Summary
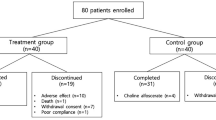
Inhibition of acetylcholinesterase improves symptoms of dementia in patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD). Dementia in PD has a cumulative incidence of up to 80% and is mainly caused by a distinct cholinergic deficit. Objectives of this investigator initiated multicenter open label trial were to confirm the efficacy of donepezil in the treatment of dementia in PD patients and to investigate the tolerability and safety of donepezil. The Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE)-score significantly increased in patients, who finished the trial. A detailed analysis of the various items of the MMSE revealed, that only task performance of orientation and recall significantly improved. Scores of the short syndrome test and the Clinical Global Impression Scale improved, motor impairment did not increase. Only 14 out of 24 PD patients finished the trial due to predominant onset of vomiting, nausea, dizziness and confusion. This may result from the titration regime of donepezil, that allows only 5 and 10mg dosages. Participants with premature study termination had a significant longer duration of PD, less motivation and sleep disturbances at night. Treatment with donepezil was only effective in PD patients with dementia, who experience nearly no side effects from the drug.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarsland D, Tandberg E, Larsen JP, Cummings JL (1996) Frequency of dementia in Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 53: 538–542
Bohnen N, Kaufer D, Hendrickson R, Ivanco L, Moore R, DeKosky S (2004) Effects of donepezil on motor function in patients with Alzheimer disease. J Clin Psychopharmacol 24: 354–356
Di Lazzaro, V, Oliviero A, Pilato F, Saturno E, Dileone M, Marra C, Daniele A, Ghirlanda S, Gainotti G, Tonali PA (2004) Motor cortex hyperexcitability to transcranial magnetic stimulation in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75: 555–559
Edwards K, Therriault OJ, Gorman C (2004) Switching from donepezil or rivastigmine to galantamine in clinical practice. J Am Geriatr Soc 52:1965
Emre M(2004) Dementia in Parkinson’s disease: cause and treatment. Curr Opin Neurol 17: 399–404
Emre M, Aarsland D, Albanese A, Byrne EJ, Deuschl G, De Deyn PP, Durif F, Kulisevsky J, van Laar T, Lees A, Poewe W, Robillard A, Rosa MM, Wolters E, Quarg P, Tekin S, Lane R (2004) Rivastigmine for dementia associated with Parkinson’s disease. N Engl J Med 351: 2509–2518
Giladi N, Shabtai H, Gurevich T, Benbunan B, Anca M, Korczyn AD (2003) Rivastigmine (Exelon) for dementia in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neurol Scand 108: 368–373
Goetz CG, LeWitt PA, Weidenman M (2003) Standardized training tools for the UPDRS activities of daily living scale: newly available teaching program. Mov Disord 18: 1455–1458
Hegerl U, Mergl R, Henkel V, Gallinat J, Kotter G, Muller-Siecheneder F, Pogarell O, Juckel G, Schroter A, Bahra R, Emir B, Laux G, Moller HJ (2003) Kinematic analysis of the effects of donepezil hydrochloride on hand motor function in patients with Alzheimer dementia. J Clin Psychopharmacol 23: 214–216
Heinze M, Andreae D, Grohmann R (2002) Rivastigmin and impaired motor function. Pharmacopsychiatry 35: 79–80
Hughes AJ, Daniel SE, Kilford L, Lees AJ (1992) Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: a clinico-pathological study of 100 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 55: 181–184
Koch HJ, Gurtler K, Szecsey A (2005) Correlation of Mini-Mental-State-Examination (MMSE), Syndrom-Kurztest (SKT) and Clock test (CT) scores in patients with cognitive impairment assessed by means of multiple regression and response surface analysis. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 40: 7–14
Leroi I, Brandt J, Reich SG, Lyketsos CG, Grill S, Thompson R, Marsh L (2004) Randomized placebo-controlled trial of donepezil in cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 19: 1–8
Overall JE, Schaltenbrand R (1992) The SKT neuropsychological test battery. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol 5: 220–227
Poirier J (2002) Evidence that the clinical effects of cholinesterase inhibitors are related to potency and targeting of action. Int J Clin Pract Suppl: 6–19
Richard IH, Justus AW, Greig NH, Marshall F, Kurlan R (2002) Worsening of motor function and mood in a patient with Parkinson’s disease after pharmacologic challenge with oral rivastigmine. Clin Neuropharmacol 25: 296–299
Tiraboschi P, Hansen LA, Alford M, Sabbagh MN, Schoos B, Masliah E, Thal LJ, Corey-Bloom J (2000) Cholinergic dysfunction in diseases with Lewy bodies. Neurology 54: 407–411
Wahle M, Haller S, Spiegel R (1996) Validation of the NOSGER (Nurse’s Observation Scale for Geriatric Patients): reliability and validity of a caregiver rating instrument. Int Psychogeriatr 8: 525–547
Weinstock M (1999) Selectivity of cholinesterase inhibition — Clinical implications for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. CNS Drugs 12: 307–323
Werber EA, Rabey JM (2001) The beneficial effect of cholinesterase inhibitors on patients suffering from Parkinson’s disease and dementia. J Neural Transm 108: 1319–1325
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2006 Springer-Verlag
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Muüller, T., Welnic, J., Fuchs, G., Baas, H., Ebersbach, G., Reichmann, H. (2006). The DONPAD-study — Treatment of dementia in patients with Parkinson’s disease with donepezil. In: Parvez, H., Riederer, P. (eds) Oxidative Stress and Neuroprotection. Journal of Neural Transmission. Supplementa, vol 71. Springer, Vienna. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-211-33328-0_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-211-33328-0_3
Publisher Name: Springer, Vienna
Print ISBN: 978-3-211-33327-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-211-33328-0
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)