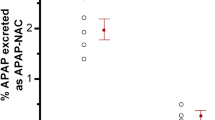
Abstract
Acetaminophen (APAP) induced hepatic centrilobular necrosis has been associated with cytochrome P-450-mediated generation of an electrophilic, reactive metabolite which covalently binds to cellular macromolecules as glutathione becomes depleted (Jollow, et al., 1973; Mitchell, et al., 1973a; 1973b; Potter, et al., 1973; 1974). Covalent binding has been well-correlated with the incidence and severity of liver necrosis and prior cytochrome P450 inhibition blocks both covalent binding and the atotoxicity (Jollow, et al., 1973; Potter, et al., 1973, 1974; Mitchell, et al., 1973a). In addition, administration of the cytochrome P-450 inhibitor, piperonyl butoxide (Pip B), 2 hrs after APAP, the time of maximal covalent binding (Jollow,et al., 1973, Ginsberg and Cohen, 1985) reduced the severity of liver damage (Brady, et al., 1988). The present study demonstrates that Pip B’s post-treatment protection is associated with alterations in selective protein arylation by APAP without a change in total covalent binding.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartolone, J.B., Sparks, K., Cohen, S.D. and Khairallah, E.A. (1987). Immunochemical detection of acetaminophen bound liver proteins. Biochem. Pharmacol. 36, 1193–1196.
Bartolone, J.B., Birge, R.B., Sparks, K., Cohen, S.D. and Khairallah, E.A. (1988). Immunochemical analysis of acetaminophen covalent binding to proteins: Partial characterization of the major acetaminophen-binding liver proteins. Biochem. Pharmacol. 37, 4763–4774.
Bartolone, J.B., Beierschmitt, W.P., Birge, R.B., Emeigh, Hart, S.G., Wyand, D.S., Cohen, S.D. and Khairallah, E.A. (1989). Selective acetaminophen metabolite binding to extrahepatic proteins: An in vivo and in vitro analysis. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 99, 240–249.
Beierschmitt, W.P., Brady, J.T., Bartolone, J.B., Wyand, D.S., Khairallah, E.A. and Cohen, S.D. (1989). Selective protein arylation and the age-dependency of acetaminophen hepatotoxicity in mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 98, 517–529.
Birge, R.B., Bartolone, J.B., McCann, D.J., Mangold, J.B., Cohen, S.D. and Khairallah, E.A. (1989). Selective protein arylation and 2,6-dimethyl acetaminophen in cultured mouse hepatocytes from phenobarbital-induced and uninduced mice: relationship to cytotoxicity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 31, 3745–3749.
Birge, R.B., Bartolone, J.B., Nishanian, E.V., Bruno, M.K., Mangold, J.B., Cohen, S.D. and Khairallah, E.A. (1988). Dissociation of covalent binding from the oxidative effects of acetaminophen: studies using dimethylated acetaminophen derivatives. Biochem. Pharmacol. 38, 4429–4439.
Brady, J.T., Montelius, D.A., Beierschmitt, W.P., Wyand, D.S., Khairallah, E.A. and Cohen, S.D. (1988). The effect of piperonyl butoxide post-treatment on acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 37, 2097–2099.
Dahlin, D.C., Miwa, G.T., Lu, A.Y.H. and Nelson, S.D. (1984). N-acetyl-pbenzoquinone imine: a cytochrome P-450-mediated oxidation product of acetaminophen. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 81, 1327–1331.
Gillette, J.R. (1974). A perspective on the role of chemically reactive metabolites of foreign compounds in toxicity: I. Correlation of changes in covalent binding of reactive metabolites with changes in the incidence and severity of toxicity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 23 2785–2794.
Ginsberg, G.L. and Cohen,.SD. (1985). Plasma membrane alterations andcovalent binding to hepatic organelles after an hepatotoxicdose of acetaminophen (APAP). The Toxicologist 5, 154.
Jollow, D.J., Mitchell, J.R., Potter, W.Z., Davis, D.C., Gillette, J.R. and Brodie, B.B. (1973). Acetaminophen-induced hepatic necrosis. II. Role of covalent binding in vivo. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 187, 185–194.
Mitchell, J.R., Jollow, D.J., Potter, W.Z., Davis, D.C., Gillette, J.R., and Brodie, B.B. (1973a). Acetaminophen-induced hepatic necrosis. I. Role of drug metabolism. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Therap. 187, 185–194.
Mitchell, J.R., Jollow, D.J., Potter, W.Z., Gillette, J.R. and Brodie, B.B. (1973b). Acetaminophen-induced hepatic necrosis. IV. Protective role of glutathione. J. Pharmacol. Exper. Therap. 187, 211–217.
Placke, M.E., Wyand, D.S. and Cohen, S.D. (1987). Extrahepatic lesions induced by acetaminophen in the mouse. Toxicologic Pathol. 15, 381–387.
Potter, W.Z., Davis, D.C., Mitchell, J.R., Jollow, D.J., Gillette, J.R. and Brodie, B.B. (1973). Acetaminophen-induced hepatic necrosis. III. Cytochrome-P450 mediated covalent binding in vitro. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 187, 203–210.
Potter, W.Z., Thorgeirsson, S.S., Jollow, D.J. and Mitchell, J.R. (1974). Acetaminophen-induced hepatic necrosis. V. Correlation of hepatic necrosis, covalent binding and glutathione depletion in hamsters. Pharmacol. 12, 129–143.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1991 Plenum Press, New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Brady, J.T., Birge, R.B., Khairallah, E.A., Cohen, S.D. (1991). Post-Treatment Protection with Piperonyl Butoxide Against Acetaminophen Hepatotoxicity is Associated with Changes in Selective but Not Total Covalent Binding. In: Witmer, C.M., Snyder, R.R., Jollow, D.J., Kalf, G.F., Kocsis, J.J., Sipes, I.G. (eds) Biological Reactive Intermediates IV. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 283. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-5877-0_88
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-5877-0_88
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4684-5879-4
Online ISBN: 978-1-4684-5877-0
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive