Abstract
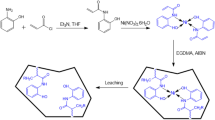
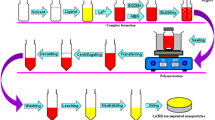
In the present study, yttrium(III) ion imprinted polymers (Y(III)-IIPs) and non-imprinted polymers (and non-Y(III)-IIPs) materials were synthesized. The materials were characterized by FTIR spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM)-EDS studies. Characterization by FTIR showed that the IIPs have been successfully synthesized as indicated by the absence of a peak for the alkene functional group at 3000–3300 cm–1. From the FTIR data and SEM-EDS images showed that Y(III) ions have been successfully released from the polymer. The retention properties by batch procedure showed that the adsorption capacity of Y(III)-IIPs was 10.26 mg/g at pH 7 with a contact time of 10 min. Y(III) ions adsorption onto Y(III)-IIPs follows the Langmuir adsorption isotherm with a correlation coefficient of 0.9671, which showed a maximum adsorption capacity value of 14.68 mg/g and follows the Lagergren pseudo-second order kinetics model. The IIPs materials selectivity against other rare earth metals showed a better selectivity than NIPs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haque, N., Hughes, A., Lim, S., and Vernon, C., Rare earth elements: Overview of mining, mineralogy, uses, sustainability and environmental impact, Resources, 2014, vol. 3, no. 4, p. 614.
Connelly, N.G., Nomenclature of inorganic chemistry: IUPAC recommendations. The red book. Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, 2005, p. 51.
Dinér, P., Yttrium from Ytterby, Nature Chem., 2016, vol. 8, p. 192.
Stacy, A., Badding, J.V., Geselbracht, M.J., Ham, W.K., Holland, G.F., Hoskins, R., et al., High-temperature superconductivity in yttrium-barium-copper oxide: Identification of a copper-rich superconducting phase, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1987, vol. 109, no. 8, p. 2528.
Wike, J.S., Guyer, C.E., Ramey, D.W., and Phillpis, B.P., Chemistry for commercial scale production of yttrium-90 for medical research, Int. J. Rad. Appl. Instrum. Part A, 1990, vol. 41, no. 9, p. 861.
Panayiotakis, G., Cavouras, D., Kandarakis, I., and Nomicos, C., A study of X-ray luminescence and spectral compatibility of europium-activated yttrium-vanadate (YVO4:Eu) screens for medical imaging applications, Appl. Phys. A, 1996, vol. 62, no. 5, p. 483.
Naumov, A.V., Review of the world market of rareearth metals, Russ. J. Non-Ferrous Met., 2008, vol. 49, no. 1, p. 14.
Du, J., Molecular dynamics simulations of the structure and properties of low silica yttrium aluminosilicate glasses, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2009, vol. 92, no. 1, p. 87.
Silver, J., Martinez-Rubio, M.I., Irelend, T.G., Fern, G.R., and Withrall, R., The effect of particle morphology and crystallite size on the upconversion luminescence properties of erbium and ytterbium codoped yttrium oxide phosphors, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2001, vol. 105, no. 5, p. 948.
Stewart, D., Induced radioactivity in strontium and yttrium; nuclear isomers in strontium, Phys. Rev., 1939, vol. 56, no. 7, p. 629.
Horwitz, P.A., US Patent 5 368 736, 1994.
Minagawa, Y.K., Yttrium purification by solvent extraction, in The Rare Earths in Modern Science and Technology, 1980, p. 139.
Carlson, O.N., Schimid, F.A., and Peterson, D.T., Purification of rare-earth metals by electrotransport, J. Less Common. Met., 1975, vol. 39, no. 2, p. 277.
Minagawa, Y. and Yajima, F., Selective separation of yttrium ions from other rare earth ions using nonequilibrium extraction, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn., 1992, vol. 65, no. 1, p. 29.
Hubicki, Z., Hubicka, H., and Olszak, M., Investigations into the separation of nitrate complexes of yttrium(III) from neodymium(III) on anion exchangers of different cross-linking in the system CH3OH–H2O–HNO3, Hydrometallurgy, 1994, vol. 34, no. 3, p. 307.
Zachmann, D.W., Matrix effects in the separation of rare earth elements, scandium, and yttrium and their determination by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry, Anal. Chem., 1988, vol. 60, no. 5, p. 420.
Brown, C.G. and Sherrington, L.G., Solvent extraction used in industrial separation of rare earths, J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol., 1979, vol. 29, no. 4, p. 193.
Crock, J.G., Lichte, F.E., Riddle, G.O, and Beech, C.L., Separation and preconcentration of the rare-earth elements and yttrium from geological materials by ionexchange and sequential acid elution, Talanta, 1986, vol. 33, no. 7, p. 601.
Hamaguchi, H., Ohuchi, A., Shimizu, T., Onuma, N., and Kuroda, R., Separation of scandium from yttrium, rare earths, thorium, zirconium, uranium, and other elements by anion exchange chromatography in ammonium sulfate media, Anal. Chem., 1964, vol. 36, no. 12, p. 2304.
Ochsenkühn-Petropulu, M., Lyberopulu, T., and Parissakis, G., Selective separation and determination of scandium from yttrium and lanthanides in red mud by a combined ion exchange/solvent extraction method, Anal. Chim. Acta, 1995, vol. 315, no. 1, p. 231.
Wood, D.J., Elshani, S., Du, H.S., Natale, N.R., and Wai, C.M., Separation of yttrium-90 from strontium-90 by solvent extraction with ionizable crown ethers, Anal. Chem., 1993, vol. 65, no. 10, p. 1350.
Sun, X., Zhao, J., Meng, S., and Li, D., Synergistic extraction and separation of yttrium from heavy rare earths using mixture of sec-octylphenoxy acetic acid and bis (2,4,4-trimethylpentyl) phosphinic acid, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2005, vol. 533, no. 1, p. 83.
Sun, X., Peng, B., Ji, Y., Chen, J., and Li, D., The solid–liquid extraction of yttrium from rare earths by solvent (ionic liquid) impreganated resin coupled with complexing method, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2008, vol. 63, no. 1, p. 61.
Weiss, D., Paukert, T., and Rubeska, I., Determination of rare earth elements and yttrium in rocks by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry after separation by organic solvent extraction, J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 1990, vol. 5, no. 5, p. 371.
Sun, Y., Detailed study on simultaneous separation of rare earth elements by capillary electrophoresis, J. Chromatogr. A, 2004, vol. 1048, no. 2, p. 245.
de Gyves, J. and de San Miguel, E.R., Metal ion separations by supported liquid membranes, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 1999, vol. 38, no. 6, p. 2182.
Ramakul, P., Supajaroon, T., Prapasawat, T., Pancharoen, U., and Lothongkum, A.W., Synergistic separation of yttrium ions in lanthanide series from rare earths mixture via hollow fiber supported liquid membrane, J. Ind. Eng. Chem., 2009, vol. 15, no. 2, p. 224.
Gaikwad, A.G. and Rajput, A.M., Transport of yttrium metal ions through fibers supported liquid membrane solvent extraction, J. Rare Earths, 2010, vol. 28, no. 1, p. 1.
Moeller, T., Observations on rare earths double sodium sulfate precipitation for separation of the terbium and yttrium earths, Ind. Eng. Chem. Anal. Ed., 1945, vol. 17, no. 1, p. 44.
de Vasconcellos, M.E., da S. Queiroz, C.A., and Abrão, A., Sequential separation of the yttrium-heavy rare earths by fractional hydroxide precipitation, J. Alloys Compounds, 2004, vol. 374, no. 1, p. 405.
Suzuki, T, Itoh, K., Ikeda, A., Aida, M., Ozawa, M., and Fujii Y., Separation of rare earth elements by tertiary pyridine type resin, J. Alloys Compounds, 2006, vol. 408–412, p. 1013.
Tong, J., Clark, D., Hoban, M., and O’Hayre, R., Cost-effective solid-state reactive sintering method for high conductivity proton conducting yttrium-doped barium zirconium ceramics, Solid State Ionics, 2010, vol. 181, no. 11, p. 496.
Rao, P.T., Daniel, S., and Gladis, J.M., Tailored materials for preconcentration or separation of metals by ion-imprinted polymers for solid-phase extraction (IIP-SPE), TrAC Trends in Anal. Chem., 2004, vol. 23, no. 1, p. 28.
