Abstract
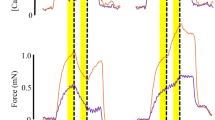
Previous studies have shown that radial compression of calcium-activated skinned skeletal muscle fibers, with attendant reduction of filament lattice spacing, reduces isometric force generation. In relaxed skinned fibers, radial compression produces a marked increase in axial elastic modulus, and the response to a small amplitude length perturbation resembles that of a muscle in rigor. We interpret these results as indicating that radial compression of the myofilament lattice produces “hindered” cross-bridges which are load bearing but not force generating.
The experiments reported here were designed to study the effect(s) of “hindered” cross-bridges on both the time course of isometric force responses following Ca2+ activation and fiber width and length perturbations. The experiments were carried out at room temperature on radially compressed skinned single rabbit soleus fibers. Force development following step-wise Ca2+ activation and step-wise changes of fiber width was “slow” (80–90 sec) compared to that in normal width fibers (~1 sec), and could be approximated by a single exponential curve. Force redevelopment following a length release in compressed fibers was both more rapid and more complicated than force development following activation and width steps, and required a double exponential curve for an adequate description. The results are consistent with the notion that hindered cross-bridges form as a result of lattice compression, and that the hindered bridges affect the force responses following width and length perturbations.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
April, E.W., Farrell, M. and Schreder, J. (1977). Osmotically induced changes in the filament lattice of skinned striated muscle fibers. Biophys. J. 17: 174a.
April, E.W. and Maughan, D.W. (1982). Correlation between interfilament spacing and force generation in striated muscle. Biophys. J. 37 (2): 129a.
Berman, M.R. and Maughan, D.W. (1962). Axial elastic modulus as a function of relative fiber width in relaxed skinned muscle fibers. Pflugers Arch. 393: 99–103.
Eisenberg. E. and Greene, L.E. (1980). The relation of muscle biochemistry to muscle physiology. Ann. Rev. Physiol. 42: 293–309.
Fabiato, A. and Fabiato, F. (1978). Myofilament-generated tension oscillations during partial calcium activation and activation dependence of the sarcomere length-tension relation of skinned cardiac cells. J. Gen. Physiol. 72: 667–699.
Ford, L.E., Huxley, A.F. and Simmons, R.M. (1977). Tension responses to sudden length change in stimulated frog muscle fibres near slack length. J. Physiol. 269: 441–515.
Godt, R.E. and Maughan, D.W. (1981). Influence of osmotic compression on calcium activation and tension in skinned muscle fibers of the rabbit. Pflug. Arch. 391: 334–337.
Goldman, Y.E., Matsubara, I. and Simmons, R M (1979). Lateral filamentary spacing in frog skinned muscle fibers in the relaxed and rigor states. J. Physiol. ( Lond. ) 295: 81p.
Griffiths, P.G., Kuhn, H.J., Güth, K. and Rüegg, J.C. (1979). Rate of isometric tension development in relation to calcium binding of skinned muscle fibers. Pflugers Arch. 382: 165–170.
Kramer, B. and Maughan, D. (1981). Dextran T500 decreases skinned fiber width, tension and ATPase. Biophys. J. 33: 27a.
Magid, A. and Reedy, M.K. (1980). X-ray diffraction observations of chemically skinned frog skeletal muscle processed by an improved method. Biophys. J. 30: 27–40.
Maughan, D. and Berman, M. (1982). Radial compression of functionally-skinned cardiac bundles abolishes calcium activated force. Biophys. J. 37: 363a.
Maughan, D.W. and Godt, R.E. (1981). Inhibition of force production in compressed skinned muscle fibers of the frog. Pflugers Arch. 390: 161–163.
Millman, B.M. and Nickel, B.G. (1980). Electrostatic forces in muscle and cylindrical gel systems Biophys. J. 32 (1): 49–63.
Moisecu, D.G. and Thieleczek, R. (1978). Calcium and strontium concentration changes within skinned muscle preparations following a change in the external bathing solution. J. Physiol. 275: 241–262.
Orentlicher, M., Reuben, J.P., Grundfest, H. and Brandt, P.W. (1974). Calcium binding and tension development in detergent-treated muscle fibers. J. Gen. Physiol. 83: 168–186.
Stephenson, D.G. and Williams, D.A. (1981). Calcium-activated force responses in fast-and slow-twitch skinned muscle fibres of the rat at different temperatures. J. Physiol. 317: 281–302.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1984 Plenum Press, New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Maughan, D.W., Berman, M.R. (1984). Force Response to Width and Length Peturbations in Compressed Skinned Skeletal Muscle Fibers. In: Pollack, G.H., Sugi, H. (eds) Contractile Mechanisms in Muscle. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 37. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-4703-3_65
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-4703-3_65
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4684-4705-7
Online ISBN: 978-1-4684-4703-3
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive