Abstract
By means of the unitary Gabor transform one can relate operators on signals to operators on the space of Gabor transforms. In order to obtain a translation and modulation invariant operator on the space of signals, the corresponding operator on the reproducing kernel space of Gabor transforms must be left invariant, i.e. it should commute with the left regular action of the reduced Heisenberg group H r. By using the left invariant vector fields on H r and the corresponding left-invariant vector fields on phase space in the generators of our transport and diffusion equations on Gabor transforms we naturally employ the essential group structure on the domain of a Gabor transform. Here we mainly restrict ourselves to non-linear adaptive left-invariant convection (reassignment), while maintaining the original signal.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Notes
- 1.
As we explain in [118, Appendices B and C] the Gabor domain is a principal fiber bundle
 equipped with the Cartan connection form \(\omega_{g}(X_{g})= \langle\mathrm{d}s + \frac{1}{2}(p\,\mathrm{d}q -q\, \mathrm{d}p) , X_{g}\rangle\), or equivalently, it is a contact manifold, cf. [54, p. 6], [118, Appendix B, Definition B.14],
equipped with the Cartan connection form \(\omega_{g}(X_{g})= \langle\mathrm{d}s + \frac{1}{2}(p\,\mathrm{d}q -q\, \mathrm{d}p) , X_{g}\rangle\), or equivalently, it is a contact manifold, cf. [54, p. 6], [118, Appendix B, Definition B.14], 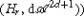 .
. - 2.
The metric tensor is degenerate on H r, but we consider a contact manifold
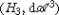 where tangent vectors along horizontal curves do not have an
where tangent vectors along horizontal curves do not have an 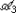 -component.
-component. - 3.
References
Akian, M., Quadrat, J., Viot, M.: Bellman Processes. Lecture Notes in Control and Information Science, vol. 199, pp. 302–311. Springer, Berlin (1994)
Auger, F., Flandrin, P.: Improving the readability of time-frequency and time-scale representations by the reassignment method. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 43(5), 1068–1089 (1995)
Bryant, R.L., Chern, S.S., Gardner, R.B., Goldschmidt, H.L., Griffiths, P.A.: Exterior Differential Systems. Mathematical Sciences Research Institute Publications, vol. 18. Springer, New York (1991)
Burgeth, B., Weickert, J.: An explanation for the logarithmic connection between linear and morphological systems. In: Griffin, L.D., Lillholm, M. (eds.) Scale-Space Methods in Computer Vision: Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference, Scale-Space 2003, Isle of Skye, UK, June 2003. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 2695, pp. 325–339. Springer, Berlin (2003)
Chassande-Mottin, E., Daubechies, I., Auger, F., Flandrin, P.: Differential reassignment. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 4(10), 293–294 (1997)
Crandall, M.G., Lions, P.-L.: Viscosity solutions of Hamilton-Jacobi equations. Trans. Am. Math. Soc. 277(1), 1–42 (1983)
Daudet, L., Morvidone, M., Torrésani, B.: Time-frequency and time-scale vector fields for deforming time-frequency and time-scale representations. In: Proceedings of the SPIE Conference on Wavelet Applications in Signal and Image Processing, pp. 2–15. SPIE, Bellingham (1999)
Dieudonné, J.: Treatise on Analysis, vol. 5. Academic Press, New York (1977). Translated by I.G. Macdonald, Pure and Applied Mathematics, vol. 10-V
Duits, R.: Perceptual organization in image analysis. PhD thesis, Eindhoven University of Technology, Department of Biomedical Engineering, The Netherlands (2005)
Duits, R., Burgeth, B.: Scale spaces on Lie groups. In: Sgallari, F., Murli, A., Paragios, N. (eds.) Scale Space and Variational Methods in Computer Vision: Proceedings of the 1st International Conference, SSVM 2007, Ischia, Italy, May–June 2007. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 4485, pp. 300–312. Springer, Berlin (2007)
Duits, R., Franken, E.M.: Left invariant parabolic evolution equations on SE(2) and contour enhancement via invertible orientation scores, part II: Nonlinear left-invariant diffusion equations on invertible orientation scores. Q. Appl. Math. 68, 293–331 (2010)
Duits, R., Franken, E.M.: Left invariant parabolic evolution equations on SE(2) and contour enhancement via invertible orientation scores, part I: Linear left-invariant diffusion equations on SE(2). Q. Appl. Math. 68, 255–292 (2010)
Duits, R., Franken, E.M.: Left-invariant diffusions on the space of positions and orientations and their application to crossing-preserving smoothing of HARDI images. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 92(3), 231–264 (2011)
Duits, R., van Almsick, M.: The explicit solutions of linear left-invariant second order stochastic evolution equations on the 2D-Euclidean motion group. Q. Appl. Math. 66, 27–67 (2008)
Duits, R., Felsberg, M., Granlund, G., ter Haar Romeny, B.M.: Image analysis and reconstruction using a wavelet transform constructed from a reducible representation of the Euclidean motion group. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 72(1), 79–102 (2007)
Duits, R., Führ, H., Janssen, B.J.: Left invariant evolution equations on Gabor transforms. Technical report CASA-report nr. 9, 2009, Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, Eindhoven University of Technology (2009)
Duits, R., Führ, H., Janssen, B.J., Bruurmijn, L.C.M.: Left invariant reassignment and diffusion on Gabor transforms. ACHA (2011, submitted)
Evans, L.C.: Partial Differential Equations. Graduate Studies in Mathematics, vol. 19. American Mathematical Society, Providence (2002)
Franken, E.M.: Enhancement of crossing elongated structures in images. PhD thesis, Eindhoven University of Technology, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Eindhoven, The Netherlands (2008). http://bmia.bmt.tue.nl/people/efranken/PhDThesisErikFranken.pdf
Franken, E.M., Duits, R.: Crossing preserving coherence-enhancing diffusion on invertible orientation scores. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 85(3), 253–278 (2009)
Franken, E., Duits, R.: Crossing-preserving coherence-enhancing diffusion on invertible orientation scores. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 85(3), 253–278 (2009)
Gabor, D.: Theory of communication. J. Inst. Electr. Eng. 93, 429–457 (1946)
Gröchenig, K.: Foundations of Time-Frequency Analysis. Applied and Numerical Harmonic Analysis. Birkhäuser Boston, Boston (2001)
Helstrom, C.: An expansion of a signal in Gaussian elementary signals. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 12(1), 81–82 (1966)
Hörmander, L.: Hypoelliptic second order differential equations. Acta Math. 119, 147–171 (1967)
Janssen, A.J.E.M.: The Zak transform: a signal transform for sampled time-continuous signals. Philips J. Res. 43(1), 23–69 (1988)
Janssen, B.J.: Representation and manipulation of images based on linear functionals. PhD thesis, Eindhoven University of Technology, Eindhoven, The Netherlands (2009)
Kodera, K., de Villedary, C., Gendrin, R.: A new method for the numerical analysis of non-stationary signals. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 12(2–3), 142–150 (1976)
Lions, J.L., Magenes, E.: Non-homogeneous Boundary Value Problems and Applications, vols. 1–3. Springer, Berlin (1972–1973)
Taylor, T.: A parametrix for step-two hypoelliptic diffusion equations. Trans. Am. Math. Soc. 296, 191–215 (1986)
Acknowledgements
The Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research (NWO) is gratefully acknowledged for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer-Verlag London Limited
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Duits, R., Führ, H., Janssen, B. (2012). Left Invariant Evolution Equations on Gabor Transforms. In: Florack, L., Duits, R., Jongbloed, G., van Lieshout, MC., Davies, L. (eds) Mathematical Methods for Signal and Image Analysis and Representation. Computational Imaging and Vision, vol 41. Springer, London. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4471-2353-8_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4471-2353-8_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, London
Print ISBN: 978-1-4471-2352-1
Online ISBN: 978-1-4471-2353-8
eBook Packages: Mathematics and StatisticsMathematics and Statistics (R0)


 equipped with the Cartan connection form
equipped with the Cartan connection form 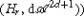 .
.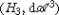 where tangent vectors along horizontal curves do not have an
where tangent vectors along horizontal curves do not have an  -component.
-component.