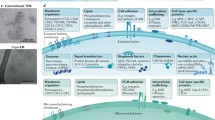
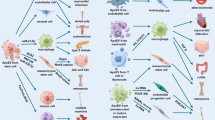
Abstract
Extracellular vesicles are heterogenous, nano-sized, membrane-limited structures which not only represent a specific way of intercellular communication but also endow cells with many capabilities. Apoptotic bodies created during apoptosis, microvesicles shed from the plasma membrane, and exosomes originated inside the cell and released to extracellular space upon fusion with the plasma membrane, they all belong to extracellular vesicles. Extracellular vesicles contain lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. In this review, we describe their biogenesis, release and uptake by recipient cells, their composition, functions and potential therapeutic and diagnostic applications.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EVs:
-
Extracellular vesicles
- MVs:
-
Microvesicles
- MVBs:
-
Multi-vesicular bodies
- ILVs:
-
Intraluminal vesicles
- ARF6:
-
ADP-ribosylation factor 6
- PLD:
-
Phospholipase D
- ERK:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- MLCK:
-
Myosin light chain kinase
- MHC-I:
-
Major histocompatibility complex class-I molecules
- VAMP3:
-
Vesicle-associated membrane protein 3
- MT1-MMP:
-
Membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase
- ESCRT:
-
Endosomal sorting complex required for transport
- VPS4:
-
Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 4
- ALIX:
-
ALG-2-interacting protein X
- TSG101:
-
Tumour susceptibility gene 101
- ARRDC1:
-
Arrestin 1 domain–containing protein 1
- VPS4:
-
Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 4
- WWP2:
-
E3 ligase WW domain-containing protein 2
- TCRs:
-
T cell receptors
- LAMP-3:
-
Lysosomal-associated membrane protein 3
- nSMase:
-
Neutral sphingomyelinase
- MFGE8:
-
Milk fat globule-EGF factor 8
- TIM4:
-
T cell immunoglobulin mucin 4
- TSP:
-
Thrombospondin
- MMPs:
-
Matrix metalloproteinases
- ADAM10:
-
A disintegrin and metalloprotease 10
- TACE:
-
Tumour necrosis factor α-converting enzyme
- siRNA:
-
Small interfering RNA
- TGF-β:
-
transforming growth factor beta
- LFA-1:
-
lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1
- ICAM-1:
-
Intercellular adhesion molecule 1
- HSPs:
-
Heat shock proteins
- DC:
-
Dendritic cell
- STB:
-
Syncytiotrophoblast
- TLR4:
-
Toll-like receptor 4
- PI3K/Akt:
-
Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinases/protein kinase B
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells
- Tspan8:
-
Tetraspanin 8
- MCL:
-
Mantle cell lymphoma
- DC-SIGN:
-
Dendritic cell-specific ICAM-grabbing non-integrin
- MUC1:
-
Mucin 1
- TIM1:
-
T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain 1
- BAI1:
-
Brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor 1
- uPAR:
-
Urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor
- EGFRvIII:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor variant III
- RHEB:
-
Ras homolog enriched in brain
- IFN-γ:
-
Interferon gamma
- STAT:
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription
- VSV-G:
-
Vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein
References
Admyre C, Grunewald J, Thyberg J, Gripenbäck S, Tornling G, Eklund A, Scheynius A, Gabrielsson S (2003) Exosomes with major histocompatibility complex class II and co-stimulatory molecules are present in human BAL fluid. Eur Respir J 22:578–583. https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.03.00041703
Admyre C, Johansson SM, Qazi KR, Filén JJ, Lahesmaa R, Norman M, Neve EP, Scheynius A, Gabrielsson S (2007) Exosomes with immune modulatory features are present in human breast milk. J Immunol 179:1969–1978. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.179.3.1969
Akers JC, Gonda D, Kim R, Carter BS, Chen CC (2013) Biogenesis of extracellular vesicles (EV): exosomes, microvesicles, retrovirus-like vesicles, and apoptotic bodies. J Neuro-Oncol 113:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-013-1084-8
Al-Nedawi K, Meehan B, Micallef J, Lhotak V, May L, Guha A, Rak J (2008) Intercellular transfer of the oncogenic receptor EGFRvIII by microvesicles derived from tumour cells. Nat Cell Biol 10:619–624. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1725
Alvarez-Erviti L, Seow Y, Yin H, Betts C, Lakhal S, Wood MJ (2011) Delivery of siRNA to the mouse brain by systemic injection of targeted exosomes. Nat Biotechnol 29:341–345. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1807
Andre F, Schartz NEC, Movassagh M, Flament C, Pautier P, Morice P, Pomel C, Lhomme C, Escudier B, Le Chevalier T, Tursz T, Amigorena S, Raposo G, Angevin E, Zitvogel L (2002) Malignant effusions and immunogenic tumour-derived exosomes. Lancet 360:295–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(02)09552-1
