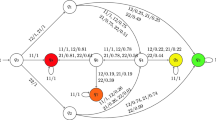
Abstract
Model checking of strategic abilities is a notoriously hard problem, even more so in the realistic case of agents with imperfect information. Assume-guarantee reasoning can be of great help here, providing a way to decompose the complex problem into a small set of exponentially easier subproblems. In this paper, we propose two schemes for assume-guarantee verification of alternating-time temporal logic with imperfect information. We prove the soundness of both schemes, and discuss their completeness. We illustrate the method by examples based on known benchmarks, and show experimental results that demonstrate the practical benefits of the approach.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
Provided in the supplementary material, available at https://github.com/agrprima22/sup.
- 2.
By a slight abuse of notation, the valuation of a single variable is identified with its value.
References
Alur, R., Henzinger, T.: Reactive modules. Form. Meth. Syst. Des. 15(1), 7–48 (1999)
Alur, R., Henzinger, T., Kupferman, O.: Alternating-time temporal logic. J. ACM 49, 672–713 (2002)
Alur, R., Henzinger, T.A., Mang, F.Y.C., Qadeer, S., Rajamani, S.K., Tasiran, S.: MOCHA: modularity in model checking. In: Hu, A.J., Vardi, M.Y. (eds.) CAV 1998. LNCS, vol. 1427, pp. 521–525. Springer, Heidelberg (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BFb0028774
Alur, R., Henzinger, T., Vardi, M.: Parametric real-time reasoning. In: Proceedings of STOC, pp. 592–601. ACM (1993)
Bulling, N., Dix, J., Jamroga, W.: Model checking logics of strategic ability: complexity. In: Dastani, M., Hindriks, K., Meyer, J.J. (eds.) Specification and Verification of Multi-agent Systems, pp. 125–159. Springer, Boston (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-6984-2_5
Busard, S., Pecheur, C., Qu, H., Raimondi, F.: Reasoning about memoryless strategies under partial observability and unconditional fairness constraints. Inf. Comp. 242, 128–156 (2015)
Cermák, P., Lomuscio, A., Murano, A.: Verifying and synthesising multi-agent systems against one-goal strategy logic specifications. In: Proceedings of AAAI, pp. 2038–2044 (2015)
Chatterjee, K., Henzinger, T.A.: Assume-guarantee synthesis. In: Grumberg, O., Huth, M. (eds.) TACAS 2007. LNCS, vol. 4424, pp. 261–275. Springer, Heidelberg (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-71209-1_21
Chen, Y.-F., et al.: Comparing learning algorithms in automated assume-guarantee reasoning. In: Margaria, T., Steffen, B. (eds.) ISoLA 2010. LNCS, vol. 6415, pp. 643–657. Springer, Heidelberg (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-16558-0_52
Clarke, E., Long, D., McMillan, K.: Compositional model checking. In: Proceeding of LICS, pp. 353–362. IEEE Computer Society Press (1989)
Devereux, B.: Compositional reasoning about aspects using alternating-time logic. In: Proceedings of FOAL, pp. 45–50 (2003)
Dima, C., Tiplea, F.: Model-checking ATL under imperfect information and perfect recall semantics is undecidable. CoRR abs/1102.4225 (2011)
Fijalkow, N., Maubert, B., Murano, A., Vardi, M.: Assume-guarantee synthesis for prompt linear temporal logic. In: Proceedings of IJCAI, pp. 117–123. ijcai.org (2020)
Finkbeiner, B., Passing, N.: Compositional synthesis of modular systems. Innov. Syst. Softw. Eng. 18, 1–15 (2022)
Giannakopoulou, D., Pasareanu, C., Barringer, H.: Component verification with automatically generated assumptions. Autom. Softw. Eng. 12(3), 297–320 (2005)
Guelev, D., Dima, C., Enea, C.: An alternating-time temporal logic with knowledge, perfect recall and past: axiomatisation and model-checking. J. Appl. Non-Classical Log. 21(1), 93–131 (2011)
He, F., Mao, S., Wang, B.-Y.: Learning-based assume-guarantee regression verification. In: Chaudhuri, S., Farzan, A. (eds.) CAV 2016. LNCS, vol. 9779, pp. 310–328. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-41528-4_17
Henzinger, T.A., Qadeer, S., Rajamani, S.K.: You assume, we guarantee: methodology and case studies. In: Hu, A.J., Vardi, M.Y. (eds.) CAV 1998. LNCS, vol. 1427, pp. 440–451. Springer, Heidelberg (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BFb0028765
Hoare, C.: An axiomatic basis for computer programming. Commun. ACM 12(10), 576–580 (1969)
