Abstract
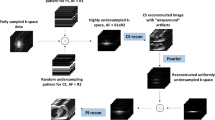
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (CMR) has been widely used in clinical practice for the medical diagnosis of cardiac diseases. However, the long acquisition time hinders its development in real-time applications. Here, we propose a novel self-consistency guided multi-prior learning framework named k-t CLAIR to exploit spatiotemporal correlations from highly undersampled data for accelerated dynamic parallel MRI reconstruction. The k-t CLAIR progressively reconstructs faithful images by leveraging multiple complementary priors learned in the x-t, x-f, and k-t domains in an iterative fashion, as dynamic MRI exhibits high spatiotemporal redundancy. Additionally, k-t CLAIR incorporates calibration information for prior learning, resulting in a more consistent reconstruction. Experimental results on cardiac cine and T1W/T2W images demonstrate that k-t CLAIR achieves high-quality dynamic MR reconstruction in terms of both quantitative and qualitative performance.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal, H.K., Mani, M.P., Jacob, M.: MoDL: model-based deep learning architecture for inverse problems. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 38(2), 394–405 (2018)
Akçakaya, M., Moeller, S., Weingärtner, S., Uğurbil, K.: Scan-specific robust artificial-neural-networks for k-space interpolation (RAKI) reconstruction: database-free deep learning for fast imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 81(1), 439–453 (2019)
Eo, T., Jun, Y., Kim, T., Jang, J., Lee, H.J., Hwang, D.: Kiki-net: cross-domain convolutional neural networks for reconstructing undersampled magnetic resonance images. Magn. Reson. Med. 80(5), 2188–2201 (2018)
Fabian, Z., Tinaz, B., Soltanolkotabi, M.: Humus-net: hybrid unrolled multi-scale network architecture for accelerated MRI reconstruction. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 35, 25306–25319 (2022)
Griswold, M.A., et al.: Generalized autocalibrating partially parallel acquisitions (GRAPPA). Magn. Reson. Med. Official J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 47(6), 1202–1210 (2002)
Hammernik, K., et al.: Learning a variational network for reconstruction of accelerated MRI data. Magn. Reson. Med. 79(6), 3055–3071 (2018)
Han, Y., Sunwoo, L., Ye, J.C.: k-space deep learning for accelerated MRI. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 39(2), 377–386 (2020)
Jung, H., Sung, K., Nayak, K.S., Kim, E.Y., Ye, J.C.: k-t FOCUSS: a general compressed sensing framework for high resolution dynamic MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. Official J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 61(1), 103–116 (2009)
Küstner, T., et al.: Cinenet: deep learning-based 3D cardiac cine MRI reconstruction with multi-coil complex-valued 4D spatio-temporal convolutions. Sci. Rep. 10(1), 13710 (2020)
Lingala, S.G., Hu, Y., DiBella, E., Jacob, M.: Accelerated dynamic MRI exploiting sparsity and low-rank structure: kt SLR. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 30(5), 1042–1054 (2011)
Lustig, M., Donoho, D., Pauly, J.M.: Sparse MRI: the application of compressed sensing for rapid MR imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. Official J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 58(6), 1182–1195 (2007)
Lustig, M., Pauly, J.M.: Spirit: iterative self-consistent parallel imaging reconstruction from arbitrary k-space. Magn. Reson. Med. 64(2), 457–471 (2010)
Otazo, R., Candes, E., Sodickson, D.K.: Low-rank plus sparse matrix decomposition for accelerated dynamic MRI with separation of background and dynamic components. Magn. Reson. Med. 73(3), 1125–1136 (2015)
Pruessmann, K.P., Weiger, M., Scheidegger, M.B., Boesiger, P.: Sense: sensitivity encoding for fast MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. Official J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 42(5), 952–962 (1999)
Qin, C., et al.: Complementary time-frequency domain networks for dynamic parallel MR image reconstruction. Magn. Reson. Med. 86(6), 3274–3291 (2021)
Qin, C., Schlemper, J., Caballero, J., Price, A.N., Hajnal, J.V., Rueckert, D.: Convolutional recurrent neural networks for dynamic MR image reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 38(1), 280–290 (2018)
Qin, C., Schlemper, J., Duan, J., Seegoolam, G., Price, A., Hajnal, J., Rueckert, D.: k-t NEXT: dynamic MR image reconstruction exploiting spatio-temporal correlations. In: Shen, D., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2019. LNCS, vol. 11765, pp. 505–513. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32245-8_56
Ran, M., et al.: MD-Recon-Net: a parallel dual-domain convolutional neural network for compressed sensing MRI. IEEE Trans. Radiat. Plasma Med. Sci. 5(1), 120–135 (2020)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Ryu, K., Alkan, C., Choi, C., Jang, I., Vasanawala, S.: K-space refinement in deep learning MR reconstruction via regularizing scan specific spirit-based self consistency. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 4008–4017 (2021)
Schlemper, J., Caballero, J., Hajnal, J.V., Price, A.N., Rueckert, D.: A deep cascade of convolutional neural networks for dynamic MR image reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 37(2), 491–503 (2017)
Sriram, A., et al.: End-to-end variational networks for accelerated MRI reconstruction. In: Martel, A.L., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2020. LNCS, vol. 12262, pp. 64–73. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59713-9_7
Sriram, A., Zbontar, J., Murrell, T., Zitnick, C.L., Defazio, A., Sodickson, D.K.: Grappanet: combining parallel imaging with deep learning for multi-coil MRI reconstruction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 14315–14322 (2020)
Wang, C., et al.: Recommendation for cardiac magnetic resonance imaging-based phenotypic study: imaging part. Phenomics 1, 151–170 (2021)
Wang, C., et al.: Cmrxrecon: an open cardiac MRI dataset for the competition of accelerated image reconstruction. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.10836 (2023)
Wang, S., et al.: Dimension: dynamic MR imaging with both k-space and spatial prior knowledge obtained via multi-supervised network training. NMR Biomed. 35(4), e4131 (2022)
Yang, G., et al.: Dagan: deep de-aliasing generative adversarial networks for fast compressed sensing MRI reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 37(6), 1310–1321 (2017)
Zbontar, J., et al.: fastMRI: an open dataset and benchmarks for accelerated MRI. arXiv preprint arXiv:1811.08839 (2018)
Zhang, L., Li, X., Chen, W.: Camp-net: consistency-aware multi-prior network for accelerated MRI reconstruction. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.11238 (2023)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from Innovation and Technology Commission of the Hong Kong SAR (MRP/046/20X); and by a Faculty Innovation Award from the Faculty of Medicine of The Chinese University of Hong Kong.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhang, L., Chen, W. (2024). k-t CLAIR: Self-consistency Guided Multi-prior Learning for Dynamic Parallel MR Image Reconstruction. In: Camara, O., et al. Statistical Atlases and Computational Models of the Heart. Regular and CMRxRecon Challenge Papers. STACOM 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14507. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-52448-6_30
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-52448-6_30
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-52447-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-52448-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)