Metilda, P., Gladis, J.M., and Rao, T.P., Influence of binary/ternary complex of imprint ion on the preconcentration of uranium(VI) using ion imprinted polymer materials, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2004, vol. 512, no. 1, p. 63.
Otero-Romaní, J., Moreda-Pineiro, A., Bermejo-Barrera, P., and Martin-Esteban, A., Inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry/mass spectrometry for the determination of Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn in seawater after ionic imprinted polymer based solid phase extraction, Talanta, 2009, vol. 79, no. 3, p. 723.
Arbab-Zavar, M.H., Chamsaz, M., Zohuri, G., and Darroudi, A., Synthesis and characterization of nanopore thallium(III) ion-imprinted polymer as a new sorbent for separation and preconcentration of thallium, J. Hazard. Mater., 2011, vol. 185, no. 1, p. 38.
Markowitz, M.S., US Patent 6310110, 2011.
Luo, X., Luo, S., Zhan, Y., Shu, H., Huang, Y., and Tu, X., Novel Cu(II) magnetic ion imprinted materials prepared by surface imprinted technique combined with a sol-gel process, J. Hazard. Mater., 2011, vol. 192, no. 3, p. 949.
Shirvani-Arani, S., Ahmadi, S.J., Bahrami-Samani, A., and Ghannadi-Maragheh, M., Synthesis of nano-pore samarium(III)-imprinted polymer for preconcentrative separation of samarium ions from other lanthanide ions via solid phase extraction, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2008, vol. 623, no. 1, p. 82.
Gao, B., Meng, J., Xu, Y., and Zhang, Y., Preparation of Fe(III) ion surface-imprinted material for removing Fe(III) impurity from lanthanide ion solutions, J. Ind. Eng. Chem., 2015, vol. 24, p. 351.
Daniel, S., Gladis, J.M., and Rao, T.P., Synthesis of imprinted polymer material with palladium ion nanopores and its analytical application, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2003, vol. 488, no. 2, p. 173.
Saraji, M. and Yousefi, H., Selective solid-phase extraction of Ni(II) by an ion-imprinted polymer from water samples, J. Hazard. Mater., 2009, vol. 167, no. 1, p. 1152.
Prasad, K., Kala, R., Rao, T.P, and Naidu, G.R.K., Ion imprinted polymer based ion-selective electrode for the trace determination of dysprosium(III) ions, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2006, vol. 566, no. 1, p. 69.
Kala, R., Biju, V.M., and Rao, T.P., Synthesis, characterization, and analytical applications of erbium(III) ion imprinted polymer particles prepared via γ-irradiation with different functional and crosslinking monomers, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2005, vol. 549, no. 1, p. 51.
Guo, J., Cai, J., and Su, Q., Ion imprinted polymer particles of neodymium: synthesis, characterization and selective recognition, J. Rare Earths, 2009, vol. 27, no. 1, p. 22.
Krishna, P.G., Gladis, J.M., Rao, T.P., and Naidu, G.R., Selective recognition of neodymium(III) using ion imprinted polymer particles, J. Mol. Recognit., 2005, vol. 18, no. 1, p. 109.
Biju, V.M., Gladis J.M., and Rao, T.P., Ion imprinted polymer particles: synthesis, characterization and dysprosium ion uptake properties suitable for analytical applications, Analytica Chim. Acta, 2003, vol. 478, p. 43.
Lide, D.R., CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, New York: CRC Press, 2007, p. 1363.
Fish, R.H., Molecular and ion recognition with imprinted polymers, in ACS Symposium, Series 703, Bastsch, R.A. and Maeda, M., Eds., Washington, DC: American Chemical Society, 1998, p. 238.
Vigneau, O., Pinel, C., and Lemaire, M., Solid-liquid separation of lanthanide/lanthanide and lanthanide/actinide using ionic imprinted polymer based on a DTPA derivative, Chem. Lett., 2002, vol. 2, p. 202.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
About this article
Cite this article
Zulfikar, M.A., Zarlina, R., Rusnadi et al. Separation of Yttrium from Aqueous Solution Using Ionic Imprinted Polymers. Russ. J. Non-ferrous Metals 58, 614–624 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1067821217060189
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1067821217060189