Abstract
We present Multiparty Classical Choreographies (MCC), a language model where global descriptions of communicating systems (choreographies) implement typed multiparty sessions. Typing is achieved by generalising classical linear logic to judgements that explicitly record parallelism by means of hypersequents. Our approach unifies different lines of work on choreographies and processes with multiparty sessions, as well as their connection to linear logic. Thus, results developed in one context are carried over to the others. Key novelties of MCC include support for server invocation in choreographies, as well as logic-driven compilation of choreographies with replicated processes.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Notes
- 1.
It may be surprising that some of the rules also include a restriction to a vector \(\tilde{z}\), and a session using a vector of processes \(\tilde{S}\), whose shape we do not inspect. This follows from the shape of coherence rules: rules such as
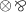 , \( \oplus {\, \& \,}\) and \(0\top \) contain an additional context \(\varGamma \), captured here by \(\tilde{z}\).
, \( \oplus {\, \& \,}\) and \(0\top \) contain an additional context \(\varGamma \), captured here by \(\tilde{z}\).
References
Atkey, R.: Observed communication semantics for classical processes. In: Yang, H. (ed.) ESOP 2017. LNCS, vol. 10201, pp. 56–82. Springer, Heidelberg (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-54434-1_3
Balzer, S., Pfenning, F.: Manifest sharing with session types. PACMPL 1(ICFP), 37:1–37:29 (2017)
Caires, L., Pérez, J.A.: Linearity, control effects, and behavioral types. In: Yang, H. (ed.) ESOP 2017. LNCS, vol. 10201, pp. 229–259. Springer, Heidelberg (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-54434-1_9
Caires, Luís, Pfenning, Frank: Session types as intuitionistic linear propositions. In: Gastin, Paul, Laroussinie, François (eds.) CONCUR 2010. LNCS, vol. 6269, pp. 222–236. Springer, Heidelberg (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15375-4_16
Carbone, M., Cruz-Filipe, L., Montesi, F., Murawska, A.: Multiparty classical choreographies. CoRR, abs/1808.05088 (2018)
Carbone, M., Honda, K., Yoshida, N.: Structured communication-centered programming for web services. ACM TOPLAS 34(2), 8 (2012)
Carbone, M., Lindley, S., Montesi, F., Schürmann, C., Wadler, P.: Coherence generalises duality: a logical explanation of multiparty session types. In: CONCUR, LIPIcs, vol. 59 , pp. 33:1–33:15. Schloss Dagstuhl - Leibniz-Zentrum fuer Informatik (2016)
Carbone, M., Montesi, F.: Deadlock-freedom-by-design: multiparty asynchronous global programming. In: POPL, pp. 263–274 (2013)
Carbone, M., Montesi, F., Schürmann, C.: Choreographies, logically. Distrib. Comput. 31(1), 51–67 (2018)
Carbone, M., Montesi, F., Schürmann, C., Yoshida, N.: Multiparty session types as coherence proofs. Acta Inf. 54(3), 243–269 (2017). Also: CONCUR 2015
Cruz-Filipe, L., Larsen, K.S., Montesi, F.: The paths to choreography extraction. In: Esparza, J., Murawski, A.S. (eds.) FoSSaCS 2017. LNCS, vol. 10203, pp. 424–440. Springer, Heidelberg (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-54458-7_25
DeYoung, H., Caires, L., Pfenning, F., Toninho, B.: Cut reduction in linear logic as asynchronous session-typed communication. In: CSL, LIPIcs, vol. 16, pp. 228–242. Schloss Dagstuhl - Leibniz-Zentrum fuer Informatik (2012)
Honda, K., Yoshida, N., Carbone, M.: Multiparty asynchronous session types. J. ACM 63(1), 91–967 (2016)
JBoss Community and Red Hat. Testable Architecture. http://www.jboss.org/savara/
Lange, J., Tuosto, E., Yoshida, N.: From communicating machines to graphical choreographies. In: POPL, pp. 221–232. ACM (2015)
Lindley, S., Morris, J.G.: Talking bananas: structural recursion for session types. In: ICFP, pp. 434–447. ACM (2016)
Montesi, F.: Choreographic Programming. Ph.D. thesis, IT University of Copenhagen (2013). http://www.itu.dk/people/fabr/papers/phd/thesis.pdf
Montesi, F.: Classical higher-order processes. In: Bouajjani, A., Silva, A. (eds.) FORTE 2017. LNCS, vol. 10321, pp. 171–178. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-60225-7_12
Montesi, F., Yoshida, N.: Compositional choreographies. In: D’Argenio, P.R., Melgratti, H. (eds.) CONCUR 2013. LNCS, vol. 8052, pp. 425–439. Springer, Heidelberg (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-40184-8_30
OpenID. OpenID specifications. http://openid.net/developers/specs/
Toninho, B., Caires, L., Pfenning, F.: Higher-order processes, functions, and sessions: a monadic integration. In: Felleisen, M., Gardner, P. (eds.) ESOP 2013. LNCS, vol. 7792, pp. 350–369. Springer, Heidelberg (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-37036-6_20
Wadler, P.: Propositions as sessions. J. Funct. Program. 24(2–3), 384–418 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Carbone, M., Cruz-Filipe, L., Montesi, F., Murawska, A. (2019). Multiparty Classical Choreographies. In: Mesnard, F., Stuckey, P. (eds) Logic-Based Program Synthesis and Transformation. LOPSTR 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11408. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-13838-7_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-13838-7_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-13837-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-13838-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)


 ,
,