communications Technologies, vol 6. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-59463-7_55
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-59463-7_55
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-59462-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-59463-7
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)