Abstract
This Chapter, dealing with nuclear and electronic angular momenta in magnetic fields, further develops topics already discussed in Chaps. 4 and 5. The new arguments involve some aspects of spin statistics and of magnetic resonance (namely how to drive the angular and magnetic moments and to change their components along a magnetic field). The magnetic resonance experiment in most cases is equivalent to induce magnetic dipole transitions among Zeeman-like levels.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Notes
- 1.
It can be remarked that having assumed a site-independent interaction, this model corresponds to the mean-field description, or equivalently to an infinite range of the interactions (see Chap. 17).
- 2.
It is reminded that
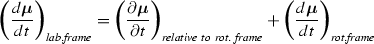
the latter being
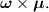 For \(H_x= H_1 cos\omega _{RF}t\), \(H_y= H_1 sin\omega _{\textit{RF}}t\) and \(H_z= H_0\), in the rotating frame the magnetic field is constant: \(H'_x= H_1\), \(H'_y=0\) and \(H'_z= H_0\) (see Fig. 6.6).
For \(H_x= H_1 cos\omega _{RF}t\), \(H_y= H_1 sin\omega _{\textit{RF}}t\) and \(H_z= H_0\), in the rotating frame the magnetic field is constant: \(H'_x= H_1\), \(H'_y=0\) and \(H'_z= H_0\) (see Fig. 6.6). - 3.
\(<M|I_{+}|M-1>\,= \sqrt{(I+M)(I-M+1)}, <M|I_{-}|M+1>\,= \sqrt{(I-M)(I+M+1)},\) all other elements being zero.
- 4.
\(ln(1+e^{-x})\simeq ln2 + ln\left( 1- \frac{x}{2} + \frac{x^2}{4}\right) \simeq ln2 - \frac{x}{2} + \frac{x^2}{8}.\)
Specific References and Further Reading
D.J. Amit and Y. Verbin, Statistical Physics - An Introductory course, (World Scientific, 1999).
C.P. Slichter, Principles of Magnetic Resonance, (Springer Verlag, Berlin, 1990).
H. Haken and H.C. Wolf, Atomic and Quantum Physics, (Springer Verlag, Berlin, 1987).
B.H. Bransden and C.J. Joachain, Physics of atoms and molecules, (Prentice Hall, 2002).
D. Budker, D.F. Kimball and D.P. De Mille, Atomic Physics - An Exploration Through Problems and Solutions, (Oxford University Press, 2004).
B. Cagnac and J.C. Pebay - Peyroula, Physique atomique, tome 2, (Dunod Université, Paris, 1971).
R. Fieschi e R. De Renzi, Struttura della Materia, (La Nuova Italia Scientifica, Roma, 1995).
A.P. Guimaraes, Magnetism and Magnetic Resonance in Solids, (J. Wiley and Sons, 1998).
C. Kittel, Elementary Statistical Physics, (J. Wiley and Sons, 1958).
M.A. Morrison, T.L. Estle and N.F. Lane, Quantum States of Atoms, Molecules and Solids, (Prentice -Hall Inc., New Jersey, 1976).
H. Semat, Introduction to Atomic and Nuclear Physics, (Chapman and Hall LTD, 1962).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Rigamonti, A., Carretta, P. (2015). Spin Statistics, Magnetic Resonance, Spin Motion and Echoes. In: Structure of Matter. UNITEXT for Physics. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-17897-4_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-17897-4_6
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-17896-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-17897-4
eBook Packages: Physics and AstronomyPhysics and Astronomy (R0)


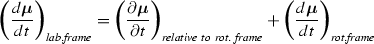

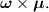 For
For