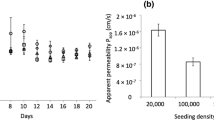
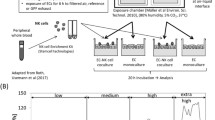
Abstract
Airborne agents enter the body for the most part by first contacting some part of the respiratory epithelium. Particulates and gases may cross the epithelium by solution in the cell membranes or pinocytosis. Insoluble particles may be engulfed and removed by macrophages and mucociliary clearance mechanisms, but macrophages engorged with particulate materials may remain in the lung for prolonged times and serve as a source for continued exposure of other cells to potential toxins.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. G. Plopper, D. L. Dungworth and W. S. Tyler, Morphometric evaluation of pulmonary lesions in rats exposed to ozone. Am. J. Pathol. 71: 395–408 (1973).
M. J. Evans, R. J. Stephens, L. J. Cabral and G. Freeman, Cell renewal in the lungs of rats exposed to low levels of NO2. Arch. Environ. Health 27: 180–188 (1972).
C. E. Cross, A. J. de Lucia, A. K. Reddy, M. Z. Hussain, C. K. Chow and M. G. Mustafa, Ozone interactions with tissue: Biochemical approaches. Am. J. Med. 60: 929–935 (1976).
B. D. Goldstein, C. Lodi, C. Collinson and O. J. Balchum, Ozone and lipid peroxidation. Arch. Environ. Health 18: 631–635 (1969).
Y. Berwald and L. Sachs, In vitro transformation of normal cells to tumor cells by carcinogenic hydrocarbons. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 35:641–661 (1965).
J. DiPaolo and P. Donovan, Properties of Syrian hamster cells transformed in the presence of carcinogenic hydrocarbons. Exptl. Cell Res. 48: 361–377 (1967).
R. J. Mason, M. C. Williams, R. D. Greenleaf and J. A. Clements, Isolation and properties of Type II alveolar cells. Am. Rev. Resp. Pis. 115: 1015–1026 (1977).
Y. Kikkawa and K. Yoneda, The Type II epithelial cell of the lung. Lab. Invest. 30: 76–84 (1974).
T. R. Devereaux and J. R. Fouts, The nonciliated cell bronchiolar epithelial (Clara) cell of the rabbit lung: Isolation and identification. Fed. Proc. 1092 (1980).
D. M. Pace, J. R. Thompson, B. T. Aftonomos and H. G. O. Hoick, The effects of NO2 and salts of NO2 upon established cell lines. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 39: 1247–1255 (1961).
R. H. Fetner, Ozone-induced chromosome breakage in human cell cultures. Nature 194: 793–794 (1962).
C. Voisin, C. Aerts, E. Jakubczak and A. B. Tonnel, La culture cellulaire en phase gazeuse. Bull. Europ. phisopath. Resp. 13: 69–82 (1977).
G. M. Alink, J. C. M. van der Hoeven, F. M. H. Debets, W. S. M. ven de Ven and J. H. Koeman, A new exposure model for in vitro testing of effects of gaseous pollutants on mammalian cells by means of gas diffusion through plastic films. Chemosphere 2: 63–73 (1979).
R. B. Painter, Rapid test to detect agents that damage human DNA. Nature 265: 650–651 (1977).
P. Perry and S. Wolff, A new giemsa method for the differential Nature 251: 156–158 (1974).
G. S. Samuelsen, R. E. Rasmussen, B. K. Nair and T. T. Crocker, Novel culture and exposure system for measurement of effects of airborne pollutants on mammalian cells. Env. Sci. Techno1. 12: 426–430 (1978).
H. J. Phillips, Dye exclusion tests for cell viability, in: Tissue Culture Methods and Applications, P. F. Kruse, Jr., and M. K. Patterson, Jr., Eds., Academic Press, New York, 406–408 (1973).
P. C. Gooch, D. A. Creasia and J. G. Brewen, The cytogenetic effects of ozone: Inhalation and in vitro exposures. Environ. Res. 12: 188–195 (1976).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1982 Plenum Press, New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Rasmussen, R.E., Crocker, T.T. (1982). Lung Cells Grown on Cellulose Membrane Filters as an In Vitro Model of the Respiratory Epithelium. In: Tice, R.R., Costa, D.L., Schaich, K.M. (eds) Genotoxic Effects of Airborne Agents. Environmental Science Research, vol 25. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-3455-2_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-3455-2_9
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4613-3457-6
Online ISBN: 978-1-4613-3455-2
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive