Abstract
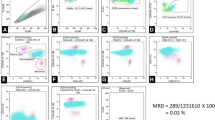
Complete remission for hematolymphoid neoplasms affecting the bone marrow was traditionally considered to mean absence of morphologically detectable disease in the bone marrow with restoration of normal blood findings. Minimal residual disease (MRD) is the presence of the malignant cells at very low level (typically between 1% and 0.001% of total nucleated cells) in blood and/or bone marrow, detectable only by high sensitivity ancillary technics. MRD detection is clinically used in lymphoblastic leukemia, acute myeloid leukemia, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and plasma cell myeloma because it offers independent prognostic information, can guide additional therapy, and/or is useful as a surrogate endpoint for novel treatments for these diseases. Multiparameter flow cytometry and molecular methods are currently used, the latter including real-time quantitative PCR and next-generation sequencing assays. While molecular methods can be 1–3 logs more sensitive than flow cytometric methods, they often have technical and practical drawbacks. Flow cytometry methods can be applied more universally but require considerable experience in interpretation of results. Several case studies are presented to familiarize the reader with this testing modality.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheson BD, Bennett JM, Kopecky KJ, Buchner T, Willman CL, Estey EH, et al. Revised recommendations of the International Working Group for Diagnosis, standardization of response criteria, treatment outcomes, and reporting standards for therapeutic trials in acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21(24):4642–9.
Harousseau JL, Attal M, Avet-Loiseau H. The role of complete response in multiple myeloma. Blood. 2009;114(15):3139–46.
van Dongen JJ, van der Velden VH, Bruggemann M, Orfao A. Minimal residual disease diagnostics in acute lymphoblastic leukemia: need for sensitive, fast, and standardized technologies. Blood. 2015;125(26):3996–4009.
Berry DA, Zhou S, Higley H, Mukundan L, Fu S, Reaman GH, et al. Association of minimal residual disease with clinical outcome in pediatric and adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3(7):e170580.
Hourigan CS, Gale RP, Gormley NJ, Ossenkoppele GJ, Walter RB. Measurable residual disease testing in acute myeloid leukaemia. Leukemia. 2017;31(7):1482–90.
Grimwade D, Freeman SD. Defining minimal residual disease in acute myeloid leukemia: which platforms are ready for “prime time”? Blood. 2014;124(23):3345–55.
Thompson M, Brander D, Nabhan C, Mato A. Minimal residual disease in chronic lymphocytic leukemia in the era of novel agents: a review. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4(3):394–400.
Ghia P, Rawstron A. Minimal residual disease analysis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a way for achieving more personalized treatments. Leukemia. 2018;32(6):1307–16.
Kumar S, Paiva B, Anderson KC, Durie B, Landgren O, Moreau P, et al. International Myeloma Working Group consensus criteria for response and minimal residual disease assessment in multiple myeloma. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17(8):e328–e46.
Harousseau JL, Avet-Loiseau H. Minimal residual disease negativity is a new end point of myeloma therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(25):2863–5.
Borowitz MJ, Devidas M, Hunger SP, Bowman WP, Carroll AJ, Carroll WL, et al. Clinical significance of minimal residual disease in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia and its relationship to other prognostic factors: a Children’s Oncology Group study. Blood. 2008;111(12):5477–85.
Yin JA, O’Brien MA, Hills RK, Daly SB, Wheatley K, Burnett AK. Minimal residual disease monitoring by quantitative RT-PCR in core binding factor AML allows risk stratification and predicts relapse: results of the United Kingdom MRC AML-15 trial. Blood. 2012;120(14):2826–35.
Bottcher S, Ritgen M, Fischer K, Stilgenbauer S, Busch RM, Fingerle-Rowson G, et al. Minimal residual disease quantification is an independent predictor of progression-free and overall survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a multivariate analysis from the randomized GCLLSG CLL8 trial. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(9):980–8.
Paiva B, Gutierrez NC, Rosinol L, Vidriales MB, Montalban MA, Martinez-Lopez J, et al. High-risk cytogenetics and persistent minimal residual disease by multiparameter flow cytometry predict unsustained complete response after autologous stem cell transplantation in multiple myeloma. Blood. 2012;119(3):687–91.
Garand R, Beldjord K, Cave H, Fossat C, Arnoux I, Asnafi V, et al. Flow cytometry and IG/TCR quantitative PCR for minimal residual disease quantitation in acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a French multicenter prospective study on behalf of the FRALLE, EORTC and GRAALL. Leukemia. 2013;27(2):370–6.
