Abstract
A general overview of the existing difference ring theory for symbolic summation is given. Special emphasis is put on the user interface: the translation and back translation of the corresponding representations within the term algebra and the formal difference ring setting. In particular, canonical (unique) representations and their refinements in the introduced term algebra are explored by utilizing the available difference ring theory. Based on that, precise input-output specifications of the available tools of the summation package Sigma are provided.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Notes
- 1.
For a ring
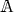 we denote by
we denote by 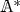 the set of units. If
the set of units. If 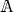 is a field, this means
is a field, this means  .
. - 2.
We also write p instead of f ⊙ p if f = 1; similarly we write f instead of f ⊙ p if p = 1.
- 3.
The sum-product reduced form is not necessary, but simplifies the proof given on page 25.
- 4.
In general, we might need a larger field
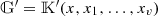 or
or 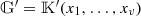 where the field
where the field 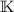 is extended to
is extended to  .
. - 5.
Note that
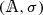 is a difference ring extension of
is a difference ring extension of 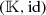 .
. - 6.
If t is an A-monomial, we have \(\operatorname {ev}(t,n)=\alpha ^n\).
- 7.
This step is not necessary for the proof, but avoids unneccesary copies of APS-monomials. When we refine this construction later, this step will be highly relevant.
- 8.
Here we get
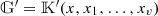 or
or 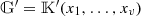 where
where 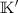 is a field extension of
is a field extension of 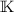 ; if
; if 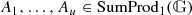 , one can restrict to the special case
, one can restrict to the special case 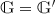 .
. - 9.
For an alternative algorithm we refer to [118, Section 6].
- 10.
If the extension is basic, we only need the case k = 1.
- 11.
Since W is depth-optimal, it follows in particular that d(G′) ≤d(G).
References
J. Ablinger, Extensions of the AZ-algorithm and the package MultiIntegrate, in Anti-Differentiation and the Calculation of Feynman Amplitudes, ed. by J. Blümlein, C. Schneider, Texts and Monographs in Symbolic Computuation (Springer, Berlin, 2021). arXiv:2101.11385.
J. Ablinger, J. Blümlein, C. Schneider, Harmonic sums and polylogarithms generated by cyclotomic polynomials. J. Math. Phys. 52(10), 1–52 (2011). arXiv:1007.0375
J. Ablinger, A. Behring, J. Blümlein, A. De Freitas, A. von Manteuffel, C. Schneider, The 3-loop pure singlet heavy flavor contributions to the structure function F 2(x, Q 2) and the anomalous dimension. Nucl. Phys. B 890, 48–151 (2014). arXiv:1409.1135
J. Ablinger, J. Blümlein, C.G. Raab, C. Schneider, Iterated binomial sums and their associated iterated integrals. J. Math. Phys. 55(112301), 1–57 (2014). arXiv:1407.1822
