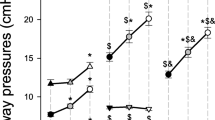
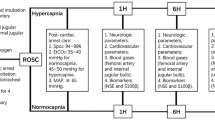
Abstract
Patients with severe head injury frequently suffer from general hypoxia in the early posttraumatic phase. General hypoxia must be considered a major cause of secondary brain damage. The anesthetic methods used for diagnostic or therapeutical procedures in these patients thus may have an influence on the formation of secondary damage by modifying blood flow and metabolism of the brain. As these mechanisms are still incompletely understood, we analysed the influence of different anesthetic agents on regional cerebral blood flow, brain surface pO2 and edema formation in an experimental model of head injury combined with systemic hypoxia.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kessler M, Lübbers DW (1966) Aufbau und Anwendungsmöglichkeiten verschiedener pO2-Elektroden. Pflügers Archiv 291: 82
Klatzo I, Piraux A, Laskowski EJ (1958) The relationship between edema, blood-brain-barrier and tissue elements in a local brain injury. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 17: 548–564
Murr R, Berger S, Schürer L, Baethmann A (1989) Regional cerebral blood flow and tissue pO2 after focal trauma: effects of isoflurane and fentanyl. In: Hammersen F, Messmer K, (Eds.) Cerebral Microcirculation. Progr Appl Microcirc, Vol. 16, Karger, Basel, pp. 61–70
Tengvar C, Forssen M, Hultström D, Olsson Y, Pertoft H, Petterson A (1982) Measurement of edema in the nervous system. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 57: 143–150
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1992 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Berger, S., Murr, R., Schürer, L., Enzenbach, R., Peter, K., Baethmann, A. (1992). Brain Surface pO2 and rCBF in Rabbits with a Focal Cerebral Lesion and Pulmonary Hypoxia under Fentanyl-, Isoflurane- or Thiopental-Anesthesia. In: Erdmann, W., Bruley, D.F. (eds) Oxygen Transport to Tissue XIV. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 317. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-3428-0_87
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-3428-0_87
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4613-6516-7
Online ISBN: 978-1-4615-3428-0
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive