Abstract
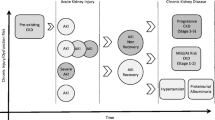
For many years, the emphasis in CF care has been on the careful monitoring of nutrition and aggressive management of lung disease in order to improve the life span and quality of life of individuals with CF. However, as people with CF live longer, “hidden” complications of CF and CF therapies, such as renal disease, become increasingly important. While CFTR is expressed in the kidney, a direct renal phenotype of CFTR dysfunction has not been clearly defined. However, acute kidney injury, chronic kidney disease, and nephrolithiasis are all more commonly reported in CF compared to the general population, particularly post-lung transplant. Acute kidney injury typically relates to dehydration and aminoglycoside-related nephrotoxicity. For chronic kidney disease, CF-related diabetes requiring insulin is a significant risk factor both pre- and post-lung transplant. Other rarer causes of chronic kidney disease observed in CF relate to uncontrolled infection and inflammation including amyloid A (AA) amyloidosis and IgA nephropathy. A number of CF-related factors increase the risk of calcium oxalate kidney stones including the frequent use of antibiotics, malabsorption, and dehydration. Future studies need to focus on more reliable biomarkers to monitor renal function and detect renal damage in the CF population. Furthermore, preventative strategies are urgently required to mitigate the impact of CFRD on the risk of chronic kidney disease.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wilcock MJ, Ruddick A, Gyi KM, Hodson ME. Renal diseases in adults with cystic fibrosis: a 40 year single Centre experience. J Nephrol. 2015;28(5):585–91.
Morales MM, Carroll TP, Morita T, Schwiebert EM, Devuyst O, Wilson PD, et al. Both the wild type and a functional isoform of CFTR are expressed in kidney. Am J Phys. 1996;270(6 Pt 2):F1038–48.
Crawford I, Maloney PC, Zeitlin PL, Guggino WB, Hyde SC, Turley H, et al. Immunocytochemical localization of the cystic fibrosis gene product CFTR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991;88(20):9262–6.
Devuyst O, Burrow CR, Schwiebert EM, Guggino WB, Wilson PD. Developmental regulation of CFTR expression during human nephrogenesis. Am J Phys. 1996;271(3 Pt 2):F723–35.
Souza-Menezes J, da Silva FG, Morales MM. CFTR and TNR-CFTR expression and function in the kidney. Biophys Rev. 2014;6(2):227–36.
Stanton BA. Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) and renal function. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 1997;109(12–13):457–64.
Touw DJ. Clinical pharmacokinetics of antimicrobial drugs in cystic fibrosis. Pharm World Sci. 1998;20(4):149–60.
Rey E, Treluyer JM, Pons G. Drug disposition in cystic fibrosis. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1998;35(4):313–29.
Wang JP, Unadkat JD, al-Habet SM, O’Sullivan TA, Williams-Warren J, Smith AL, et al. Disposition of drugs in cystic fibrosis. IV. Mechanisms for enhanced renal clearance of ticarcillin. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1993;54(3):293–302.
Vinks AA, Den Hollander JG, Overbeek SE, Jelliffe RW, Mouton JW. Population pharmacokinetic analysis of nonlinear behavior of piperacillin during intermittent or continuous infusion in patients with cystic fibrosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003;47(2):541–7.
Li H, Yang W, Mendes F, Amaral MD, Sheppard DN. Impact of the cystic fibrosis mutation F508del-CFTR on renal cyst formation and growth. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012;303(8):F1176–86.
Hanaoka K, Devuyst O, Schwiebert EM, Wilson PD, Guggino WB. A role for CFTR in human autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Am J Phys. 1996;270(1 Pt 1):C389–99.
O’Sullivan DA, Torres VE, Gabow PA, Thibodeau SN, King BF, Bergstralh EJ. Cystic fibrosis and the phenotypic expression of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 1998;32(6):976–83.
