Abstract
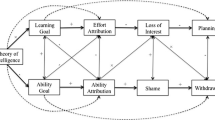
The study of the attributions has given researchers of achievement motivation a powerful key to understanding thoughts, feelings, and behaviors in achievement situations (Brown & Weiner, 1984; Diener & Dweck, 1978, 1980; Dweck & Elliott, 1983; Mueller & Dweck, 1998; Weiner, 1985; Weiner, Graham, & Chandler, 1982; CitationRef Weiner & Kukla, 1971). Decades of research has demonstrated that different attributions lead to unique patterns of coping. Indeed, Weiner has mapped the attribution-affect-behavior linkages for the major classes of attributions (see Weiner, 1985, for a review).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ames, C., & Archer, J. (1988). Achievement goals in the classroom: Students’ learning strategies and motivation processes. Journal of Educational Psychology, 80, 260–267.
Brown, J., & Weiner, B. (1984). Affective consequences of ability versus effort ascriptions: Controversies, resolutions, and quandries. Journal of Educational Psychology, 76(l), 146–158.
Crystal, D. S., Chen, C., Fuligni, A. J., Stevenson, H. W., Hsu, C. C., Ko, H. J., Kitamura, S., & Kimura, S. (1994). Psychological maladjustment and academic achievement: A cross-cultural study of Japanese, Chinese, and American high school students. Child Development, 65, 738–753.
Crystal, D. S., & Stevenson, H. W. (1991). Mothers’ perceptions of children’s problems with mathematics: A cross-national comparison. Journal of Educational Psychology, 83(3), 372–376.
Diener, C. I., & Dweck, C. S. (1978). An analysis of learned helplessness: Continuous changes in performance, strategy, and achievement cognitions following failure. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 36(5), 451–462.
Diener, C. I., & Dweck, C. S. (1980). An analysis of learned helplessness: II. The processing of success. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 39(5), 940–952.
Dweck, C. S. (1975). The role of expectations and attributions in the alleviation of learned helplessness. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 31(4), 674–685.
Dweck, C. S., & Bush, E. (1976). Sex differences in learned helplessness: I. Differential debilitation with peer and adult evaluators. Developmental Psychology, 12, 147–156.
Dweck, C. S., & Elliott, E. S. (1983). Achievement motivation. In P. Mussen & E. M. Hetherington (Eds.), Handbook of child psychology. New York: Wiley.
Dweck, C. S., & Leggett, E. L. (1988). A social-cognitive approach to motivation and personality. Psychological Review, 95, 256–273.
Elliott, E. S., & Dweck, C. S. (1988). Goals: An approach to motivation and achievement. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 54, 5–12.
Harackiewicz, J. M., Baron, K. E., Carter, S. M., Lehto, A. T., & Elliot, A. J. (1997). Predictors and consequences of achievement goals in the college classroom: Maintaining interest and making the grade. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 73, 1284–1295.
Hess, R. D., Chih-Mei, C., & McDevitt, T. M. (1982). Cultural variations in family beliefs about children’s performance in mathematics: Comparisons among People’s Republic of China, Chinese-American, and Caucasian-American families. Journal of Educational Psychology, 79(2), 179–188.
Hong, Y. Y., Chiu, C., Dweck, C. S., Lin, D., & Wan, W. (1999). Implicit theories, attributions, and coping. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 77(3), 588–599.
Kim, N. M., Grant, H., & Dweck, C. S. (1999). Views of intelligence: A comparative study of effort and ability viewpoints in Korean and American students’ constructs of intelligence. Unpublished manuscript, Columbia University.
Licht, B. & Dweck, C. S. (1984). Determinants of academic achievement: The interaction of children’s achievement orientations with skill area. Developmental Psychology, 20, 628–636.
Markus, H. R., & Kitayama, S. (1991). Culture and the self: Implications for cognition, emotion, and motivation. Psychological Review. 98(2), 224–253.
Morris, P., & Sweeting, A. (1995). Education and development in East Asia. New York: Garland Publishing.
Mueller, C. M., & Dweck, C. S. (1998). Praise for intelligence can undermine children’s motivation and performance. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 75(l) 33–52.
Nichols, J. G. (1984). Achievement motivation: Conceptions of ability, subjective experience, task choice, and performance. Psychological Review, 91, 328–346.
Peterson, C., & Barrett, L. C. (1987). Explanatory style and academic performance among university freshmen. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 53(3), 603–607.
Peterson, C., & Seligman, M. E. P. (1984). Causal explanations as a risk factor for depression: Theory and evidence. Psychological Review, 91, 346–374.
Shikanai, K. (1978). Effects of self-esteem on attribution of success-failure. Japanese Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 18, 47–55.
Sorich, L., & Dweck, C. S. (1997). Implicit theories and endorsement of punishment and rehabilitation. Unpublished manuscript, Columbia University.
Stigler, J. W., Smith, S., & Mao, L. (1985). The self-perception of competence by Chinese children. Child Development, 56, 1259–1270.
Stipek, D. J., & Gralinski, J. H. (1991). Gender differences in children’s achievement-related beliefs and emotional responses to success and failure in mathematics. Journal of Educational Psychology, 83(3), 361–371.
Stipek, D. J., & Kowalski, P. S. (1989). Learned helplessness in task-orienting versus performance-orienting testing conditions. Journal of Educational Psychology, 81(3), 384–391.
Stone, J., & Dweck, C. S. (1999). Theories of intelligence and the meaning of achievement goals. Unpublished manuscript, Columbia University.
Suzuki, B. H. (1980). The Asian-American family. In M. D. Fantini & R. Cardenas (Eds.), Parenting in a multi-cultural society (pp.74–102). New York: Longman.
Thomas, J. E. (1996). Modern Japan: A social history since 1868. New York: Longman.
Triandis, H. C. (1989). The self and social behavior in differing cultural contexts. Psychological Review, 96(3), 506–520.
Weiner, B. (1985). An attributional theory of achievement motivation and emotion. Psychological Review, 92(4), 548–573.
Weiner, B., Graham, S., & Chandler, C. (1982). Pity, anger, and guilt: An attributional analysis. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 8(2), 226–232.
Weiner, B., & Kukla, A. (1971). An attributional analysis of achievement motivation. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 15(l), 1–20.
Wilson, R. W., & Pusey (1982). Achievement motivation and small business relationship patterns in Chinese society. In S. L. Greenblatt, R. W. Wilson, & A. A. Wilson (Eds.), Social interaction in Chinese society (pp. 195–208). New York: Praeger.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2001 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Grant, H., Dweck, C.S. (2001). Cross-Cultural Response to Failure: Considering Outcome Attributions with Different Goals. In: Salili, F., Chiu, C.Y., Hong, Y.Y. (eds) Student Motivation. Plenum Series on Human Exceptionality. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-1273-8_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-1273-8_10
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4613-5472-7
Online ISBN: 978-1-4615-1273-8
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive