Abstract
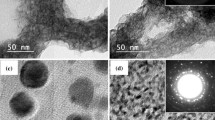
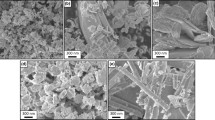
This study investigated the effects of an excess of bismuth in Bi0.5K0.5TiO3 (BKT) on its structural and morphological properties. Two types of BKT samples were prepared using bismuth stoichiometry, where one with a Bi:K molar ratio of 1:1 (S-BKT) and the other with a ratio of 1.1:1 with 10 mol% excess of Bi (10% BKT). These samples were prepared using the hydrothermal synthesis method. When the X-ray diffraction (XRD) data for the two samples were compared, the 10% BKT shows a 1.3 times larger than that for the S-BKT sample in the ratio of the secondary phase peak to the BKT (101) peak at approximately 29.3°. Morphology analysis showed that both samples had agglomerations with diameters of approximately 200 nm and nanowires with lengths of 1–2 μm and diameters of 8 nm. The fractions of the total area occupied by agglomerations in the two samples were estimated at approximately 95% for 10% BKT and approximately 45% for S-BKT. These results indicate that an excess of bismuth affects the secondary phase and agglomeration formation. Nanogenerators were prepared by mixing S-BKT, and their output voltages were 1.8 V and their outputs currents were 4 nA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Wu et al., ACS Nano 6, 6231 (2012).
J. Kim et al., Nano Lett. 8, 1813 (2008).
J. K. Han et al., Sci. Rep. 6, 29562 (2016).
J. K. Han et al., Nanomaterials 7, 308 (2017).
Z. L. Wang and J. Song, Science 321, 242 (2006).
C. F. Buhrer, J. Chem. Phys. 36, 798 (1962).
A. Sasaki, T. Chiba, Y. Mamiya and E. Otsuki, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 38, 5564 (1999).
R. Zuo, X. Fang and C. Ye, J. Am. Ceram. 90, 2424 (2007).
H. Matsuo et al., J. Appl. Phys. 108, 104103 (2010).
Y. Hiruma, R. Aoyagi, H. Nagata and T. Takenaka, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 44, 5040 (2005).
Y. Hiruma, H. Nagata and T. Takenaka, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 46, 1081(2007).
K. Tabuchi, H. Nagata and T. Takenaka, J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 121, 623 (2013).
J. König et al., J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 29, 1695 (2009).
T. Zaremba, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 74, 653 (2003).
M. Hagiwara and S. Fujihara, J. Mater. Sci. 50, 5970 (2015).
M. Yoshimura and K. Byrappa, J. Mater. Sci. 43, 2085 (2007).
M. M. Lencka, M. Oledzka and R. E. Riman, Chem. Mater. 12, 1323 (2000).
J. Chen and J. Cheng, J. Alloys. Comp. 589, 115 v.
A. Z. Simões et al., Mater. Lett. 59, 656 (2005).
S. Y. Cho et al., Curr. Appl. Phys. 15, 1332 (2015).
S. A. Yang, B. H. Kim and S. D. Bu, Ferroelectrics 533, 49 (2018).
S. W. Kang et al., J. Korean Phys. Soc. 72, 1209 (2018).
S. W. Kang, S. Y. Cho, S. D. Bu and J. K. Han, J. Korean Phys. Soc. 72, 800 (2018).
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by “Research Base Construction Fund Support Program” funded by Chonbuk National University in 2018, and by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (No. NRF-2018R1A2B6006740), and by a cooperation project of “SI1803-01 (Development of smart chemical materials for IoT devices)” by the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology (KRICT).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S.Y., Kim, E.Y., Bu, S.D. et al. Influence of Bi Excess on the Structural and Morphological Properties of Bi0.5K0.5TiO3 Synthesized by Using the Hydrothermal Method and Its Nanogenerator Properties. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 74, 1027–1031 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.74.1027
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.74.1027