Xu N, Glockner JF, Rossetti S, Babovich-Vuksanovic D, Harris PC, Torres VE. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease coexisting with cystic fibrosis. J Nephrol. 2006;19(4):529–34.
Zhang JT, Wang Y, Chen JJ, Zhang XH, Dong JD, Tsang LL, et al. Defective CFTR leads to aberrant beta-catenin activation and kidney fibrosis. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):5233.
Al-Aloul M, Miller H, Alapati S, Stockton P, Walshaw ML. Renal impairment in cystic fibrosis patients due to repeated intravenous aminoglycoside use. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2005;39(1):15–20.
Soulsby N, Greville H, Coulthard K, Doecke C. What is the best method for measuring renal function in adults and children with cystic fibrosis? J Cyst Fibros. 2010;9(2):124–9.
Al-Aloul M, Jackson M, Bell G, Ledson M, Walshaw M. Comparison of methods of assessment of renal function in cystic fibrosis (CF) patients. J Cyst Fibros. 2007;6(1):41–7.
Jain K, Prayle A, Lewis S, Watson A, Knox A, Dewar J, et al. Assessment of renal function in cystic fibrosis patients by estimated and measured glomerular filtration rate; a cross-sectional study. J Cyst Fibros. 2012;11:S52.
Tenstad O, Roald AB, Grubb A, Aukland K. Renal handling of radiolabelled human cystatin C in the rat. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1996;56(5):409–14.
Prayle AP, Jain K, Knox AJ, Watson AR, Smyth AR. Urinary kidney injury molecule-1 is superior to creatinine and cystatin-C based formulas at predicting chronic kidney disease in patients with cystic fibrosis. J Cyst Fibros. 2013;12:S13.
Mora-Gutierrez JM, Garcia-Fernandez N, Slon Roblero MF, Paramo JA, Escalada FJ, Wang DJ, et al. Arterial spin labeling MRI is able to detect early hemodynamic changes in diabetic nephropathy. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2017;46(6):1810–7.
Sugiyama K, Inoue T, Kozawa E, Ishikawa M, Shimada A, Kobayashi N, et al. Reduced oxygenation but not fibrosis defined by functional magnetic resonance imaging predicts the long-term progression of chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfy324. [Epub ahead of print]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30418615.
Li LP, Tan H, Thacker JM, Li W, Zhou Y, Kohn O, et al. Evaluation of renal blood flow in chronic kidney disease using arterial spin labeling perfusion magnetic resonance imaging. Kidney Int Rep. 2017;2(1):36–43.
Lu L, Sedor JR, Gulani V, Schelling JR, O’Brien A, Flask CA, et al. Use of diffusion tensor MRI to identify early changes in diabetic nephropathy. Am J Nephrol. 2011;34(5):476–82.
Bertenshaw C, Watson AR, Lewis S, Smyth A. Survey of acute renal failure in patients with cystic fibrosis in the UK. Thorax. 2007;62(6):541–5.
Smyth A, Lewis S, Bertenshaw C, Choonara I, McGaw J, Watson A. Case-control study of acute renal failure in patients with cystic fibrosis in the UK. Thorax. 2008;63(6):532–5.
Downes KJ, Patil NR, Rao MB, Koralkar R, Harris WT, Clancy JP, et al. Risk factors for acute kidney injury during aminoglycoside therapy in patients with cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Nephrol. 2015;30(10):1879–88.
Lands LC, Milner R, Cantin AM, Manson D, Corey M. High-dose ibuprofen in cystic fibrosis: Canadian safety and effectiveness trial. J Pediatr. 2007;151(3):249–54.
Kerem E, Konstan MW, De Boeck K, Accurso FJ, Sermet-Gaudelus I, Wilschanski M, et al. Ataluren for the treatment of nonsense-mutation cystic fibrosis: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2014;2(7):539–47.
Gibney EM, Goldfarb DS. The association of nephrolithiasis with cystic fibrosis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003;42(1):1–11.
