Abstract
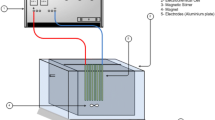
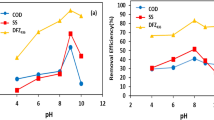
Microwave technology as new aided tool has been applied on waste water treatment and metallurgical fields. This paper explores the affected factors such as microwave power, microwave irradiation time, polyaluminium chloride (PAC) amount and addition of phosphoric acid on treatment of Blast Furnace gas washing water by utilization of coagulation associated with microwave. Through the orthogonal experiment, the optimum experimental parameters were obtained in the course of treatment of 300 ml Blast Furnace gas washing wastewater: 396 W microwave power, 2 min of microwave irradiation time, 0.12 ml Added PAC and 0.8 ml added phosphoric acid. It indicates the affected factors in descending order on removal of SS in BF gas’s washing water: Added PAC level, added phosphoric acid level, time of microwave irradiation, and microwave power while those parameters that can affect suspended solids(SS)’s hardness reduction in descending order are added phosphoric acid level, added PAC level, time of microwave irradiation, and microwave power. Also, it demonstrates those parameters that can affect washing water’s turbidity in descending order: Added PAC level, time of microwave irradiation, added phosphoric acid level, and microwave power. The results showed that PAC coagulation associated with microwave on treatment of Blast Furnace gas washing wastewater has several benefits: short treatment time, strong sedimentation velocity and other excellent characteristics, it can effectively remove suspended solids in wastewater, the SS hardness and turbidity can be reduced.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.-L. Wang, J.-C. Gu, Application of microwave technology in water treatment. Adm. Tech. Environ. Monit. 19(4), 36–39 (2007). (in Chinese)
X.-P. Qu, X.-H. Wu, X.-H. Lu et al., Treatment of coking wastewater by activated carbon combined microwave irradiation. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. 22(4), 79–81 (2005)
M.-X. Fan, Z. Zhang, Study on treatment of coke plant wastewater by microwave combined activated carbon and fenton reagent oxidation process. J. Hubei Univ. Technol. 26(5), 36–39 (2011)
Z.-W. Deng, P. Yu, Y.-B. Luo, Study on removal of COD and colority from coking wastewater by microwave combined fenton reagent. Ind. Water Wastewater 40(6), 40–43 (2009)
H.-C. Xu, X.-J. Xu, X.-H. Xu, Effect and mechanical analysis of washing coal water by microwave. J. Qingdao Technol. Univ. 29(1), 60–62 (2008)
L. Lin, X.-H. Lu, Q.-Y. Li, Effect on removal of ammonia nitrogen and COD in coking wastewater by microwave combined activated carbon. J. Yangtze River Sci. Res. Inst. 28(11), 19–21 (2011)
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported by funds sponsored by National Science Foundation of China (NO. 51474124, NO. 51504131, NO. 51504132 NO. 51674139 NO. 51604148) and Anshan Science and technology project (NO. 4104).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhang, J., Pang, Q., He, Z., Tian, C., Wu, T. (2017). Treatment of Blast Furnace Gas Washing Water by Utilization of Coagulation Associated with Microwave. In: Wang, S., Free, M., Alam, S., Zhang, M., Taylor, P. (eds) Applications of Process Engineering Principles in Materials Processing, Energy and Environmental Technologies. The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-51091-0_55
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-51091-0_55
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-51090-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-51091-0
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)