J. Ablinger, J. Blümlein, A. De Freitas, A. Hasselhuhn, A. von Manteuffel, M. Round, C. Schneider, F. Wissbrock, The transition matrix element A gq(N) of the variable flavor number scheme at \(O(\alpha _s^3)\). Nucl. Phys. B 882, 263–288 (2014). arXiv:1402.0359
J. Ablinger, A. Behring, J. Blümlein, A. De Freitas, A. Hasselhuhn, A. von Manteuffel, M. Round, C. Schneider, F. Wißbrock, Heavy flavour corrections to polarised and unpolarised deep-inelastic scattering at 3-loop order, in Proceedings of QCD Evolution 2016, vol. PoS(QCDEV2016)052 (2016), pp. 1–16. arXiv:1611.01104
J. Ablinger, A. Behring, J. Blümlein, A. De Freitas, C. Schneider, Algorithms to solve coupled systems of differential equations in terms of power series, in Proceedings of Loops and Legs in Quantum Field Theory - LL 2016, ed. by J. Blümlein, P. Marquard, T. Riemann, vol. PoS(LL2016)005 (2016), pp. 1–15. arXiv:1608.05376
J. Ablinger, A. Behring, J. Blümlein, A. De Freitas, A. von Manteuffel, C. Schneider, Calculating three loop ladder and V-topologies for massive operator matrix elements by computer algebra. Comput. Phys. Commun. 202, 33–112 (2016). arXiv:1509.08324
J. Ablinger, J. Blümlein, A. De Freitas, C. Schneider, A toolbox to solve coupled systems of differential and difference equations, in Proceedings of the 13th International Symposium on Radiative Corrections (Applications of Quantum Field Theory to Phenomenology), vol. PoS(RADCOR2015)060 (2016), pp. 1–13. arXiv:1601.01856
J. Ablinger, A. Behring, J. Blümlein, A. De Freitas, A. von Manteuffel, C. Schneider, The three-loop splitting functions \(P_{qg}^{(2)}\) and \(P_{gg}^{(2, N_F)}\). Nucl. Phys. B 922, 1–40 (2017). arxiv:1705.01508
J. Ablinger, J. Blümlein, A.De Freitas, M. van Hoeij, E. Imamoglu, C. Raab, C.-S. Radu, C. Schneider, Iterated elliptic and hypergeometric integrals for Feynman diagrams. J. Math. Phys. 59(062305), 1–55 (2018). arXiv:1706.01299
J. Ablinger, J. Blümlein, P. Marquard, N. Rana, C. Schneider, Heavy quark form factors at three loops in the planar limit. Phys. Lett. B 782, 528–532 (2018). arXiv:1804.07313
J. Ablinger, J. Blümlein, A. De Freitas, A. Goedicke, C. Schneider, K. Schönwald, The two-mass contribution to the three-loop gluonic operator matrix element \(A_{gg,Q}^{(3)}\). Nucl. Phys. B 932, 129–240 (2018). arXiv:1804.02226
J. Ablinger, J. Blümlein, A. De Freitas, M. Saragnese, C. Schneider, K. Schönwald, The three-loop polarized pure singlet operator matrix element with two different masses. Nucl. Phys. B 952(114916), 1–18 (2020). arXiv:1911.11630
J. Ablinger, J. Blümlein, C. Schneider, Analytic and algorithmic aspects of generalized harmonic sums and polylogarithms. J. Math. Phys. 54(8), 1–74 (2013). arXiv:1302.0378
J. Ablinger, C. Schneider, Algebraic independence of sequences generated by (cyclotomic) harmonic sums. Ann. Combin. 22(2), 213–244 (2018). arXiv:1510.03692
J. Ablinger, C. Schneider, Solving linear difference equations with coefficients in rings with idempotent representations, in Proceedings of the 2021 International Symposium on Symbolic and Algebraic Computation (Proc. ISSAC 21), ed. by M. Mezzarobba (2021), pp. 27–34. arXiv:2102.03307.
