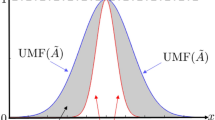
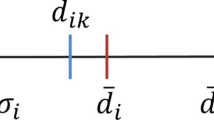Abstract
Fuzzy models have excellent capability of describing nonlinear system, so that a wide variety of models is proposed. However, these models are difficult to train and interpret with a hypothesis of data independence. Base on the above problems, an improved generalized fuzzy model is proposed by rules centralization, a new mixture model is built by substituting Epanechnikov quadratic kernel for Gaussian kernel of Gaussian mixture model, and the mutual transformation between the two models is proved. The proposed fuzzy model can not only provide good interpretability, but also easily estimate the parameters of the fuzzy model using the proposed mixture model. In addition, this proposed fuzzy model has higher segmentation efficiency for the input space with consideration of data correlation. The experimental results of a well-known nonlinear system identification show that the proposed fuzzy model has the best performance with fewer fuzzy rules and better generalization ability than some popular models.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Bezdek, M.J.C., Editorial. Fuzzy models? What are they, and why?, IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst., 1993, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 1–6.
Ming-Tao Gan, Madasu Hanmandlu, and Tan, A.H., From a Gaussian mixture model to additive fuzzy systems, IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst., 2005, vol. 13, no. 3, pp. 303–316.
Verma, N.K. and Madasu Hanmandlu, From a Gaussian mixture model to non-additive fuzzy systems, IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst., 2007, vol. 15, no. 2, pp. 1–19.
Maciel, L., Ballini, R., and Gomide, R., Evolving possibilistic fuzzy modelling, J. Stat. Comput. Simul., 2017, vol. 87, no. 7, pp. 1446–1466.
Md. Rafiul Hassan, Baikunth Nath, Michael Kirley, and Joarder Kamruzzaman, A hybrid of multiobjective Evolutionary Algorithm and HMM-Fuzzy model for time series prediction, Neurocomputing, 2012, vol. 81, no. 2, pp. 1–11.
Qian Wang, Zhi-gang Su, Babak Rezaee, and Pei-hong Wang, Constructing T–S fuzzy model from imprecise and uncertain knowledge represented as fuzzy belief functions, Neurocomputing, 2015, vol. 166, no. 5, pp. 319–336.
Skrjanc, I., et al., Evolving fuzzy-model-based design of experiments with supervised hierarchical clustering, IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst., 2015, vol. 23, no. 4, pp. 861–871.
Killian, M., Mayer, B., Schirrer, A., and Kozek, M., Cooperative fuzzy and model-predictive control, IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst., 2016, vol. 24, no. 2, pp. 471–482.
Hartmann, B., Banfer, O., Nelles, O., Sodja, A., Teslic, L., and Skrjanc, I., Supervised hierarchical clustering in fuzzy model identification, IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst., 2011, vol. 19, no. 6, pp. 1163–1176.
Rezaee, B. and Fazel Zarandi, M.H., Data-driven fuzzy modeling for Takagi–Sugeno–Kang fuzzy system, Inf. Sci., 2010, vol. 180, no. 2, pp. 241–255.
Parras-Gutierrez, E., Garcia Arenas, M., and Rivas, V.M., Coevolution of lags and RBFNs for time series forecasting: L-Co-R algorithm, Soft Comput., 2012, vol. 16, no. 6, pp. 919–942.
Zhang Chen, Xia Shixiong, and Liu Bing, A robust fuzzy kernel clustering algorithm, Appl. Math., 2013, vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 1005–1012.
Abonyi, J., Babuska, R., and Szeifert, F., Fuzzy modelling with multivariate membership functions: Gray-box identification and control design, IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern., 2001, vol. 31, no. 5, pp. 755–767.
Marwan Bikdash, A highly interpretable form of Sugeno inference systems, IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst., 1999, vol. 7, no. 6, pp. 686–696.
Sevcan Yilmaz and Yusuf Oysal, Fuzzy wavelet neural network models for prediction and identification of dynamical systems, IEEE Trans. Neural Networks, 2010, vol. 21, no. 10, pp. 1599–1609.
Castro, J.R., Castillo, O., Melin, P., and Rodríguez-Díaz, A., A hybrid learning algorithm for a class of interval type-2 fuzzy neural networks, Inf. Sci., 2009, vol. 179, no. 13, pp. 2175–2193.
Azeem, Y.M.F., Hanmandlu, M., and Ahmad, N., Generalization of adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference systems, IEEE Trans. Neural Networks, 2000, vol. 11, no. 6, pp. 1332–1346.
