Abstract
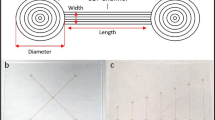
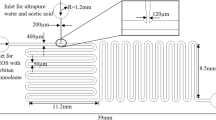
A mixture of reactants in a PDMS(Polydimethylsiloxane)-based microfluidic channel is a very important factor. A mixture of the fluid in a microfluidic channel is frequently achieved by using some special structure such as grooves or form by inducing a high rate flow that results in a high Reynold number (over 24943 ≫ 2000). However, these methods are accompanied by a complicated procedure like lithography or a special attachment protocol between PDMS and glass. In this study, we introduce a PDMS-based screw-wall microfluidic channel (SMC) as a functionalized channel. The SMC can be developed using a simple protocol and skipping some complicated procedures. Nevertheless, a turbulent flow showing the same mixing performance at low flow rate can be formed. The turbulent flow in the SMC is supported by a computational simulation and is observed by using a mixture of red ink and blue ink under a microscope. Furthermore, its effectiveness for commercial application is confirmed with the synthesis of nanoparticles. The dispersion coefficient (DR) is suggested in a computational simulation and is calculated for three different ratios of the screw thread diameter to the pipe line diameter. This shows that the more effective the mixture by turbulent flow in the SMC is, the nearer to 1 the ratio is. In experiments, a comparison study of a SMC and a plain wall microchannel shows clear differences in the mixtures performance. Finally, nanoparticles are synthesized for 5 different SMCs with pipe line diameters of 120, 170, 200, 500, and 1000 um and a single-peaked distribution for the sizes of the nanoparticles is observed when a 120 um SMC is applied. These results prove that the SMC developed by using our suggesting simple protocol can form a turbulent flow at low flow rate and is good enough to be used as a mixer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. L. Chiang, C. S. Sung, T. F. Wu, C. Y. Chen and C. Y. Hsu, J. Chromatogr B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 822, 1 (2005).
B. J. Zheng, D. Tice, L. S. Roach and R. F. Ismagilov, Angew Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 43, 19 (2004).
L. H. Hung, K. M. Choi, W. Y. Tseng, Y. C. Tan, K. J. Shea and A. P. Lee, Lab Chip 6, 2 (2006).
Y. Song, J. Hormes and C. S. Kumar, Small 4, 6 (2008).
K. S. Elvira, X. C. Solvas and R. C. Wootton, Nat. Chem. 5, 11 (2013).
K. Jain, C. Wu, S. V. Atre, G. Jovanovic, V. Narayanan, S. Kimura, V. Sprenkle, N. Canfield and S. Roy, NSTI Nanotech. Technical Proceedings 3, 391 (2007).
X. Z. Lin, A. D. Terepka and H. Yang, Nano Lett. 4, 11 (2004).
S. Y. Yang, F. Y. Cheng, C. S. Yeh and G. B. Lee, Microfluid Nanofluidics 8, 3 (2010).
V. S. Cabeza, S. Kuhn, A. A. Kulkarni and K. F. Jensen, Langmuir 28, 17 (2012).
I. Shestopalov, J. D. Tice and R. F. Ismagilov, Lab Chip 4, 4 (2004).
J. BurmáKyong and E. Kyuá Lee, Analyst 130, 7 (2005).
L. H. Hung, K. M. Choi, W. Y. Tseng, Y. C. Tan, K. J. Shea and A. P. Lee, Lab Chip 6, 2 (2006).
R. Karnik, F. Gu, P. Basto, C. Cannizzaro, L. Dean, W. Kyei-Manu, R. Langer and O. C. Farokhzad, Nano Lett. 8, 9 (2008).
Q. Zhang, J. J. Xu, Y. Liu and H. Y. Chen, Lab Chip 8, 2 (2008).
S. Marre and K. F. Jensen, Chem. Soc. Rev. 39, 3 (2010).
D. Liu, S. Cito, Y. Zhang, C. F. Wang, T. M. Sikanen and H. A. Santos, Adv. Mater. 27, 14 (2015).
B. Yu, X. Sun, X. Liu, H. Cong, Y. Wang, X. Shu, H. Yuan, D. Wang and J. Tang, Sci. Adv. Mater. 7, 5 (2015).
J. B. You, K. I. Min, B. Lee, D. P. Kim and S. G. Im, Lab Chip 13, 7 (2013).
J. B. You, K. Kang, T. T. Tran, H. Park, W. R. Hwang, J. M. Kim and S. G. Im, Lab Chip 15, 7 (2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, JM., Lim, J., Lee, TR. et al. PDMS-based Screw-wall Microfluidic Channel Forming a Turbulent Flow at Low Reynold Number. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 73, 60–64 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.73.60
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.73.60