Aplin AE, Howe A, Alahari SK, Juliano RL (1998) Signal transduction and signal modulation by cell adhesion receptors: the role of integrins, cadherins, immunoglobulin-cell adhesion molecules, and selectins. Pharmacol Rev 50:197–263
Atay S, Gercel-Taylor C, Taylor DD (2011) Human trophoblast-derived exosomal fibronectin induces pro-inflammatory IL-1β production by macrophages. Am J Reprod Immunol 66:259–269. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0897.2011.00995.x
Bakhti M, Winter C, Simons M (2011) Inhibition of myelin membrane sheath formation by oligodendrocyte-derived exosome-like vesicles. J Biol Chem 286:787–796. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.190009
Barreca MM, Spinello W, Cavalieri V, Turturici G, Sconzo G, Kaur P, Tinnirello R, Asea AAA, Geraci F (2017) Extracellular Hsp70 Enhances Mesoangioblast Migration via an Autocrine Signaling Pathway. J Cell Physiol 232:1845–1861. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.25722
Barrés C, Blanc L, Bette-Bobillo P, André S, Mamoun R, Gabius HJ, Vidal M (2010) Galectin-5 is bound onto the surface of rat reticulocyte exosomes and modulates vesicle uptake by macrophages. Blood 115:696–705. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2009-07-231449
Berckmans RJ, Sturk A, van Tienen LM, Schaap MC, Nieuwland R (2011) Cell-derived vesicles exposing coagulant tissue factor in saliva. Blood 117:3172–3180. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2010-06-290460
Berditchevski F, Odintsova E (2007) Tetraspanins as regulators of protein trafficking. Traffic 8:89-96. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0854.2006.00515.x
Blanchard N, Lankar D, Faure F, Regnault A, Dumont C, Raposo G, Hivroz C (2002) TCR activation of human T cells induces the production of exosomes bearing the TCR/CD3/zeta complex. J Immunol 168:3235–3241. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.168.7.3235
Bobrie A, Théry C (2013) Exosomes and communication between tumours and the immune system: are all exosomes equal? Biochem Soc Trans 41:263–267. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20120245
Boilard E, Nigrovic PA, Larabee K, Watts GF, Coblyn JS, Weinblatt ME, Massarotti EM, Remold-O'Donnell E, Farndale RW, Ware J, Lee DM (2010) Platelets amplify inflammation in arthritis via collagen-dependent microparticle production. Science 327:580–583. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1181928
Busch A, Quast T, Keller S, Kolanus W, Knolle P, Altevogt P, Limmer A (2008) Transfer of T cell surface molecules to dendritic cells upon CD4+ T cell priming involves two distinct mechanisms. J Immunol 181:3965–3973. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.181.6.3965
Buschow SI, Nolte-‘t Hoen EN, van Niel G, Pols MS, ten Broeke T, Lauwen M, Ossendorp F, Melief CJ, Raposo G, Wubbolts R, Wauben MH, Stoorvogel W (2009) MHC II in dendritic cells is targeted to lysosomes or T cell-induced exosomes via distinct multivesicular body pathways. Traffic 10:1528–1542. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0854.2009.00963.x
Caby MP, Lankar D, Vincendeau-Scherrer C, Raposo G, Bonnerot C (2005) Exosomal-like vesicles are present in human blood plasma. Int Immunol 17:879–887. https://doi.org/10.1093/intimm/dxh267
Candela ME, Geraci F, Turturici G, Taverna S, Albanese I, Sconzo G (2010) Membrane vesicles containing matrix metalloproteinase-9 and fibroblast growth factor-2 are released into the extracellular space from mouse mesoangioblast stem cells. J Cell Physiol 224:144–151. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.22111
Carayon K, Chaoui K, Ronzier E, Lazar I, Bertrand-Michel J, Roques V, Balor S, Terce F, Lopez A, Salomé L, Joly E (2011) The proteolipidic composition of exosomes changes during reticulocyte maturation. J Biol Chem 286:34426–34439. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.257444
Chen TS, Lai RC, Lee MM, Choo AB, Lee CN, Lim SK (2010) Mesenchymal stem cell secretes microparticles enriched in pre-microRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 38:215–224. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkp857
Choudhuri K, Llodrá J, Roth EW, Tsai J, Gordo S, Wucherpfennig KW, Kam LC, Stokes DL, Dustin ML (2014) Polarized release of T-cell-receptor-enriched microvesicles at the immunological synapse. Nature 507:118–123. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12951