S.A. Abramov, On the summation of rational functions. Zh. vychisl. mat. Fiz. 11, 1071–1074 (1971)
S.A. Abramov, The rational component of the solution of a first-order linear recurrence relation with a rational right-hand side. U.S.S.R. Comput. Maths. Math. Phys. 15, 216–221 (1975). Transl. from Zh. vychisl. mat. mat. fiz. 15, pp. 1035–1039 (1975)
S.A. Abramov, Rational solutions of linear differential and difference equations with polynomial coefficients. U.S.S.R. Comput. Math. Math. Phys. 29(6), 7–12 (1989)
S.A. Abramov, M. Bronstein, Hypergeometric dispersion and the orbit problem, in Proceedings of ISSAC’00, ed. by C. Traverso (ACM Press, New York, 2000)
S.A. Abramov, M. Petkovšek, D’Alembertian solutions of linear differential and difference equations, in Proceedings of ISSAC’94, ed. by J. von zur Gathen (ACM Press, New York, 1994), pp. 169–174
S.A. Abramov, M. Petkovšek, Polynomial ring automorphisms, rational (w, σ)-canonical forms, and the assignment problem. J. Symb. Comput. 45(6), 684–708 (2010)
S.A. Abramov, E.V. Zima, D’Alembertian solutions of inhomogeneous linear equations (differential, difference, and some other), in Proceedings of ISSAC’96 (ACM Press, New York, 1996), pp. 232–240
S.A. Abramov, P. Paule, M. Petkovšek, q-Hypergeometric solutions of q-difference equations. Discrete Math. 180(1–3), 3–22 (1998)
S.A. Abramov, M. Bronstein, M. Petkovšek, C. Schneider, On rational and hypergeometric solutions of linear ordinary difference equations in Π Σ∗-field extensions. J. Symb. Comput. 107, 23–66 (2021). arXiv:2005.04944 [cs.SC]
L. Adams, C. Bogner, A. Schweitzer, S. Weinzierl, The kite integral to all orders in terms of elliptic polylogarithms. J. Math. Phys. 57(12), 122302 (2016)
G.E. Andrews, P. Paule, C. Schneider, Plane partitions VI: Stembridge’s TSPP theorem. Adv. Appl. Math. 34(4), 709–739 (2005)
M. Apagodu, D. Zeilberger, Multi-variable Zeilberger and Almkvist-Zeilberger algorithms and the sharpening of Wilf-Zeilberger theory. Adv. Appl. Math. 37, 139–152 (2006)
M. Barkatou, On rational solutions of systems for linear differential equations. J. Symb. Comput. 28, 547–567 (1999)
A. Bauer, M. Petkovšek, Multibasic and mixed hypergeometric Gosper-type algorithms. J. Symb. Comput. 28(4–5), 711–736 (1999)
A. Behring, J. Blümlein, A. De Freitas, A. Hasselhuhn, A. von Manteuffel, C. Schneider, The \(O(\alpha _s^3)\) heavy flavor contributions to the charged current structure function xF 3(x, Q 2) at large momentum transfer. Phys. Rev. D 92(114005), 1–19 (2015). arXiv:1508.01449
A. Behring, J. Blümlein, A. De Freitas, A. von Manteuffel, C. Schneider, The 3-loop non-singlet heavy flavor contributions to the structure function g 1(x, Q 2) at large momentum transfer. Nucl. Phys. B 897, 612–644 (2015). arXiv:1504.08217
A. Behring, J. Blümlein, G. Falcioni, A. De Freitas, A. von Manteuffel, C. Schneider, The asymptotic 3-loop heavy flavor corrections to the charged current structure functions \(F_L^{W^+-W^-}(x,Q^2)\) and \(F_2^{W^+-W^-}(x,Q^2)\).Phys. Rev. D 94(11), 1–19 (2016). arXiv:1609.06255
A. Behring, J. Blümlein, A. De Freitas, A. Goedicke, S. Klein, A. von Manteuffel, C. Schneider, K. Schönwald, The polarized three-loop anomalous dimensions from on-shell massive operator matrix elements. Nucl. Phys. B 948(114753), 1–41 (2019). arXiv:1908.03779
J. Blümlein, Algebraic relations between harmonic sums and associated quantities. Comput. Phys. Commun. 159(1), 19–54 (2004). arXiv:hep-ph/0311046
