Abstract
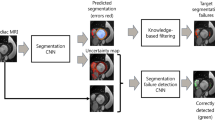
One of the challenges in developing deep learning algorithms for medical image segmentation is the scarcity of annotated training data. To overcome this limitation, data augmentation and semi-supervised learning (SSL) methods have been developed. However, these methods have limited effectiveness as they either exploit the existing data set only (data augmentation) or risk negative impact by adding poor training examples (SSL). Segmentations are rarely the final product of medical image analysis - they are typically used in downstream tasks to infer higher-order patterns to evaluate diseases. Clinicians take into account a wealth of prior knowledge on biophysics and physiology when evaluating image analysis results. We have used these clinical assessments in previous works to create robust quality-control (QC) classifiers for automated cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) analysis. In this paper, we propose a novel scheme that uses QC of the downstream task to identify high quality outputs of CMR segmentation networks, that are subsequently utilised for further network training. In essence, this provides quality-aware augmentation of training data in a variant of SSL for segmentation networks (semiQCSeg). We evaluate our approach in two CMR segmentation tasks (aortic and short axis cardiac volume segmentation) using UK Biobank data and two commonly used network architectures (U-net and a Fully Convolutional Network) and compare against supervised and SSL strategies. We show that semiQCSeg improves training of the segmentation networks. It decreases the need for labelled data, while outperforming the other methods in terms of Dice and clinical metrics. SemiQCSeg can be an efficient approach for training segmentation networks for medical image data when labelled datasets are scarce.
E. Puyol-Antón—Joint first authors.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai, W., et al.: Semi-supervised learning for network based cardiac MR image segmentation. In: Descoteaux, M., Maier-Hein, L., Franz, A., Jannin, P., Collins, D.L., Duchesne, S. (eds.) MICCAI 2017, Part II. LNCS, vol. 10434, pp. 253–260. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-66185-8_29
Bai, W., et al.: Automated cardiovascular magnetic resonance image analysis with fully convolutional networks. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 20(1), 65 (2018)
Bozorgtabar, B., et al.: Informative sample generation using class aware generative adversarial networks for classification of chest X rays. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 184, 57–65 (2019)
Cheplygina, V., de Bruijne, M., Pluim, J.P.: Not-so-supervised: a survey of semi-supervised, multi-instance, and transfer learning in medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 54, 280–296 (2019)
Hann, E., et al.: Quality control-driven image segmentation towards reliable automatic image analysis in large-scale cardiovascular magnetic resonance aortic cine imaging. In: Shen, D., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2019, Part II. LNCS, vol. 11765, pp. 750–758. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32245-8_83
Hung, W.C., Tsai, Y.H., Liou, Y.T., Lin, Y.Y., Yang, M.H.: Adversarial learning for semi-supervised semantic segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1802.07934 (2018)
Kerfoot, E., Clough, J., Oksuz, I., Lee, J., King, A.P., Schnabel, J.A.: Left-ventricle quantification using residual U-Net. In: Pop, M., Sermesant, M., Zhao, J., Li, S., McLeod, K., Young, A., Rhode, K., Mansi, T. (eds.) STACOM 2018. LNCS, vol. 11395, pp. 371–380. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-12029-0_40
Kervadec, H., Dolz, J., Granger, É., Ben Ayed, I.: Curriculum semi-supervised segmentation. In: Shen, D., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2019, Part II. LNCS, vol. 11765, pp. 568–576. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32245-8_63
Oksuz, I., et al.: Automatic CNN-based detection of cardiac MR motion artefacts using k-space data augmentation and curriculum learning. Med. Image Anal. 55, 136–147 (2019)
Petersen, S.E., et al.: UK biobank’s cardiovascular magnetic resonance protocol. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 18(1), 8 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12968-016-0227-4
Qiao, S., Shen, W., Zhang, Z., Wang, B., Yuille, A.: Deep co-training for semi-supervised image recognition. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018, Part XV. LNCS, vol. 11219, pp. 142–159. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01267-0_9
Radosavovic, I., Dollár, P., Girshick, R., Gkioxari, G., He, K.: Data distillation: towards omni-supervised learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4119–4128 (2018)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015, Part III. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Ruijsink, B., et al.: Fully automated, quality-controlled cardiac analysis from CMR: validation and large-scale application to characterize cardiac function. JACC Cardiovas. Imaging 13(3), 684–695 (2020)
Sandfort, V., Yan, K., Pickhardt, P.J., Summers, R.M.: Data augmentation using generative adversarial networks (CycleGAN) to improve generalizability in CT segmentation tasks. Sci. Rep. 9(1), 1–9 (2019)
Shorten, C., Khoshgoftaar, T.M.: A survey on image data augmentation for deep learning. J. Big Data 6(1), 60 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537-019-0197-0
Acknowledgements
Dr. Bram Ruijsink is supported by the NIHR Cardiovascular MedTech Co-operative awarded to the Guy’s and St Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust. This work was further supported by the EPSRC (EP/R005516/1 and EP/P001009/1), the Wellcome EPSRC Centre for Medical Engineering at King’s College London (WT 203148/Z/16/Z) and National Institute for Health Research (NIHR). This research has been conducted using the UK Biobank Resource under Application Number 17806.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ruijsink, B. et al. (2021). Quality-Aware Semi-supervised Learning for CMR Segmentation. In: Puyol Anton, E., et al. Statistical Atlases and Computational Models of the Heart. M&Ms and EMIDEC Challenges. STACOM 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12592. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-68107-4_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-68107-4_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-68106-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-68107-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)