Abstract
Due to the increasing demands for modeling large-scale and complex systems, designing optimal controls, and conducting optimization tasks, many real-world applications require sophisticated models. Geometric methods are designed to capture the underlying structure of the system at hand and to preserve the global qualitative or geometric properties of the flow, such as symplecticity, volume preservation and symmetry. A survey on three of such structure preserving numerical methods is proposed in the present article. Testing the validity of such simulations is achieved by exhibiting analytically solvable models and comparing the result of simulations with their exact behavior.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Notes
- 1.
Here we made the assumption that
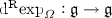 is invertible, which is the case for SO(3) whenever \(\Vert \varOmega \Vert <\pi \).
is invertible, which is the case for SO(3) whenever \(\Vert \varOmega \Vert <\pi \). - 2.
At least four since many generating functions can be constructed.
References
Arnol’d, V.I.: Mathematical Methods of Classical Mechanics, vol. 60. Springer, New York (2013)
Channell, P.J., Scovel, C.: Symplectic integration of hamiltonian systems. Nonlinearity 3(2), 231 (1990)
de Diego, D.M.: Lie-Poisson integrators. arXiv e-prints arXiv:1803.01427, March 2018
Demoures, F., Gay-Balmaz, F., Kobilarov, M., Ratiu, T.S.: Multisymplectic lie group variational integrator for a geometrically exact beam in R3. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 19(10), 3492–3512 (2014)
Demoures, F., Gay-Balmaz, F., Ratiu, T.S.: Multisymplectic variational integrators and space/time symplecticity. Anal. Appl. 14(03), 341–391 (2016)
Ge, Z., Marsden, J.E.: Lie-Poisson Hamilton-Jacobi theory and Lie-Poisson integrators. Phys. Lett. A 133(3), 134–139 (1988)
Hairer, E., Lubich, C., Wanner, G.: Geometric Numerical Integration: Structure-Preserving Algorithms for Ordinary Differential Equations, vol. 31. Springer, Heidelberg (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-30666-8
Li, S.T., Qin, M.: A note for Lie-Poisson Hamilton-Jacobi equation and Lie-Poisson integrator. Comput. Math. Appl. 30(7), 67–74 (1995)
Marsden, J.E., Pekarsky, S., Shkoller, S.: Discrete Euler-Poincaré and Lie-Poisson equations. Nonlinearity 12(6), 1647–1662 (1999)
Marsden, J.E., West, M.: Discrete mechanics and variational integrators. Acta Numerica 10, 357–514 (2001)
Marsen, J., Ratiu, T.: Introduction to Mechanics and Symmetry: A Basic Exposition of Classical Mechanical Systems. Texts in Applied Mathematics, vol. 17. Springer, New York (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-21792-5
Munthe-Kaas, H.: High order Runge-Kutta methods on manifolds. Appl. Numer. Math. 29(1), 115–127 (1999)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Bensoam, J., Carré, P. (2019). Geometric Numerical Methods with Lie Groups. In: Nielsen, F., Barbaresco, F. (eds) Geometric Science of Information. GSI 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11712. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-26980-7_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-26980-7_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-26979-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-26980-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)


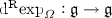 is invertible, which is the case for SO(3) whenever
is invertible, which is the case for SO(3) whenever