Hiatt RA, Dales LG, Friedman GD, Hunkeler EM. Frequency of urolithiasis in a prepaid medical care program. Am J Epidemiol. 1982;115(2):255–65.
Bohles H, Gebhardt B, Beeg T, Sewell AC, Solem E, Posselt G. Antibiotic treatment-induced tubular dysfunction as a risk factor for renal stone formation in cystic fibrosis. J Pediatr. 2002;140(1):103–9.
Dharmsathaphorn K, Freeman DH, Binder HJ, Dobbins JW. Increased risk of nephrolithiasis in patients with steatorrhea. Dig Dis Sci. 1982;27(5):401–5.
Knauf F, Thomson RB, Heneghan JF, Jiang Z, Adebamiro A, Thomson CL, et al. Loss of cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator impairs intestinal oxalate secretion. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;28(1):242–9.
Perez-Brayfield MR, Caplan D, Gatti JM, Smith EA, Kirsch AJ. Metabolic risk factors for stone formation in patients with cystic fibrosis. J Urol. 2002;167(2 Pt 1):480–4.
Reungjui S, Prasongwatana V, Premgamone A, Tosukhowong P, Jirakulsomchok S, Sriboonlue P. Magnesium status of patients with renal stones and its effect on urinary citrate excretion. BJU Int. 2002;90(7):635–9.
Nouisa-Arvanitakis S, Stapleton FB, Linshaw MA, Kennedy J. Therapeutic approach to pancreatic extract-induced hyperuricosuria in cystic fibrosis. J Pediatr. 1977;90(2):302–5.
Hurley MN, Prayle AP, Flume P. Intravenous antibiotics for pulmonary exacerbations in people with cystic fibrosis. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2015;16(4):246–8.
Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Acute Kidney Injury Work Group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2012;Supplement 2:1–138.
Prayle AP, Jain K, Touw DJ, Koch BC, Knox AJ, Watson A, et al. The pharmacokinetics and toxicity of morning vs. evening tobramycin dosing for pulmonary exacerbations of cystic fibrosis: a randomised comparison. J Cyst Fibros. 2016;15(4):510–7.
McWilliam S, Antoine D, Rosala-Hallas A, Jones A, MacLean C, Prayle A, et al. The protekt study – a phase IIA, randomised, controlled, open-label trial of rosuvastatin for the prevention of aminoglycoside-induced kidney toxicity in children with cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2017;52(s47):353.
Rowbotham NJ, Smith S, Leighton PA, Rayner OC, Gathercole K, Elliott ZC, et al. The top 10 research priorities in cystic fibrosis developed by a partnership between people with CF and healthcare providers. Thorax. 2018;73(4):388–90.
Ellis ML, Shaw KJ, Jackson SB, Daniel SL, Knight J. Analysis of commercial kidney stone probiotic supplements. Urology. 2015;85(3):517–21.
Miller OF, Kane CJ. Time to stone passage for observed ureteral calculi: a guide for patient education. J Urol. 1999;162(3 Pt 1):688–90; discussion 90–1.
Coll DM, Varanelli MJ, Smith RC. Relationship of spontaneous passage of ureteral calculi to stone size and location as revealed by unenhanced helical CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002;178(1):101–3.
Wang RC, Smith-Bindman R, Whitaker E, Neilson J, Allen IE, Stoller ML, et al. Effect of tamsulosin on stone passage for ureteral stones: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Emerg Med. 2017;69(3):353–61. e3
Quon BS, Mayer-Hamblett N, Aitken ML, Smyth AR, Goss CH. Risk factors for chronic kidney disease in adults with cystic fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011;184(10):1147–52.
Nazareth D, Walshaw M. A review of renal disease in cystic fibrosis. J Cyst Fibros. 2013;12(4):309–17.
Quon BS, Mayer-Hamblett N, Aitken ML, Goss CH. Risk of post-lung transplant renal dysfunction in adults with cystic fibrosis. Chest. 2012;142(1):185–91.
