Abstract
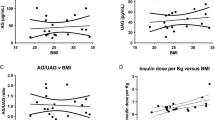
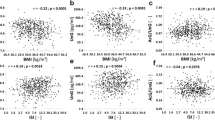
Background: Ghrelin circulates in blood as acylated (AG) and unacylated (UAG) ghrelin. The physiological role of the two forms is poorly understood, in particular in childhood. Aim of the study was to evaluate the AG and UAG levels in obese and normal weight (NW) children, pre-pubertal and pubertal, and their relationship with insulin, leptin and adiponectin levels. Subjects and methods: A population-based study in which AG, UAG, leptin, adiponectin, glucose, insulin, testosterone or estradiol levels, insulinemic indexes were evaluated in 82 NW and 58 obese (OB) children. Results: Both ghrelin forms in NW were higher (AG, p<0.02; UAG, p<0.0001) than in OB subjects, with similar ratio AG/UAG. While no differences were observed for gender, puberty AG (p<0.01) and UAG (p<0.0001) levels were higher in pre-pubertal than pubertal NW and OB subjects. Adiponectin levels in NW subjects were higher (p<0.001), while leptin and insulin levels were lower (p<0.0001) than in OB subjects. NW children showed homeostasis model assessment (HOMA) and HOMAβ indices lower than OB children (p<0.0001) with a higher a quantitative insulin sensitivity check index (p<0.0001). AG and UAG levels correlated to each other (p<0.0001), each showing a negative correlation to age, height, weight and body mass index. Both forms, but more strongly UAG, correlated with adiponectin, leptin, and insulin. Conclusions: OB children show lower levels of both AG and UAG when compared to NW subjects, with lower levels during puberty. These results demonstrate a peculiar strong relationship between UAG levels and metabolic parameters in the pediatric population, suggesting a role for UAG in metabolic functions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
van der Lely AJ, Tschop M, Heiman ML, Ghigo E. Biological, physiological, pathophysiological, and pharmacological aspects of ghrelin. Endocr Rev 2004, 25: 426–57.
Wiedmer P, Nogueiras R, Broglio F, d’Alessio D, Tschöp MH. Ghrelin, obesity and diabetes. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab 2007, 3: 705–12.
Gil-Campos M, Aguilera CM, Cañete R, Gil A. Ghrelin: a hormone regulating food intake and energy homeostasis. Br J Nutr 2006, 96: 201–26.
Gualillo O, Caminos J, Blanco M, et al. Ghrelin, a novel placental-derived hormone. Endocrinology 2001, 142: 788–94.
Cortelazzi D, Cappiello V, Morpurgo PS, et al. Circulating levels of ghrelin in human fetuses. Eur J Endocrinol 2003, 149: 111–6.
Chanoine JP, Yeung LP, Wong AC, Birmingham CL. Immunoreactive ghrelin in human cord blood: relation to anthropometry, leptin, and growth hormone. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2002, 35: 282–6.
Bellone S, Rapa A, Vivenza D, et al. Circulating ghrelin levels in the newborn are positively associated with gestational age. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2004, 60: 613–7.
Soriano-Guillén L, Barrios V, Chowen JA, et al. Ghrelin levels from fetal life through early adulthood: relationship with endocrine and metabolic and anthropometric measures. J Pediatr 2004, 144: 30–5.
Whatmore AJ, Hall CM, Jones J, Westwood M, Clayton PE. Ghrelin concentrations in healthy children and adolescents. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2003, 59: 649–54.
Pomerants T, Tillmann V, Jürimäe J, Jürimäe T. Relationship between ghrelin and anthropometrical, body composition parameters and testosterone levels in boys at different stages of puberty. J Endocrinol Invest 2006, 29: 962–7.
Lebenthal Y, Gat-Yablonski G, Shtaif B, Padoa A, Phillip M, Lazar L Effect of sex hormone administration on circulating ghrelin levels in peripubertal children. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2006, 91: 328–31.
Farquhar J, Heiman M, Wong AC, Wach R, Chessex P, Chanoine JP. Elevated umbilical cord ghrelin concentrations in small for gestational age neonates. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003, 88: 4324–7.
Méndez-Ramírez F, Barbosa-Sabanero G, Romero-Gutiérrez G, Malacara JM. Ghrelin in small-for-gestational age (SGA) newborn babies: a cross-sectional study. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2009, 70: 41–6.
Bunt JC, Salbe AD, Tschöp MH, DelParigi A, Daychild P, Tataranni PA. Cross-sectional and prospective relationships of fasting plasma ghrelin concentrations with anthropometric measures in pima Indian children. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003, 88: 3756–61.
Stock S, Leichner P, Wong AC, Ghatei MA, et al. Ghrelin, peptide YY, glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide, and hunger responses to a mixed meal in anorexic, obese, and control female adolescents. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005, 90: 2161–8.
Ikezaki A, Hosoda H, Ito K, et al. Fasting plasma ghrelin levels are negatively correlated with insulin resistance and PAI-1, but not with leptin, in obese children and adolescents. Diabetes 2002, 51: 3408–11.