Christianson HC, Svensson KJ, van Kuppevelt TH, Li JP, Belting M (2013) Cancer cell exosomes depend on cell-surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans for their internalization and functional activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:17380–17385. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1304266110
Clayton A, Harris CL, Court J, Mason MD, Morgan BP (2003) Antigen-presenting cell exosomes are protected from complement-mediated lysis by expression of CD55 and CD59. Eur J Immunol 33:522–531. https://doi.org/10.1002/immu.200310028
Colombo M, Raposo G, Théry C (2014) Biogenesis, Secretion, and Intercellular Interactions of Exosomes and Other Extracellular Vesicles. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 30:255–289. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-cellbio-101512-122326
Cossetti C, Iraci N, Mercer TR, Leonardi T, Alpi E, Drago D, Alfaro-Cervello C, Saini HK, Davis MP, Schaeffer J, Vega B, Stefanini M, Zhao C, Muller W, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Mathivanan S, Bachi A, Enright AJ, Mattick JS, Pluchino S (2014) Extracellular vesicles from neural stem cells transfer IFN-γ via Ifngr1 to activate Stat1 signaling in target cells. Mol Cell 56:193–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2014.08.020
Dai S, Wan T, Wang B, Zhou X, Xiu F, Chen T, Wu Y, Cao X (2005) More efficient induction of HLA-A*0201-restricted and carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)-specific CTL response by immunization with exosomes prepared from heat-stressed CEA-positive tumor cells. Clin Cancer Res 11:7554–7563. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0810
DeKruyff RH, Bu X, Ballesteros A, Santiago C, Chim YL, Lee HH, Karisola P, Pichavant M, Kaplan GG, Umetsu DT, Freeman GJ, Casasnovas JM (2010) T cell/transmembrane, Ig, and mucin-3 allelic variants differentially recognize phosphatidylserine and mediate phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. J Immunol 184:1918–1930. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.0903059
Denzer K, van Eijk M, Kleijmeer MJ, Jakobson E, de Groot C, Geuze HJ (2000) Follicular dendritic cells carry MHC class II-expressing microvesicles at their surface. J Immunol 165:1259–1265. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.165.3.1259
D'Mello V, Singh S, Wu Y, Birge RB (2009) The urokinase plasminogen activator receptor promotes efferocytosis of apoptotic cells. J Biol Chem 284:17030–17038. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.010066
Dvorak HF, Quay SC, Orenstein NS, Dvorak AM, Hahn P, Bitzer AM, Carvalho AC (1981) Tumor shedding and coagulation. Science 212:923–924. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.7195067
Edgar JR, Eden ER, Futter CE (2014) Hrs- and CD63-dependent competing mechanisms make different sized endosomal intraluminal vesicles. Traffic 15:197–211. https://doi.org/10.1111/tra.12139
Escrevente C, Keller S, Altevogt P, Costa J (2011) Interaction and uptake of exosomes by ovarian cancer cells. BMC Cancer 11:108. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-11-108
Fabbri M, Paone A, Calore F, Galli R, Gaudio E, Santhanam R, Lovat F, Fadda P, Mao C, Nuovo GJ, Zanesi N, Crawford M, Ozer GH, Wernicke D, Alder H, Caligiuri MA, Nana-Sinkam P, Perrotti D, Croce CM (2012) MicroRNAs bind to Toll-like receptors to induce prometastatic inflammatory response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:E2110–E2116. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1209414109
Fauré J, Lachenal G, Court M, Hirrlinger J, Chatellard-Causse C, Blot B, Grange J, Schoehn G, Goldberg Y, Boyer V, Kirchhoff F, Raposo G, Garin J, Sadoul R (2006) Exosomes are released by cultured cortical neurones. Mol Cell Neurosci 31:642–648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcn.2005.12.003
Feng D, Zhao WL, Ye YY, Bai XC, Liu RQ, Chang LF, Zhou Q, Sui SF (2010) Cellular internalization of exosomes occurs through phagocytosis. Traffic 11:675–687. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0854.2010.01041.x
Fevrier B, Vilette D, Archer F, Loew D, Faigle W, Vidal M, Laude H, Raposo G (2004) Cells release prions in association with exosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:9683–9688. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0308413101
Fitzner D, Schnaars M, van Rossum D, Krishnamoorthy G, Dibaj P, Bakhti M, Regen T, Hanisch UK, Simons M (2011) Selective transfer of exosomes from oligodendrocytes to microglia by macropinocytosis. J Cell Sci 124:447–458. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.074088