J. Blümlein, S. Kurth, Harmonic sums and Mellin transforms up to two-loop order. Phys. Rev. D60, 014018 (1999)
J. Blümlein, C. Schneider, The method of arbitrarily large moments to calculate single scale processes in quantum field theory. Phys. Lett. B 771, 31–36 (2017). arXiv:1701.04614
J. Blümlein, C. Schneider, Analytic computing methods for precision calculations in quantum field theory. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 33(1830015), 1–35 (2018). arXiv:1809.02889
J. Blümlein, A. Hasselhuhn, C. Schneider, Evaluation of multi-sums for large scale problems, in Proceedings of RADCOR 2011, vol. PoS(RADCOR2011)32 (2012), pp. 1–9. arXiv:1202.4303
J. Blümlein, M. Kauers, S. Klein, C. Schneider, Determining the closed forms of the \(O(a_s^3)\) anomalous dimensions and Wilson coefficients from Mellin moments by means of computer algebra. Comput. Phys. Commun. 180, 2143–2165 (2009). arXiv:0902.4091
J. Blümlein, S. Klein, C. Schneider, F. Stan, A symbolic summation approach to Feynman integral calculus. J. Symb. Comput. 47, 1267–1289 (2012). arXiv:1011.2656
J. Blümlein, M. Round, C. Schneider, Refined holonomic summation algorithms in particle physics, in Advances in Computer Algebra. WWCA 2016., ed. by E. Zima, C. Schneider. Springer Proceedings in Mathematics & Statistics, vol. 226 (Springer, Berlin, 2018), pp. 51–91. arXiv:1706.03677
J. Blümlein, P. Marquard, N. Rana, C. Schneider, The heavy fermion contributions to the massive three loop form factors. Nucl. Phys. B 949(114751), 1–97 (2019). arXiv:1908.00357
J. Blümlein, P. Paule, C. Schneider (Eds.), Elliptic Integrals, Elliptic Functions and Modular Forms in Quantum Field Theory. Texts & Monographs in Symbolic Computation (Springer, Berlin, 2019)
J. Blümlein, P. Marquard, C. Schneider, A refined machinery to calculate large moments from coupled systems of linear differential equations, in 14th International Symposium on Radiative Corrections (RADCOR2019), ed. by D. Kosower, M. Cacciari, POS(RADCOR2019)078 (2020), pp. 1–13. arXiv:1912.04390
J. Broedel, C. Duhr, F. Dulat, L. Tancredi, Elliptic polylogarithms and iterated integrals on elliptic curves. II. An application to the sunrise integral. Phys. Rev. D97, 116009 (2018)
M. Bronstein, Symbolic Integration I, Transcendental Functions (Springer, Berlin, 1997)
M. Bronstein, On solutions of linear ordinary difference equations in their coefficient field. J. Symb. Comput. 29(6), 841–877 (2000)
B. Buchberger, R. Loos, Algebraic simplification, in Computer Algebra (Springer, Vienna, 1983), pp. 11–43
S. Chen, R. Feng, G. Fu, Z. Li, On the structure of compatible rational functions, in Proceedings of ISSAC 2011 (2011), pp. 91–98
W.Y.C. Chen, Q.-H. Hou, H.-T. Jin, The Abel-Zeilberger algorithm. Electron. J. Combin. 18(2), Paper 17 (2011)
S. Chen, M. Jaroschek, M. Kauers, M.F. Singer, Desingularization explains order-degree curves for ore operators, in Proceedingsd of ISSAC’13, ed. by M. Kauers (2013), pp. 157–164
K.G. Chetyrkin, F.V. Tkachov, Integration by parts: the algorithm to calculate beta functions in 4 loops. Nucl. Phys. B 192, 159–204 (1981)
F. Chyzak, An extension of Zeilberger’s fast algorithm to general holonomic functions. Discrete Math. 217, 115–134 (2000)
F. Chyzak, M. Kauers, B. Salvy, A non-holonomic systems approach to special function identities, in Proceedings of ISSAC’09, ed. by J. May (2009), pp. 111–118
R.M. Cohn, Difference Algebra (Wiley, Hoboken, 1965)
A.I. Davydychev, M.Yu. Kalmykov, Massive Feynman diagrams and inverse binomial sums. Nucl. Phys. B 699, 3–64 (2004)
G. Ge, Algorithms related to the multiplicative representation of algebraic numbers. Ph.D. Thesis, Univeristy of California at Berkeley (1993)
S. Gerhold, Uncoupling systems of linear ore operator equations. Master’s Thesis, RISC, J. Kepler University Linz (2002)
R.W. Gosper, Decision procedures for indefinite hypergeometric summation. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 75, 40–42 (1978)
C. Hardouin, M.F. Singer, Differential Galois theory of linear difference equations. Math. Ann. 342(2), 333–377 (2008)
P.A. Hendriks, M.F. Singer, Solving difference equations in finite terms. J. Symb. Comput. 27(3), 239–259 (1999)
J.M. Henn, Multiloop integrals in dimensional regularization made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 251601 (2013)
M. Karr, Summation in finite terms. J. ACM 28, 305–350 (1981)
M. Karr, Theory of summation in finite terms. J. Symb. Comput. 1, 303–315 (1985)
M. Kauers, Summation algorithms for stirling number identities. J. Symb. Comput. 42(10), 948–970 (2007)
M. Kauers, C. Schneider, Application of unspecified sequences in symbolic summation, in Proceedings of ISSAC’06., ed. by J. Dumas (ACM Press, New York, 2006), pp. 177–183
M. Kauers, C. Schneider, Indefinite summation with unspecified summands. Discrete Math. 306(17), 2021–2140 (2006)
M. Kauers, C. Schneider, Symbolic summation with radical expressions, in Proceedings of ISSAC’07, ed. by C. Brown (2007), pp. 219–226
M. Kauers, C. Schneider, Automated proofs for some stirling number identities. Electron. J. Combin. 15(1), 1–7 (2008). R2
M. Kauers, B. Zimmermann, Computing the algebraic relations of c-finite sequences and multisequences. J. Symb. Comput. 43(11), 787–803 (2008)
M. Kauers, M. Jaroschek, F. Johansson, Ore polynomials in Sage, in Computer Algebra and Polynomials, ed. by J. Gutierrez, J. Schicho, M. Weimann. Lecture Notes in Computer Science (2014), pp. 105–125
C. Koutschan, Creative telescoping for holonomic functions, in Computer Algebra in Quantum Field Theory: Integration, Summation and Special Functions, ed. by C. Schneider, J. Blümlein. Texts and Monographs in Symbolic Computation (Springer, Berlin, 2013), pp. 171–194. arXiv:1307.4554
C. Krattenthaler, C. Schneider, Evaluation of binomial double sums involving absolute values, in Algorithmic Combinatorics: Enumerative Combinatorics, Special Functions and Computer Algebra, in Honour of Peter Paule on his 60th Birthday, ed. by V. Pillwein, C. Schneider. Texts and Monographs in Symbolic Computuation (Springer, Berlin, 2020), pp. 249–295. arXiv:1607.05314
S. Laporta, High precision calculation of multiloop Feynman integrals by difference equations. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A15, 5087–5159 (2000)
S.A. Larin, F. Tkachov, J.A.M. Vermaseren, The FORM version of Mincer. Technical Report NIKHEF-H-91-18, NIKHEF, Netherlands (1991)
R.N. Lee, Reducing differential equations for multiloop master integrals. JHEP 04, 108 (2015)
J. Liouville, Mémoire sur l’intégration d’une classe de fonctions transcendantes. J. Reine Angew. Math. 13, 93–118 (1835)
J. Middeke, C. Schneider, Denominator bounds for systems of recurrence equations using Π Σ-extensions, in Advances in Computer Algebra: In Honour of Sergei Abramov’s 70th Birthday, ed. by C. Schneider, E. Zima. Springer Proceedings in Mathematics & Statistics, vol. 226 (Springer, Berlin, 2018), pp. 149–173. arXiv:1705.00280.
S.O. Moch, P. Uwer, S. Weinzierl, Nested sums, expansion of transcendental functions, and multiscale multiloop integrals. J. Math. Phys. 6, 3363–3386 (2002)
I. Nemes, P. Paule, A canonical form guide to symbolic summation, in Advances in the Design of Symbolic Computation Systems, ed. by A. Miola, M. Temperini. Texts & Monographs in Symbolic Computation (Springer, Wien-New York, 1997), pp. 84–110
E.D. Ocansey, C. Schneider, Representing (q-)hypergeometric products and mixed versions in difference rings, in Advances in Computer Algebra. WWCA 2016., C. Schneider, E. Zima. Springer Proceedings in Mathematics & Statistics, vol. 226 (Springer, Berlin, 2018), pp. 175–213. arXiv:1705.01368
E.D. Ocansey, C. Schneider, Representation of hypergeometric products of higher nesting depths in difference rings. RISC Report Series 20-19, Research Institute for Symbolic Computation (RISC), Johannes Kepler University Linz, Schloss Hagenberg, 4232 Hagenberg, Austria (2020). arXiv:2011.08775
P. Paule, Greatest factorial factorization and symbolic summation. J. Symb. Comput. 20(3), 235–268 (1995)
P. Paule, Contiguous relations and creative telescoping, in Anti-Differentiation and the Calculation of Feynman Amplitudes, ed. by J. Blümlein, C. Schneider. Texts and Monographs in Symbolic Computuation (Springer, Berlin, 2021)
P. Paule, A. Riese, A Mathematica q-analogue of Zeilberger’s algorithm based on an algebraically motivated approach to q-hypergeometric telescoping, in Special Functions, q-Series and Related Topics, ed. by M. Ismail, M. Rahman, vol. 14 (AMS, Providence, 1997), pp. 179–210
P. Paule, C. Schneider, Computer proofs of a new family of harmonic number identities. Adv. Appl. Math. 31(2), 359–378 (2003). Preliminary version online
P. Paule, C. Schneider, Towards a symbolic summation theory for unspecified sequences, in Elliptic Integrals, Elliptic Functions and Modular Forms in Quantum Field Theory, ed. by J. Blümlein, P. Paule, C. Schneider. Texts and Monographs in Symbolic Computation (Springer, Berlin, 2019), pp. 351–390. arXiv:1809.06578
P. Paule, M. Schorn, A Mathematica version of Zeilberger’s algorithm for proving binomial coefficient identities. J. Symb. Comput. 20(5–6), 673–698 (1995)
M. Petkovšek, Hypergeometric solutions of linear recurrences with polynomial coefficients. J. Symb. Comput. 14(2–3), 243–264 (1992)
M. Petkovšek, Definite sums as solutions of linear recurrences with polynomial coefficients (2018). arXiv:1804.02964 [cs.SC]
M. Petkovšek, H.S. Wilf, D. Zeilberger, A = B (A. K. Peters, Wellesley, 1996)
M. Petkovšek, H. Zakrajšek, Solving linear recurrence equations with polynomial coefficients, in Computer Algebra in Quantum Field Theory: Integration, Summation and Special Functions, ed. by C. Schneider, J. Blümlein. Texts and Monographs in Symbolic Computation (Springer, Berlin, 2013), pp. 259–284
R. Risch, The problem of integration in finite terms. Trans. Am. Math. Soc. 139, 167–189 (1969)
M. Rosenlicht, Liouville’s theorem on functions with elementary integrals. Pac. J. Math. 24, 153–161 (1968)
C. Schneider, An implementation of Karr’s summation algorithm in Mathematica. Sem. Lothar. Combin. S43b, 1–10 (2000)
C. Schneider, Symbolic summation in difference fields. Technical Report 01-17, RISC-Linz, J. Kepler University, Ph.D. Thesis (2001)