Soriano-Guillén L, Barrios V, Lechuga-Sancho A, Chowen JA, Argente J. Response of circulating ghrelin levels to insulin therapy in children with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes mellitus. Pediatr Res 2004, 55: 830–5.
Soriano-Guillén L, Barrios V, Martos G, Chowen JA, Campos-Barros A, Argente J. Effect of oral glucose administration on ghrelin levels in obese children. Eur J Endocrinol 2004, 151: 119–21.
Bacha F, Arslanian SA. Ghrelin suppression in overweight children: a manifestation of insulin resistance? J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005, 90: 2725–30.
Baldelli R, Bellone S, Castellino N, et al. Oral glucose load inhibits circulating ghrelin levels to the same extent in normal and obese children. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2006, 64: 255–9.
Bellone S, Castellino N, Broglio F, et al. Ghrelin secretion in childhood is refractory to the inhibitory effect of feeding. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004, 89: 1662–5.
Tolle V, Kadem M, Bluet-Pajot MT, et al. Balance in ghrelin and leptin plasma levels in anorexia nervosa patients and constitutionally thin women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003, 88: 109–16.
Weigle DS, Cummings DE, Newby PD, et al. Roles of leptin and ghrelin in the loss of body weight caused by a low fat, high carbohydrate diet. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003, 88: 1577–86.
Swarbrick MM, Havel PJ. Physiological, pharmacological, and nutritional regulation of circulating adiponectin concentrations in humans. Metab Syndr Relat Disord 2008, 6: 87–102.
Cacciari E, Milani S, Balsamo A, et al. Italian cross-sectional growth charts for height, weight and BMI (2 to 20 yr). J Endocrinol Invest 2006, 29: 581–93.
Wallace TM, Levy JC, Matthews DR. Use and abuse of HOMA modeling. Diabetes Care 2004, 27: 1487–95.
Park HS, Lee KU, Kim YS, Park CY. Relationships between fasting plasma ghrelin levels and metabolic parameters in children and adolescents. Metabolism 2005, 54: 925–9.
Harada T, Nakahara T, Yasuhara D et al. Obestatin, acyl ghrelin, and des-acyl ghrelin responses to an oral glucose tolerance test in the restricting type of anorexia nervosa. Biol Psychiatry 2008, 63: 245–7.
Mackelvie KJ, Meneilly GS, Elahi D, Wong AC, Barr SI, Chanoine JP. Regulation of appetite in lean and obese adolescents after exercise: role of acylated and desacyl ghrelin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2007, 92: 648–54.
Soares JB, Leite-Moreira AF. Ghrelin, des-acyl ghrelin and obestatin: three pieces of the same puzzle. Peptides 2008, 29: 1255–70.
Liu J, Prudom CE, Nass R, et al. Novel ghrelin assays provide evidence for independent regulation of ghrelin acylation and secretion in healthy young men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2008, 93: 1980–7.
Gualillo O, Lago F, Dieguez C. Introducing GOAT: a target for obesity and anti-diabetic drugs? Trends Pharmacol Sci 2008, 29: 398–401.
Purnell JQ, Weigle DS, Breen P, Cummings DE. Ghrelin levels correlate with insulin levels, insulin resistance, and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, but not with gender, menopausal status, or cortisol levels in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003, 88: 5747–52.
Vilarrasa N, Vendrell J, Maravall J, et al. Distribution and determinants of adiponectin, resistin and ghrelin in a randomly selected healthy population. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2005, 63: 329–35.
Ghizzoni L, Mastorakos G, Vottero A, Ziveri M, Ilias I, Bernasconi S. Spontaneous growth hormone (GH) secretion is not directly affected by ghrelin in either short normal prepubertal children or children with GH neurosecretory dysfunction. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004, 89: 5488–95.
Pagotto U, Gambineri A, Vicennati V, Heiman ML, Tschöp M, Pasquali R. Plasma ghrelin, obesity, and the polycystic ovary syndrome: correlation with insulin resistance and androgen levels. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002, 87: 5625–9.
Pagotto U, Gambineri A, Pelusi C et al. Testosterone replacement therapy restores normal ghrelin in hypogonadal men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003, 88: 4139–43.
Loomba-Albrecht LA, Styne DM. Effect of puberty on body composition. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 2009, 16: 10–5.
Kalra SP, Ueno N, Kalra PS. Stimulation of appetite by ghrelin is regulated by leptin restraint: peripheral and central sites of action. J Nutr 2005, 135: 1331–5.
Chan JL, Mantzoros CS. Leptin and the hypothalamic-pituitary regulation of the gonadotropin-gonadal axis. Pituitary 2001, 4: 87–92.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Co-first authorship.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bellone, S., Prodam, F., Savastio, S. et al. Acylated and unacylated ghrelin levels in normal weight and obese children: Influence of puberty and relationship with insulin, leptin and adiponectin levels. J Endocrinol Invest 35, 191–197 (2012). https://doi.org/10.3275/7761
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3275/7761