Rawstron AC, Child JA, de Tute RM, Davies FE, Gregory WM, Bell SE, et al. Minimal residual disease assessed by multiparameter flow cytometry in multiple myeloma: impact on outcome in the Medical Research Council Myeloma IX Study. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(20):2540–7.
Terwijn M, van Putten WL, Kelder A, van der Velden VH, Brooimans RA, Pabst T, et al. High prognostic impact of flow cytometric minimal residual disease detection in acute myeloid leukemia: data from the HOVON/SAKK AML 42A study. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(31):3889–97.
Beldjord K, Chevret S, Asnafi V, Huguet F, Boulland ML, Leguay T, et al. Oncogenetics and minimal residual disease are independent outcome predictors in adult patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2014;123(24):3739–49.
Martinez-Lopez J, Lahuerta JJ, Pepin F, Gonzalez M, Barrio S, Ayala R, et al. Prognostic value of deep sequencing method for minimal residual disease detection in multiple myeloma. Blood. 2014;123(20):3073–9.
Rawstron AC, Gregory WM, de Tute RM, Davies FE, Bell SE, Drayson MT, et al. Minimal residual disease in myeloma by flow cytometry: independent prediction of survival benefit per log reduction. Blood. 2015;125(12):1932–5.
Borowitz MJ, Wood BL, Devidas M, Loh ML, Raetz EA, Salzer WL, et al. Prognostic significance of minimal residual disease in high risk B-ALL: a report from Children’s Oncology Group study AALL0232. Blood. 2015;126(8):964–71.
Rawstron AC, Fazi C, Agathangelidis A, Villamor N, Letestu R, Nomdedeu J, et al. A complementary role of multiparameter flow cytometry and high-throughput sequencing for minimal residual disease detection in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: an European Research Initiative on CLL study. Leukemia. 2016;30(4):929–36.
Kwok M, Rawstron AC, Varghese A, Evans PA, O’Connor SJ, Doughty C, et al. Minimal residual disease is an independent predictor for 10-year survival in CLL. Blood. 2016;128(24):2770–3.
Ivey A, Hills RK, Simpson MA, Jovanovic JV, Gilkes A, Grech A, et al. Assessment of minimal residual disease in standard-risk AML. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(5):422–33.
Gupta S, Devidas M, Loh ML, Raetz EA, Chen S, Wang C, et al. Flow-cytometric vs. -morphologic assessment of remission in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a report from the Children’s Oncology Group (COG). Leukemia. 2018;32(6):1370–9.
Freeman SD, Hills RK, Virgo P, Khan N, Couzens S, Dillon R, et al. Measurable residual disease at induction redefines partial response in acute myeloid leukemia and stratifies outcomes in patients at standard risk without NPM1 mutations. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(15):1486–97.
Araki D, Wood BL, Othus M, Radich JP, Halpern AB, Zhou Y, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for acute myeloid Leukemia: time to move toward a minimal residual disease-based definition of complete remission? J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(4):329–36.
Inaba H, Coustan-Smith E, Cao X, Pounds SB, Shurtleff SA, Wang KY, et al. Comparative analysis of different approaches to measure treatment response in acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(29):3625–32.
Loken MR, Alonzo TA, Pardo L, Gerbing RB, Raimondi SC, Hirsch BA, et al. Residual disease detected by multidimensional flow cytometry signifies high relapse risk in patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia: a report from Children’s Oncology Group. Blood. 2012;120(8):1581–8.
Ouyang J, Goswami M, Tang G, Peng J, Ravandi F, Daval D, et al. The clinical significance of negative flow cytometry immunophenotypic results in a morphologically scored positive bone marrow in patients following treatment for acute myeloid leukemia. Am J Hematol. 2015;90(6):504–10.
O’Connor D, Moorman AV, Wade R, Hancock J, Tan RM, Bartram J, et al. Use of minimal residual disease assessment to redefine induction failure in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(6):660–7.
Vora A, Goulden N, Mitchell C, Hancock J, Hough R, Rowntree C, et al. Augmented post-remission therapy for a minimal residual disease-defined high-risk subgroup of children and young people with clinical standard-risk and intermediate-risk acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (UKALL 2003): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15(8):809–18.
Pieters R, de Groot-Kruseman H, Van der Velden V, Fiocco M, van den Berg H, de Bont E, et al. Successful therapy reduction and intensification for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia based on minimal residual disease monitoring: study ALL10 from the Dutch Childhood Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(22):2591–601.
Pui CH, Pei D, Raimondi SC, Coustan-Smith E, Jeha S, Cheng C, et al. Clinical impact of minimal residual disease in children with different subtypes of acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated with response-adapted therapy. Leukemia. 2017;31(2):333–9.
Balsat M, Renneville A, Thomas X, de Botton S, Caillot D, Marceau A, et al. Postinduction minimal residual disease predicts outcome and benefit from allogeneic stem cell transplantation in acute myeloid leukemia with NPM1 mutation: a study by the acute Leukemia French Association Group. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(2):185–93.
Zhu HH, Zhang XH, Qin YZ, Liu DH, Jiang H, Chen H, et al. MRD-directed risk stratification treatment may improve outcomes of t(8;21) AML in the first complete remission: results from the AML05 multicenter trial. Blood. 2013;121(20):4056–62.
Schultz KR, Pullen DJ, Sather HN, Shuster JJ, Devidas M, Borowitz MJ, et al. Risk- and response-based classification of childhood B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a combined analysis of prognostic markers from the Pediatric Oncology Group (POG) and Children’s Cancer Group (CCG). Blood. 2007;109(3):926–35.
Dohner H, Estey E, Grimwade D, Amadori S, Appelbaum FR, Buchner T, et al. Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2017 ELN recommendations from an international expert panel. Blood. 2017;129(4):424–47.
Hallek M, Cheson BD, Catovsky D, Caligaris-Cappio F, Dighiero G, Dohner H, et al. Guidelines for diagnosis, indications for treatment, response assessment and supportive management of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2018;
Paiva B, van Dongen JJ, Orfao A. New criteria for response assessment: role of minimal residual disease in multiple myeloma. Blood. 2015;125(20):3059–68.
Campana D, Coustan-Smith E, Janossy G. The immunologic detection of minimal residual disease in acute leukemia. Blood. 1990;76(1):163–71.
van Dongen JJ, Breit TM, Adriaansen HJ, Beishuizen A, Hooijkaas H. Detection of minimal residual disease in acute leukemia by immunological marker analysis and polymerase chain reaction. Leukemia. 1992;6(Suppl 1):47–59.
van der Velden VH, Cazzaniga G, Schrauder A, Hancock J, Bader P, Panzer-Grumayer ER, et al. Analysis of minimal residual disease by Ig/TCR gene rearrangements: guidelines for interpretation of real-time quantitative PCR data. Leukemia. 2007;21(4):604–11.
Farina L, Carniti C, Dodero A, Vendramin A, Raganato A, Spina F, et al. Qualitative and quantitative polymerase chain reaction monitoring of minimal residual disease in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia: early assessment can predict long-term outcome after reduced intensity allogeneic transplantation. Haematologica. 2009;94(5):654–62.
Ladetto M, Ferrero S, Drandi D, Festuccia M, Patriarca F, Mordini N, et al. Prospective molecular monitoring of minimal residual disease after non-myeloablative allografting in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma. Leukemia. 2016;30(5):1211–4.
Puig N, Sarasquete ME, Balanzategui A, Martinez J, Paiva B, Garcia H, et al. Critical evaluation of ASO RQ-PCR for minimal residual disease evaluation in multiple myeloma. A comparative analysis with flow cytometry. Leukemia. 2014;28(2):391–7.
Schnittger S, Kern W, Tschulik C, Weiss T, Dicker F, Falini B, et al. Minimal residual disease levels assessed by NPM1 mutation-specific RQ-PCR provide important prognostic information in AML. Blood. 2009;114(11):2220–31.
Gabert J, Beillard E, van der Velden VH, Bi W, Grimwade D, Pallisgaard N, et al. Standardization and quality control studies of ‘real-time’ quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction of fusion gene transcripts for residual disease detection in leukemia - a Europe against cancer program. Leukemia. 2003;17(12):2318–57.
Faham M, Zheng J, Moorhead M, Carlton VE, Stow P, Coustan-Smith E, et al. Deep-sequencing approach for minimal residual disease detection in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2012;120(26):5173–80.
Ladetto M, Bruggemann M, Monitillo L, Ferrero S, Pepin F, Drandi D, et al. Next-generation sequencing and real-time quantitative PCR for minimal residual disease detection in B-cell disorders. Leukemia. 2014;28(6):1299–307.
Wu D, Sherwood A, Fromm JR, Winter SS, Dunsmore KP, Loh ML, et al. High-throughput sequencing detects minimal residual disease in acute T lymphoblastic leukemia. Sci Transl Med. 2012;4(134):134ra63.
Wood B, Wu D, Crossley B, Dai Y, Williamson D, Gawad C, et al. Measurable residual disease detection by high-throughput sequencing improves risk stratification for pediatric B-ALL. Blood. 2018;131(12):1350–9.
Jongen-Lavrencic M, Grob T, Hanekamp D, Kavelaars FG, Al Hinai A, Zeilemaker A, et al. Molecular minimal residual disease in acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(13):1189–99.
Cancer Genome Atlas Research N, Ley TJ, Miller C, Ding L, Raphael BJ, Mungall AJ, et al. Genomic and epigenomic landscapes of adult de novo acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(22):2059–74.
Klco JM, Miller CA, Griffith M, Petti A, Spencer DH, Ketkar-Kulkarni S, et al. Association between mutation clearance after induction therapy and outcomes in acute myeloid leukemia. JAMA. 2015;314(8):811–22.
Thol F, Kolking B, Damm F, Reinhardt K, Klusmann JH, Reinhardt D, et al. Next-generation sequencing for minimal residual disease monitoring in acute myeloid leukemia patients with FLT3-ITD or NPM1 mutations. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2012;51(7):689–95.
Salipante SJ, Fromm JR, Shendure J, Wood BL, Wu D. Detection of minimal residual disease in NPM1-mutated acute myeloid leukemia by next-generation sequencing. Mod Pathol. 2014;27(11):1438–46.
Zhou Y, Othus M, Walter RB, Estey EH, Wu D, Wood BL. Deep NPM1 sequencing following allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation improves risk assessment in adults with NPM1-mutated AML. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018;24(8):1615–20.
Morita K, Kantarjian HM, Wang F, Yan Y, Bueso-Ramos C, Sasaki K, et al. Clearance of somatic mutations at remission and the risk of relapse in acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(18):1788–97.
Salk JJ, Schmitt MW, Loeb LA. Enhancing the accuracy of next-generation sequencing for detecting rare and subclonal mutations. Nat Rev Genet. 2018;19(5):269–85.
Feller N, van der Velden VH, Brooimans RA, Boeckx N, Preijers F, Kelder A, et al. Defining consensus leukemia-associated immunophenotypes for detection of minimal residual disease in acute myeloid leukemia in a multicenter setting. Blood Cancer J. 2013;3:e129.
Kussick SJ, Wood BL. Using 4-color flow cytometry to identify abnormal myeloid populations. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2003;127(9):1140–7.
Loken MR. Residual disease in AML, a target that can move in more than one direction. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2014;86(1):15–7.
Schuurhuis GJ, Heuser M, Freeman S, Bene MC, Buccisano F, Cloos J, et al. Minimal/measurable residual disease in AML: a consensus document from the European LeukemiaNet MRD Working Party. Blood. 2018;131(12):1275–91.
Zeijlemaker W, Kelder A, Oussoren-Brockhoff YJ, Scholten WJ, Snel AN, Veldhuizen D, et al. Peripheral blood minimal residual disease may replace bone marrow minimal residual disease as an immunophenotypic biomarker for impending relapse in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2016;30(3):708–15.
Keeney M, Wood BL, Hedley BD, DiGiuseppe JA, Stetler-Stevenson M, Paietta E, et al. A QA program for MRD testing demonstrates that systematic education can reduce discordance among experienced interpreters. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2018; 94:239–249
Denys B, van der Sluijs-Gelling AJ, Homburg C, van der Schoot CE, de Haas V, Philippe J, et al. Improved flow cytometric detection of minimal residual disease in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. 2013;27(3):635–41.
Stetler-Stevenson M, Paiva B, Stoolman L, Lin P, Jorgensen JL, Orfao A, et al. Consensus guidelines for myeloma minimal residual disease sample staining and data acquisition. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2016;90(1):26–30.
Flores-Montero J, Sanoja-Flores L, Paiva B, Puig N, Garcia-Sanchez O, Bottcher S, et al. Next generation flow for highly sensitive and standardized detection of minimal residual disease in multiple myeloma. Leukemia. 2017;31(10):2094–103.
Wood BL. Flow cytometric monitoring of residual disease in acute leukemia. Methods Mol Biol. 2013;999:123–36.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Zhou, Y. (2020). Detection of Minimal Residual Disease. In: Wang, E., Lagoo, A.S. (eds) Practical Lymph Node and Bone Marrow Pathology. Practical Anatomic Pathology. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32189-5_31
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32189-5_31
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-32188-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-32189-5
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)