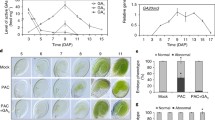
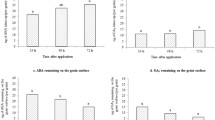
Abstract
The cereal aleurone layer has proved to be an ideal system in which to study the mechanism of gibberellin (GA) action at both the cellular and molecular levels. However, evidence that endogenous GAs are regulating the synthesis of hydrolytic enzymes in the aleurone during germination of intact grains is fragmentary and often contradictory (for reviews, see refs. 1–5). From work initiated in the 1960s, a relatively simple hormonal model for germinating cereal grains was proposed whereby GA1 (or GA3) produced in the embryo (either in the scutellum or embryonic axis) diffused to the aleurone layer where it initiated de novo synthesis of several hydrolytic enzymes, including α-amylase. These enzymes were secreted into the endosperm, and the products of reserve degradation were utilized by the growing embryo.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akazawa T, Miyata Y. Biosynthesis and secretion of a-amylase and other hydrolases in germinating cereal seeds. Essays in Biochem. 1982; 18: 41–78.
Akazawa T, Hara-Nishimura I. Topographical aspects of biosynthesis, extra-cellular secretion, and intracellular storage of proteins in plant cells. Ann Rev Plant Physiol. 1985; 36: 441–472.
Trewavas AJ. Growth substance sensitivity: The limiting factor in plant development. Physiol Plant. 1982; 55: 60–72.
Baulcombe D, Lazarus C, Martienssen R. Gibberellins and gene control in cereal aleurone cells. J Embryol Exp Morph. 1984; 83:Supplement, 119–135.
Fincher GB. Molecular and cellular biology associated with endosperm mobilisation in germinating cereal grains. Ann Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol. 1989; 40: 305–346.
Rood SB, Pharis RP, Koshioka M. Reversible conjugation of gibberellins in situ in maize. Plant Physiol. 1983; 73: 340–346.
Thomas TH, Khan AA, O’Toole DF. The location of cytokinins and gibberellins in wheat seeds. Physiol Plant. 1978; 42: 61–66.
Atzorn R, Weiler EW. The role of endogenous gibberellins in the formation of a-amylase by aleurone layers of germinating barley caryopses. Planta. 1983; 159: 289–299.
Gilmour SJ, MacMillan J. Effect of inhibitors of gibberellin biosynthesis on the induction of a-amylase in embryoless caryopses of Hordeum vulgare cv. Himalaya. Planta. 1984; 162: 89–90.
Hill RD, MacGregor AW. Cereal a-amylases in grain research and technology. In: Pomeranz Y, ed. Advances in cereal science and technology, Vol. 9. St. Paul, Minnesota: American Association of Cereal Chemists, 1988: p. 217–261.
Lenton JR, Hedden P, Gale MD. Gibberellin insensitivity and depletion in wheat—consequences for development. In: Hoad GV, Lenton JR, Jackson MB, Atkin RK, eds. Hormone action in plant development—A critical appraisal. London: Butterworths, 1987: p. 145–160.
Flintham JE, Gale MD. The Tom Thumb dwarfing gene, Rht3 in wheat, 1. Reduced pre-harvest damage to breadmaking quality. Theor Appl Genet. 1982; 62: 121–126.
Huttly AK, Baulcombe DC. Hormonal control of wheat α-amylase genes. In: Grierson D, Lycett G, eds. Genetic engineering of crop plants. London: Butterworths, 1989: p. 171–189.
Gaskin P, Kirkwood PS, Lenton JR, et al. Identification of gibberellins in developing wheat grain. Agric Biol Chem. 1980; 44: 1589–1593.
Kirkwood P, MacMillan J. Gibberellins A60, A61 and A62: Partial syntheses and natural occurrence. J Chem Soc Perkin Trans 1. 1982; 689–697.
MacGregor EA, MacGregor AW. Studies of cereal a-amylase using cloned DNA. CRC Crit Rev Biotechnol. 1987; 5: 129–142.
Jacobsen JV, Chandler PM. Gibberellin and abscisic acid in germinating cereals. In: Davies PJ, ed. Plant hormones and their role in plant growth and development. Dordrecht: Martinus Nijhoff Publishers, 1987: p. 164–193.
Chandler PM, Zwar JA, Jacobsen JV, et al. The effects of gibberellic acid and abscisic acid on a-amylase mRNA levels in barley aleurone layers; studies using an a-amylase cDNA clone. Plant Mol Biol. 1984; 3: 407–418.
Lazarus CM, Baulcombe DC, Martienssen RA. α-Amylase genes of wheat are two multigene families which are differentially expressed. Plant Mol Biol. 1985; 5: 13–24.
Sargeant JG, Walker TS. Adsorption of wheat alpha-amylase isozymes to wheat starch. Stärke. 1978; 30: 160–163.
Daussant J, Renard HA, Skakoun A. Application of direct tissue rocket-line immunoelectrophoresis to the study of α-amylase production and its localisation in wheat seeds during the early stages of germination. Electrophoresis. 1982; 3: 99–101.
Marchylo BA, Kruger JE, MacGregor AW. Production of multiple forms of alpha-amylase in germinated, incubated, whole, de-embryonated wheat kernels. Cereal Chem. 1984; 61: 305–310.
Nolan RC, Ho T-H D. Hormonal regulation of gene expression in barley aleurone layers. Planta. 1988; 174: 551–560.
Hedden P, Graebe JE. Inhibition of gibberellin biosynthesis by paclobutrazol in cell-free homogenates of Cucurbita maxima endosperm and Malus pumila embryos. Plant Growth Regul. 1985; 4: 111–112.
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1991 Springer-Verlag New York Inc.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lenton, J.R., Appleford, N.E.J. (1991). Gibberellin Production and Action during Germination of Wheat. In: Takahashi, N., Phinney, B.O., MacMillan, J. (eds) Gibberellins. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-3002-1_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-3002-1_13
Publisher Name: Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4612-7754-5
Online ISBN: 978-1-4612-3002-1
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive