Abstract
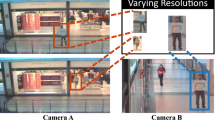
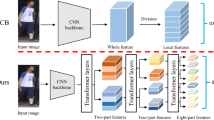
Person Re-identification (re-id) needs to tackle with the problem of changing resolutions because the pedestrians from surveillance systems or public datasets have low-resolution problem (LR-REID) including low quality, blurry textures and so on, which results in a difficult challenge to extract the identity information under various resolutions. However, most existing re-id models are trained by high-resolution (HR) images, which will achieve poor performance when conducted directly on low-resolution images. In this paper, we propose a novel Discriminative Resolution-invariant Network (DRINet) to explore the subspace where LR and HR features are highly correlated and we can extract discriminant features in the commonly shared feature space. Firstly, we adopt ResNet as the backbone and impose the softmax loss together with the triplet loss to learn distinguishing features. Secondly, we impose the KL divergence loss on the backbone features to minimize the discrepancies between LR and HR features. Finally, we integrate the sparse auto-encoder (SAE) structure to find a subspace which is robust to the resolution variations. Experimental results verify the effectiveness of the DRINet in improving the LR-REID performance and the superiority of the DRINet against the state-of-the-art methods.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chakrabarti, A., Rajagopalan, A., Chellappa, R.: Super-resolution of face images using kernel PCA-based prior. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 9(4), 888–892 (2007)
Felzenszwalb, P.F., McAllester, D.A., Ramanan, D., et al.: A discriminatively trained, multiscale, deformable part model. In: CVPR, vol. 2, p. 7 (2008)
Feng, Z., Lai, J., Xie, X.: Learning view-specific deep networks for person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 27(7), 3472–3483 (2018)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Hermans, A., Beyer, L., Leibe, B.: In defense of the triplet loss for person re-identification. arXiv preprint arXiv:1703.07737 (2017)
Jiao, J., Zheng, W.S., Wu, A., Zhu, X., Gong, S.: Deep low-resolution person re-identification. In: Thirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (2018)
Li, W., Zhao, R., Xiao, T., Wang, X.: DeepReID: deep filter pairing neural network for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 152–159 (2014)
Li, X., Zheng, W.S., Wang, X., Xiang, T., Gong, S.: Multi-scale learning for low-resolution person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 3765–3773 (2015)
Shi, J., Qi, C.: From local geometry to global structure: learning latent subspace for low-resolution face image recognition. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 22(5), 554–558 (2015)
Suh, Y., Wang, J., Tang, S., Mei, T., Lee, K.M.: Part-aligned bilinear representations for person re-identification. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) Computer Vision – ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11218, pp. 418–437. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01264-9_25
Sun, Y., Zheng, L., Yang, Y., Tian, Q., Wang, S.: Beyond part models: person retrieval with refined part pooling (and a strong convolutional baseline). In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11208, pp. 501–518. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01225-0_30
Wang, F., Xiang, X., Cheng, J., Yuille, A.L.: NormFace: L2 hypersphere embedding for face verification. In: Proceedings of the 25th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 1041–1049. ACM (2017)
Wang, G., Yuan, Y., Chen, X., Li, J., Zhou, X.: Learning discriminative features with multiple granularities for person re-identification. In: 2018 ACM Multimedia Conference on Multimedia Conference, pp. 274–282. ACM (2018)
Wang, Z., Hu, R., Yu, Y., Jiang, J., Liang, C., Wang, J.: Scale-adaptive low-resolution person re-identification via learning a discriminating surface. In: IJCAI, pp. 2669–2675 (2016)
Xiao, T., Li, H., Ouyang, W., Wang, X.: Learning deep feature representations with domain guided dropout for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1249–1258 (2016)
Yang, Y., Yang, J., Yan, J., Liao, S., Yi, D., Li, S.Z.: Salient color names for person re-identification. In: Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T. (eds.) ECCV 2014. LNCS, vol. 8689, pp. 536–551. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10590-1_35
Yi, D., Lei, Z., Liao, S., Li, S.Z.: Deep metric learning for person re-identification. In: 2014 22nd International Conference on Pattern Recognition, pp. 34–39. IEEE (2014)
Zhao, R., Ouyang, W., Wang, X.: Unsupervised salience learning for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3586–3593 (2013)
Zheng, L., Yang, Y., Hauptmann, A.G.: Person re-identification: past, present and future. arXiv preprint arXiv:1610.02984 (2016)
Zhong, Z., Zheng, L., Cao, D., Li, S.: Re-ranking person re-identification with k-reciprocal encoding. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1318–1327 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Guo, T., Lai, J., Feng, Z., Chen, Z., Xie, X., Zheng, W. (2019). Low-Resolution Person Re-identification by a Discriminative Resolution-Invariant Network. In: Sun, Z., He, R., Feng, J., Shan, S., Guo, Z. (eds) Biometric Recognition. CCBR 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11818. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-31456-9_49
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-31456-9_49
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-31455-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-31456-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)