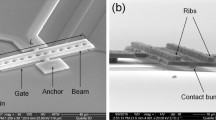
Abstract
Undesirable stiction, which results from the contact between surfaces, is a major failure mode in micro-switches. Indeed the adhesive forces can become so important that the two surfaces remain permanently glued, limiting the life-time of the MEMS. This is especially true when the contact happens between surfaces where elasto-plastic asperities deform permanently until the surfaces reach plastic accommodation, increasing the surface forces. To predict this behavior, a micro adhesive-contact model is developed, which accounts for the surfaces topography evolutions during elasto-plastic contacts. This model can be used at a higher scale to study the MEMS behavior, and thus its life-time. The MEMS devices studied here are assumed to work in a dry environment. In these operating conditions only the Van der Waals forces have to be considered for adhesion. For illustration purpose, an electrostatic-structural analysis is performed on a micro-switch. To determine the degree of plasticity involved, the impact energy of the movable electrode at pull-in is estimated. Thus the maximal adhesive force is predicted using the developed model.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Van Spengen W, Puers R, DeWolf I (2003) On the physics of stiction and its impact on the reliability of microstructures. J Adhes Sci Technol 17(4):563–582
Do C, Hill M, Lishchynska M, Cychowski M, Delaney K (2011) Modeling, simulation and validation of the dynamic performance of a single-pole single-throw RF-MEMS contact switch. In: 2011 12th international conference on thermal, mechanical and multi-physics simulation, and experiments in microelectronics and microsystems (EuroSimE), Linz, Austria, April 2011, pp 1–6
Wu L, Noels L, Rochus V, Pustan M, Golinval J-C (2011) A micro-macroapproach to predict stiction due to surface contact in microelectromechanical systems. J Microelectromech Syst 20(4):976–990
Wu L, Rochus V, Noels L, Golinval J-C (2009) Influence of adhesive rough surface contact on microswitches. J Appl Phys 106(11):113502-1–113502-10
Johnson K, Kendall K, Roberts A (1971) Surface energy and the contact of elastic solids. Proc R Soc Lond A Math Phys Sci 324(1558):301–313
Derjaguin B, Muller V, Toporov Y (1975) Effect of contact deformation on the adhesion of elastic solids. J Colloid Interface Sci 53(2):314–326
Maugis D (1992) Adhesion of spheres: the JKRDMT transition using a Dugdale model. J Colloid Interface Sci 150(1):243–269
Kim K, McMeeking R, Johnson K (1998) Adhesion, slip, cohesive zones and energy fluxes for elastic spheres in contact. J Mech Phys Solids 46(2):243–266
Greenwood J, Williamson J (1966) Contact of nominally flat surfaces. Proc R Soc Lond A Math Phys Eng Sci 295(1442):300–319
Greenwood J, Tripp J (1971) The contact of two nominally flat rough surfaces. Proc Inst Mech Eng 1847–1996 185(1970):625–633
Jones R (2004) Models for contact loading and unloading of a rough surface. Int J Eng Sci 42(17–18):1931–1947
Williams J (2005) The influence of repeated loading, residual stresses and shakedown on the behaviour of tribological contacts. Tribol Int 38(9):786–797
Majumder S, McGruer N, Adams G, Zavracky P, Morrison R, Krim J (2001) Study of contacts in an electrostatically actuated microswitch. Sens Actuat A Phys 93(1):19–26
Wu L, Golinval J-C, Noels L. A micro model for elasto-plastic adhesive-contact in micro-switches. Tribol Int (submitted)
Chang W, Etsion I, Bogy D (1987) An elasticplastic model for the contact of rough surfaces. J Tribol 109(2):257–263
Jackson R, Green I (2005) A finite element study of elasto-plastic hemispherical contact against a rigid flat. J Tribol 127(2):343–354
Etsion I, Kligerman Y, Kadin Y (2005) Unloading of an elastic–plastic loaded spherical contact. Int J Solids Struct 42(13):3716–3729
Kadin Y, Kligerman Y, Etsion I (2007) Cyclic loading of an elasticplastic adhesive spherical microcontact. J Appl Phys 104(7):073522-1–073522-8
Du Y, Chen L, McGruer N, Adams G, Etsion I (2007) A finite element model of loading and unloading of an asperity contact with adhesion and plasticity. J Colloid Interface Sci 312(2):522–528
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 The Society for Experimental Mechanics
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wu, L., Golinval, JC., Noels, L. (2013). Stiction Failure in Microswitches Due to Elasto-Plastic Adhesive Contacts. In: Shaw, G., Prorok, B., Starman, L. (eds) MEMS and Nanotechnology, Volume 6. Conference Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Mechanics Series. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-4436-7_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-4436-7_11
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4614-4435-0
Online ISBN: 978-1-4614-4436-7
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)