Abstract
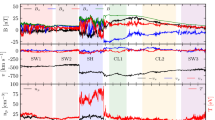
The interaction of the interplanetary coronal mass ejection (ICME) and the high-speed solar wind flux (HSSWF) associated with the coronal hole (CH) is considered. By the examples of two events at the maximum of solar cycle 24 from June 4 to June 16 and from June 30 to July 10, 2012 it is shown that the temperature-dependent parameters of the SW ionic composition appear closer to the values in the HSSWF than in the ICME due to mixing of fluxes in the corona when the ICME source is near the CH boundary.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ENLIL Solar Wind Prediction–URL: http://helioweather.net/
A. A. Mohamed, N. Gopalswamy, S. Yashiro, et al., J. Geophys. Res. 117, A01103 (2012).
B. E. Wood, C.-C. Wu, A. P. Rouillard, et al., Astrophys. J. 755, 43 (2012).
N. Gopalswamy, P. Mäkelä, H. Xie, et al., J. Geophys. Res. 114, A00A22 (2009).
P. Mäkelä, N. Gopalswamy, H. Xie, et al., Solar Phys. 284, 59 (2013).
Near-Earth Interplanetary Coronal Mass Ejections Since January 1996, compiled by Ian Richardson and Hilary Cane–URL: http://www.srl.caltech.edu/ACE/ASC/DATA/level3/icmetable2.htm
H. V. Cane and I. G. Richardson, J. Geophys. Res. 108, SSH 6–1 (2003).
I. G. Richardson and H. V. Cane, Solar Phys. 264, 189 (2010).
N. Gopalswamy, P. Mäkelä, S. Akiyama, et al., Solar Phys. 284, 17 (2013).
CDAWData Center. SOHO LASCO CME CATALOG–URL: http://cdaw.gsfc.nasa.gov/CME−list/
George Mason University Space Weather Lab. Solar Eruptive Event Detection System–URL: http://helio.gmu.edu/seeds/secchi.php
Solar Dynamics Observatory. AIA/HMI Browse Data–URL: http://sdo.gsfc.nasa.gov/
A software package for “Computer Aided CME Tracking” (CACTUS)–URL: http://sidc.oma.be/cactus/
U. Feldman, E. Landi, and N. A. Schwadron, J. Geophys. Res.: Space Phys. 110, A07109 (2005).
The ACE Science Center (ASC). ACE Level 2 (Verified) Data–URL: http://www.srl.caltech.edu/ACE/ASC/level2/index.html
U. Feldman, Physica Scripta 46, 202 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © D.G. Rodkin, Yu.S. Shugai, V.A. Slemzin, I.S. Veselovskii, 2016, published in Kratkie Soobshcheniya po Fizike, 2016, Vol. 43, No. 9, pp. 44–49.
About this article
Cite this article
Rodkin, D.G., Shugai, Y.S., Slemzin, V.A. et al. Interaction of high-speed and transient fluxes of solar wind at the maximum of solar cycle 24. Bull. Lebedev Phys. Inst. 43, 287–290 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068335616090062
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068335616090062