Pedersen SS, Jensen T, Osterhammel D, Osterhammel P. Cumulative and acute toxicity of repeated high-dose tobramycin treatment in cystic fibrosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987;31(4):594–9.
Abramowsky CR, Swinehart GL. The nephropathy of cystic fibrosis: a human model of chronic nephrotoxicity. Hum Pathol. 1982;13(10):934–9.
Al-Aloul M, Miller H, Alapati S, Stockton PA, Ledson MJ, Walshaw MJ. Renal impairment in cystic fibrosis patients due to repeated intravenous aminoglycoside use. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2005;39(1):15–20.
Stehling F, Buscher R, Grosse-Onnebrink J, Hoyer PF, Mellies U. Glomerular and tubular renal function after repeated once-daily tobramycin courses in cystic fibrosis patients. Pulm Med. 2017;2017:2602653.
Smyth A, Tan KH, Hyman-Taylor P, Mulheran M, Lewis S, Stableforth D, et al. Once versus three-times daily regimens of tobramycin treatment for pulmonary exacerbations of cystic fibrosis--the TOPIC study: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2005;365(9459):573–8.
Yahiaoui Y, Jablonski M, Hubert D, Mosnier-Pudar H, Noel LH, Stern M, et al. Renal involvement in cystic fibrosis: diseases spectrum and clinical relevance. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;4(5):921–8.
Stankovic Stojanovic K, Hubert D, Leroy S, Dominique S, Grenet D, Colombat M, et al. Cystic fibrosis and AA amyloidosis: a survey in the French cystic fibrosis network. Amyloid. 2014;21(4):231–7.
Mc Laughlin AM, Crotty TB, Egan JJ, Watson AJ, Gallagher CG. Amyloidosis in cystic fibrosis: a case series. J Cyst Fibros. 2006;5(1):59–61.
McGlennen RC, Burke BA, Dehner LP. Systemic amyloidosis complicating cystic fibrosis. A retrospective pathologic study. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1986;110(10):879–84.
Bhatt N, Bhatt N. IgA nephropathy in cystic fibrosis. Clin Nephrol. 2007;67(6):403–4.
Stirati G, Antonelli M, Fofi C, Fierimonte S, Pecci G. IgA nephropathy in cystic fibrosis. J Nephrol. 1999;12(1):30–1.
Davis CA, Abramowsky CR, Swinehart G. Circulating immune complexes and the nephropathy of cystic fibrosis. Hum Pathol. 1984;15(3):244–7.
Melzi ML, Costantini D, Giani M, Appiani AC, Giunta AM. Severe nephropathy in three adolescents with cystic fibrosis. Arch Dis Child. 1991;66(12):1444–7.
Ojo AO, Held PJ, Port FK, Wolfe RA, Leichtman AB, Young EW, et al. Chronic renal failure after transplantation of a nonrenal organ. N Engl J Med. 2003;349(10):931–40.
Cantarovich D, Renou M, Megnigbeto A, Giral-Classe M, Hourmant M, Dantal J, et al. Switching from cyclosporine to tacrolimus in patients with chronic transplant dysfunction or cyclosporine-induced adverse events. Transplantation. 2005;79(1):72–8.
Group DER, de Boer IH, Sun W, Cleary PA, Lachin JM, Molitch ME, et al. Intensive diabetes therapy and glomerular filtration rate in type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(25):2366–76.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge and thank Lori Van Balkom for sharing her experience living with chronic kidney disease post-lung transplantation. We would also like to thank Dr. Chris Flask and Dr. Kimberley McBennett from Case Western Reserve University and Dr. Tom McCulloch from Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust for their contributions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Prayle, A., Quon, B.S. (2020). Impact of CF on the Kidneys. In: Davis, S., Rosenfeld, M., Chmiel, J. (eds) Cystic Fibrosis. Respiratory Medicine. Humana, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-42382-7_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-42382-7_19
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-42381-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-42382-7
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)