Kollios, G., Gunopulos, D., Koudas, N., and Berchtold, S., Efficient biased sampling for approximate clustering and outlier detection in large data sets, IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng., 2003, vol. 15, no. 5, pp. 1170–1187.
Jenssen, R., Indefinite Parzen window for spectral clustering, Proceedings of IEEE Workshop on Machine Learning for Signal Processing, Thessaloniki, 2007, pp. 390–395.
Box, G.E.P. and Jenkins, G.M., Time Series Analysis, Forecasting and Control, Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons Inc, 2015.
Tong, R.M., The evaluation of fuzzy models derived from experimental data, Fuzzy Sets Syst., 1980, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 1–12.
Pedrycz, W., An identification algorithm in fuzzy relational systems, Fuzzy Sets Syst., 1984, vol. 13, no. 2, pp. 153–167.
Xu, C.W. and Lu, Y.Z., Fuzzy model identification and self-learning for dynamic systems, IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern., 1987, vol. 17, no. 4, pp. 683–689.
Sugeno, M. and Yasukawa, T., A fuzzy-logic-based approach to qualitative modeling, IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst., 1993, vol. 1, no. 1.
Sugeno, M. and Tanaka, K., Successive identification of a fuzzy model and its applications to prediction of a complex system, Fuzzy Sets Syst., 1991, vol. 42, no. 3, pp. 315–334.
Lin, Y. and Cunningham, G.A. III, A new approach to fuzzy-neural system modeling, IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst., 1995, vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 190–198.
Wang, L. and Langari, R., Building Sugeno-type models using fuzzy discretization and orthogonal parameter estimation techniques, IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst., 1995, vol. 3, no. 4, pp. 454–458.
Wang, L. and Langari, R., Complex systems modeling via fuzzy logic, IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern., 1996, vol. 26, no. 1, pp. 100–106.
Peng, X. and Wang, P., On generating linguistic rules for fuzzy model, Proc. of 2nd International Conference on Information Processing and Management of Uncertainty in Knowledge-Based Systems, 1988, Urbino, pp. 185–192.
Yoshinary, Y., Pedrycz, W., and Hirota, K., Construction of fuzzy models through clustering techniques, Fuzzy Sets Syst., 1993, vol. 54, no. 2, pp. 157–165.
Nie, J.H., Constructing fuzzy model by self-organizing counterpropagation network, IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern., 1995, vol. 25, no. 6, pp. 963–970.
Pedrycz, W., Lam, P.C.F., and Rocha, A.F., Distributed fuzzy system modeling, IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern., 1995, vol. 25, no. 5, pp. 769–780.
Delgado, M., Gomez-Skarmeta, A.F., and Martin, F., Fuzzy clustering-based rapid prototyping for fuzzy rule-based modeling, IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst., 1997, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 223–233.
Joo, Y.H., Hwang, H.S., and Kim, K.B., Fuzzy system modeling by fuzzy partition and GA hybrid schemes, Fuzzy Sets Syst., 1997, vol. 86, no. 3, pp. 279–288.
Lin, Y., Cunningham, G.A. III, and Coggeshall, S.V., Using fuzzy partitions to create fuzzy systems from input-output data and set the initial weights in a fuzzy neural network, IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst., 1997, vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 614–621.
Chen, J.Q., Xi, Y.G., and Zhang, Z.J., A clustering algorithm for fuzzy model identification, Fuzzy Sets Syst., 1998, vol. 98, no. 3, pp. 1–11.
Wang, Y. and Rong, G., A self-organizing neural-network-based fuzzy system, Fuzzy Sets Syst., 1999, vol. 103, no. 1, pp. 1–11.
Lo, J.C. and Yang, C.H., A heuristic error-feedback learning algorithm for fuzzy modeling, IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern., Part A: Syst. Hum., 1999, vol. 29, no. 6, pp. 686–691.
Euntai Kim, Minkee Park, Seungwoo Kim, and Mignon Park, A transformed input-domain approach to fuzzy modeling, IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst., 1998, vol. 6, no. 4, pp. 596–604.
Kang, S.J., Woo, C.H., Hwang, H.S., and Woo, K.B., Evolutionary design of fuzzy rule base for nonlinear system modeling and control, IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst., 2000, vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 37–45.
Kukolj, D. and Levi, E., Identification of complex systems based on neural and Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy model, IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern., Part B: Cybern., 2004, vol. 34, no. 1, pp. 272–282.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This paper is supported by the Doctor Foundation of Yulin Normal University and Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (G2018015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang Qinli, Chen Yu An Improved Generalized Fuzzy Model Based on Epanechnikov Quadratic Kernel and Its Application to Nonlinear System Identification. Aut. Control Comp. Sci. 53, 12–21 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0146411619010103
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0146411619010103