C. Schneider, A collection of denominator bounds to solve parameterized linear difference equations in Π Σ-extensions. An. Univ. Timişoara Ser. Mat.-Inform. 42(2), 163–179 (2004). Extended version of Proc. SYNASC’04
C. Schneider, Symbolic summation with single-nested sum extensions, in Proceedings of ISSAC’04, ed. by J. Gutierrez (ACM Press, New York, 2004), pp. 282–289
C. Schneider, Degree bounds to find polynomial solutions of parameterized linear difference equations in Π Σ-fields. Appl. Algebra Engrgy Comm. Comput. 16(1), 1–32 (2005)
C. Schneider, Finding telescopers with minimal depth for indefinite nested sum and product expressions, in Proceedings of ISSAC’05, ed. by M. Kauers (ACM, New York, 2005)
C. Schneider, A new Sigma approach to multi-summation. Adv. Appl. Math. 34(4), 740–767 (2005)
C. Schneider, Product representations in Π Σ-fields. Ann. Combin. 9(1), 75–99 (2005)
C. Schneider, Solving parameterized linear difference equations in terms of indefinite nested sums and products. J. Differ. Equ. Appl. 11(9), 799–821 (2005)
C. Schneider, Simplifying sums in Π Σ-extensions.J. Algebra Appl. 6(3), 415–441 (2007)
C. Schneider, Symbolic summation assists combinatorics. Sém. Lothar. Combin. 56, 1–36 (2007). Article B56b
C. Schneider, A refined difference field theory for symbolic summation. J. Symb. Comput. 43(9), 611–644 (2008). arXiv:0808.2543v1
C. Schneider, Parameterized telescoping proves algebraic independence of sums. Ann. Comb. 14, 533–552 (2010). arXiv:0808.2596; for a preliminary version see FPSAC 2007
C. Schneider, Structural theorems for symbolic summation. Appl. Algebra Engrgy Comm. Comput. 21(1), 1–32 (2010)
C. Schneider, A symbolic summation approach to find optimal nested sum representations, in Motives, Quantum Field Theory, and Pseudodifferential Operators, ed. by A. Carey, D. Ellwood, S. Paycha, S. Rosenberg. Clay Mathematics Proceedings, vol. 12 (American Mathematical Society, Providence, 2010), pp. 285–308. arXiv:0808.2543
C. Schneider, Simplifying multiple sums in difference fields, in Computer Algebra in Quantum Field Theory: Integration, Summation and Special Functions, ed. by C. Schneider, J. Blümlein. Texts and Monographs in Symbolic Computation (Springer, Berlin, 2013), pp. 325–360. arXiv:1304.4134
C. Schneider, Modern summation methods for loop integrals in quantum field theory: the packages Sigma, EvaluateMultiSums and SumProduction, in Proceedings of ACAT 2013. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, vol. 523(012037) (2014), pp. 1–17. arXiv:1310.0160
C. Schneider, A streamlined difference ring theory: indefinite nested sums, the alternating sign and the parameterized telescoping problem, in Symbolic and Numeric Algorithms for Scientific Computing (SYNASC), 2014 15th International Symposium, ed. by F. Winkler, V. Negru, T. Ida, T. Jebelean, D. Petcu, S. Watt, D. Zaharie (IEEE Computer Society, Washington, 2014), pp. 26–33. arXiv:1412.2782
C. Schneider, Fast algorithms for refined parameterized telescoping in difference fields, in Computer Algebra and Polynomials, ed. by M.W.J. Guitierrez, J. Schicho. Lecture Notes in Computer Science (LNCS), vol. 8942 (Springer, Berlin, 2015), pp. 157–191. arXiv:1307.7887.