Huang, X., van der Meyden, R.: Symbolic model checking epistemic strategy logic. In: Proceedings of AAAI, pp. 1426–1432 (2014)
Jamroga, W., Kim, Y., Kurpiewski, D., Ryan, P.Y.A.: Towards model checking of voting protocols in UPPAAL. In: Krimmer, R., et al. (eds.) E-Vote-ID 2020. LNCS, vol. 12455, pp. 129–146. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-60347-2_9
Jamroga, W., Knapik, M., Kurpiewski, D., Mikulski, Ł.: Approximate verification of strategic abilities under imperfect information. Artif. Int. 277, 103172 (2019)
Jamroga, W., Penczek, W., Sidoruk, T.: Strategic abilities of asynchronous agents: Semantic side effects and how to tame them. In: Proceedings of KR, pp. 368–378 (2021)
Jones, C.: Specification and design of (parallel) programs. In: Proceedings of IFIP, pp. 321–332. North-Holland/IFIP (1983)
Kong, S., Jung, Y., David, C., Wang, B.-Y., Yi, K.: Automatically inferring quantified loop invariants by algorithmic learning from simple templates. In: Ueda, K. (ed.) APLAS 2010. LNCS, vol. 6461, pp. 328–343. Springer, Heidelberg (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-17164-2_23
Kurpiewski, D., Marmsoler, D.: Strategic logics for collaborative embedded systems. SICS Soft. Int. Cyber-Phys. Syst. 34(4), 201–212 (2019)
Kurpiewski, D., Pazderski, W., Jamroga, W., Kim, Y.: STV+reductions: towards practical verification of strategic ability using model reductions. In: Proceedings of AAMAS, pp. 1770–1772. ACM (2021)
Kurpiewski, D., Mikulski, Ł., Jamroga, W.: STV+AGR: towards verification of strategic ability using assume-guarantee reasoning. In: Proceedings of PRIMA (2022)
Kwiatkowska, M., Norman, G., Parker, D., Qu, H.: Assume-guarantee verification for probabilistic systems. In: Esparza, J., Majumdar, R. (eds.) TACAS 2010. LNCS, vol. 6015, pp. 23–37. Springer, Heidelberg (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-12002-2_3
Lomuscio, A., Qu, H., Raimondi, F.: MCMAS: an open-source model checker for the verification of multi-agent systems. Int. J. Soft. Tools Tech. Trans. 19(1), 9–30 (2017)
Lomuscio, A., Strulo, B., Walker, N., Wu, P.: Assume-guarantee reasoning with local specifications. In: Dong, J.S., Zhu, H. (eds.) ICFEM 2010. LNCS, vol. 6447, pp. 204–219. Springer, Heidelberg (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-16901-4_15
Lomuscio, A., Strulo, B., Walker, N., Wu, P.: Assume-guarantee reasoning with local specifications. Int. J. Found. Comput. Sci. 24(4), 419–444 (2013)
Mikulski, Ł., Jamroga, W., Kurpiewski, D.: Towards assume-guarantee verification of strategic ability. In: Proceedings of of AAMAS 2022, pp. 1702–1704. IFAAMAS (2022)
Mogavero, F., Murano, A., Perelli, G., Vardi, M.: Reasoning about strategies: on the model-checking problem. ACM Trans. Comp. Log. 15(4), 1–42 (2014)
Owicki, S., Gries, D.: Verifying properties of parallel programs: an axiomatic approach. Commun. ACM 19(5), 279–285 (1976)
Pnueli, A.: In transition from global to modular temporal reasoning about programs. In: Apt, K.R. (ed.) Logics and Models of Concurrent Systems. NATO ASI Series, vol. 13, pp. 123–144. Springer, Heidelberg (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-82453-1_5
Schobbens, P.: Alternating-time logic with imperfect recall. Electr. Not. Theor. Comput. Sci. 85(2), 82–93 (2004)
Acknowledgement
The work was supported by NCBR Poland and FNR Luxembourg under the PolLux/FNR-CORE project STV (POLLUX-VII/1/2019), and the CHIST-ERA grant CHIST-ERA-19-XAI-010 by NCN Poland (2020/02/Y/ST6/00064). The work of Damian Kurpiewski was also supported by the CNRS IEA project MoSART.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Mikulski, Ł., Jamroga, W., Kurpiewski, D. (2023). Assume-Guarantee Verification of Strategic Ability. In: Aydoğan, R., Criado, N., Lang, J., Sanchez-Anguix, V., Serramia, M. (eds) PRIMA 2022: Principles and Practice of Multi-Agent Systems. PRIMA 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 13753. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-21203-1_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-21203-1_11
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-21202-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-21203-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)