Abstract
This paper explores the interaction between emotions and two types of questions, namely information-seeking questions and rhetorical questions. Corpus data shows that rhetorical questions (60.3%) are more frequently used in social media than information-seeking questions (39.7%). Of the two types of questions, approximately 94% of rhetorical questions are used to express emotions, while only 23% of information-seeking questions contain emotions. Given that rhetorical questions do play an important role in emotion expressions, we examine the interaction between rhetorical questions and emotions in terms of question type. Various syntactic structures are proposed for the identification of different emotions. We believe that the linguistic account of different types of rhetorical questions in emotion expressions will paint a fuller picture of the nature of emotion.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Notes
- 1.
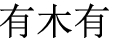 is often found in Weibo as a netizen transformation of
is often found in Weibo as a netizen transformation of
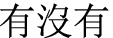 .
.
References
Bhattasali, S., Cytryn, J., Feldman, E., Park, J.: Automatic identification of rhetorical questions. ACL 2, 743–749 (2015)
Davidov, D., Tsur, O., Rappoport, A.: Semi-supervised recognition of sarcastic sentences in twitter and amazon. In: Proceedings of the 14th Conference on Computational Natural Language Learning, pp. 107–116 (2010)
Ekman, P., Cordaro, D.: What is meant by calling emotions basic. Emot. Rev. 3(4), 364–370 (2011)
Fainsilber, L., Ortony, A.: Metaphorical uses of language in the expression of emotions. Metaphor Symb. 2(4), 239–250 (1987)
Frank, J.: You call that a rhetorical question?: forms and functions of rhetorical questions in conversation. J. Pragmat. 14(5), 723–738 (1990)
Fussell, S.R.: The use of metaphor in written descriptions of emotional states. Unpublished manuscript, Carnegie Mellon University (1992)
Fussell, S.R., Moss, M.M.: Figurative language in emotional communication. In: Social and Cognitive Approaches to Interpersonal Communication, pp. 113–141 (1998)
Gibbs, R.W., Leggitt, J.S., Turner, E.A.: What’s special about figurative language in emotional communication. In: Fussell, S.R. (ed.) The Verbal Communication of Emotions: Interdisciplinary Perspectives, pp. 125–149. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Mahwah (2002)
González-Ibánez, R., Muresan, S., Wacholder, N.: Identifying sarcasm in twitter: a closer look. In: Proceedings of the 49th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies: Short Papers, vol. 2, pp. 581–586 (2011)
Kövecses, Z.: Emotion Concepts. Springer, New York (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-3312-1
Kövecses, Z.: Metaphor and Emotion: Language, Culture, and Body in Human Feeling. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2003)
Lakoff, G., Johnson, M.: Metaphors We Live by. University of Chicago Press, Chicago (1980)
Lee, S.Y.M.: A linguistic analysis of implicit emotions. In: Lu, Q., Gao, H. (eds.) CLSW 2015. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 9332, pp. 185–194. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-27194-1_19
Lee, S.Y.M.: Figurative language in emotion expressions. In: Wu, Y., Hong, J.F., Su, Q. (eds.) CLSW 2017. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 10709, pp. 408–419. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-73573-3_37
Leggitt, J.S., Gibbs, R.W.: Emotional reactions to verbal irony. Discourse Process. 29(1), 1–24 (2000)
Li, C.N., Thompson, S.A.: Mandarin Chinese: A Functional Reference Grammar. University of California Press, Berkeley (1981)
Liu, F.-h.: The scalar particle hai in Chinese. Cahiers de linguistique-Asie orientale 29(1), 41–84 (2000)
Petty, R.E., Cacioppo, J.T., Heesacker, M.: Effects of rhetorical questions on persuasion: a cognitive response analysis. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 40(3), 432 (1981)
Ranganath, S., Hu, X., Tang, J., Wang, S., Liu, H.: Identifying rhetorical questions in social media. In: ICWSM, pp. 667–670 (2016)
Reyes, A., Rosso, P., Veale, T.: A multidimensional approach for detecting irony in twitter. Lang. Resour. Eval. 47(1), 239–268 (2013)
Roberts, R.M., Kreuz, R.J.: Why do people use figurative language? Psychol. Sci. 5(3), 159–163 (1994)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by a General Research Fund (GRF) project sponsored by the Research Grants Council (Project No. B-Q50Z) and a PolyU Faculty Research Grant (Project No. 1-ZEVK).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lau, H.Y.P., Lee, S.Y.M. (2018). Information-Seeking Questions and Rhetorical Questions in Emotion Expressions. In: Hong, JF., Su, Q., Wu, JS. (eds) Chinese Lexical Semantics. CLSW 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11173. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-04015-4_31
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-04015-4_31
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-04014-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-04015-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)


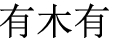 is often found in Weibo as a netizen transformation of
is often found in Weibo as a netizen transformation of
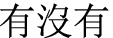 .
.