C. Schneider, A difference ring theory for symbolic summation. J. Symb. Comput. 72, 82–127 (2016). arXiv:1408.2776
C. Schneider, Symbolic summation in difference rings and applications, in Proceedings of ISSAC 2016, ed. by M. Rosenkranz (2016), pp. 9–12
C. Schneider, Summation theory II: characterizations of R Π Σ-extensions and algorithmic aspects. J. Symb. Comput. 80(3), 616–664 (2017). arXiv:1603.04285
C. Schneider, The absent-minded passengers problem: a motivating challenge solved by computer algebra. Math. Comput. Sci. (2020), https://doi.org/10.1007/s11786-020-00494-w. arXiv:2003.01921
C. Schneider, Minimal representations and algebraic relations for single nested products. Program. Comput. Softw. 46(2), 133–161 (2020). arXiv:1911.04837
C. Schneider, R. Sulzgruber, Asymptotic and exact results on the complexity of the Novelli–Pak–Stoyanovskii algorithm. Electron. J. Combin. 24(2), 1–33 (2017). #P2.28, arXiv:1606.07597
C. Schneider, W. Zudilin, A case study for ζ(4), in Proceedings of the Conference ’Transient Transcendence in Transylvania’. Proceedings in Mathematics & Statistics (Springer, Berlin, 2021). arXiv:2004.08158
M.F. Singer, Liouvillian solutions of linear differential equations with Liouvillian coefficients. J. Symb. Comput. 11(3), 251–274 (1991)
M.F. Singer, Algebraic and algorithmic aspects of linear difference equations, in Galois Theories of Linear Difference Equations: An Introduction, ed. by C. Hardouin, J. Sauloy, M.F. Singer. Mathematical Surveys and Monographs, vol. 211 (AMS, Providence, 2016)
M. Steinhauser, MATAD: a program package for the computation of MAssive TADpoles. Comput. Phys. Commun. 134, 335–364 (2001)
M. van der Put, M. Singer, Galois Theory of Difference Equations. Lecture Notes in Mathematics, vol. 1666 (Springer, Berlin, 1997)
M. van Hoeij, Finite singularities and hypergeometric solutions of linear recurrence equations. J. Pure Appl. Algebra 139(1–3), 109–131 (1999)
M. van Hoeij, M. Barkatou, J. Middeke, A family of denominator bounds for first order linear recurrence systems. Technical Report (2020). arXiv:2007.02926
J.A.M. Vermaseren, Harmonic sums, Mellin transforms and integrals. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A14, 2037–2976 (1999)
K. Wegschaider, Computer generated proofs of binomial multi-sum identities. Master’s Thesis, RISC, J. Kepler University (1997)
S. Weinzierl, Expansion around half integer values, binomial sums and inverse binomial sums. J. Math. Phys. 45, 2656–2673 (2004)
H. Wilf, D. Zeilberger, An algorithmic proof theory for hypergeometric (ordinary and “q”) multisum/integral identities. Invent. Math. 108, 575–633 (1992)
D. Zeilberger, A holonomic systems approach to special functions identities. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 32, 321–368 (1990)
D. Zeilberger, The method of creative telescoping. J. Symb. Comput. 11, 195–204 (1991)
Acknowledgements
This article got inspired during the workshop Antidifferentiation and the Calculation of Feynman Amplitudes at Zeuthen, Germany. In this regard, I would like to thank DESY for its hospitality and the Wolfgang Pauli Centre (WPC) for the financial support. In particular, I would like to thank the referee for the very thorough reading and valuable suggestions which helped me to improve the presentation.
This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie Skłodowska–Curie grant agreement No. 764850, SAGEX and from the Austrian Science Foundation (FWF) grant SFB F50 (F5005-N15) in the framework of the Special Research Program “Algorithmic and Enumerative Combinatorics”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Schneider, C. (2021). Term Algebras, Canonical Representations and Difference Ring Theory for Symbolic Summation. In: Blümlein, J., Schneider, C. (eds) Anti-Differentiation and the Calculation of Feynman Amplitudes. Texts & Monographs in Symbolic Computation. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-80219-6_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-80219-6_17
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-80218-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-80219-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)


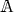 we denote by
we denote by 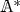 the set of units. If
the set of units. If 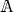 is a field, this means
is a field, this means  .
.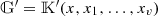 or
or 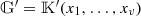 where the field
where the field 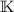 is extended to
is extended to  .
.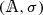 is a difference ring extension of
is a difference ring extension of 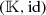 .
.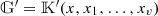 or
or 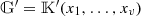 where
where 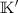 is a field extension of
is a field extension of 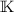 ; if
; if 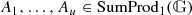 , one can restrict to the special case
, one can restrict to the special case 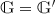 .
.