Friggeri A, Yang Y, Banerjee S, Park YJ, Liu G, Abraham E (2010) HMGB1 inhibits macrophage activity in efferocytosis through binding to the alphavbeta3-integrin. Am J Phys Cell Physiol 299:C1267–C1276. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00152.2010
Frühbeis C, Fröhlich D, Kuo WP, Amphornrat J, Thilemann S, Saab AS, Kirchhoff F, Möbius W, Goebbels S, Nave KA, Schneider A, Simons M, Klugmann M, Trotter J, Krämer-Albers EM (2013) Neurotransmitter-triggered transfer of exosomes mediates oligodendrocyte-neuron communication. PLoS Biol 11:e1001604. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1001604
Garcia-Vallejo JJ, van Kooyk Y (2013) The physiological role of DC-SIGN: a tale of mice and men. Trends Immunol 34:482–486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2013.03.001
Gasser O, Schifferli JA (2004) Activated polymorphonuclear neutrophils disseminate anti-inflammatory microparticles by ectocytosis. Blood 104:2543–2548. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2004-01-0361
Ghossoub R, Lembo F, Rubio A, Gaillard CB, Bouchet J, Vitale N, Slavík J, Machala M, Zimmermann P (2014) Syntenin-ALIX exosome biogenesis and budding into multivesicular bodies are controlled by ARF6 and PLD2. Nat Commun 5:3477. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4477
Goligorsky MS, Addabbo F, O’Riordan E (2007) Diagnostic potential of urine proteome: a broken mirror of renal diseases. J Am Soc Nephrol 18:2233–2239. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2006121399
Greenberg ME, Sun M, Zhang R, Febbraio M, Silverstein R, Hazen SL (2006) Oxidized phosphatidylserine-CD36 interactions play an essential role in macrophage-dependent phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. J Exp Med 203:2613–2625. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20060370
Gregory CD, Devitt A, Moffatt O (1998) Roles of ICAM-3 and CD14 in the recognition and phagocytosis of apoptotic cells by macrophages. Biochem Soc Trans 26:644–649. https://doi.org/10.1042/bst0260644
Hakulinen J, Sankkila L, Sugiyama N, Lehti K, Keski-Oja J (2008) Secretion of active membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase (MMP-14) into extracellular space in microvesicular exosomes. J Cell Biochem 105:1211–1218. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.21923
Han KY, Dugas-Ford J, Seiki M, Chang JH, Azar DT (2015) Evidence for the involvement of MMP14 in MMP2 processing and recruitment in exosomes of corneal fibroblasts. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 56:5323–5329. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.14-14417
Hanayama R, Tanaka M, Miwa K, Shinohara A, Iwamatsu A, Nagata S (2002) Identification of a factor that links apoptotic cells to phagocytes. Nature 417:182–187. https://doi.org/10.1038/417182a
Hanson PI, Cashikar A (2012) Multivesicular body morphogenesis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 28:337–362. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-cellbio-092910-154152
Harding C, Heuser J, Stahl P (1983) Receptor-mediated endocytosis of transferrin and recycling of the transferrin receptor in rat reticulocytes. J Cell Biol 97:329–339. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.97.2.329
Hazan-Halevy I, Rosenblum D, Weinstein S, Bairey O, Raanani P, Peer D (2015) Cell-specific uptake of mantle cell lymphoma-derived exosomes by malignant and non-malignant B-lymphocytes. Cancer Lett 364:59–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2015.04.026
Hedlund M, Nagaeva O, Kargl D, Baranov V, Mincheva-Nilsson L (2011) Thermal- and oxidative stress causes enhanced release of NKG2D ligand-bearing immunosuppressive exosomes in leukemia/lymphoma T and B cells. PLoS One 6:e16899. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0016899
Heijnen HFG, Schiel AE, Fijnheer R, Geuze HJ, Sixma JJ (1999) Activated platelets release two types of membrane vesicles: microvesicles by surface shedding and exosomes derived from exocytosis of multivesicular bodies and alpha-granules. Blood 94:3791–3800
Hemler ME (2005) Tetraspanin functions and associated microdomains. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6:801–811. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm1736
Hiemstra TF, Charles PD, Gracia T, Hester SS, Gatto L, Al-Lamki R, Floto RA, Su Y, Skepper JN, Lilley KS, Karet Frankl FE (2014) Human urinary exosomes as innate immune effectors. J Am Soc Nephrol 25:2017–2027. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2013101066
Hood JL, San RS, Wickline SA (2011) Exosomes released by melanoma cells prepare sentinel lymph nodes for tumor metastasis. Cancer Res 71:3792–3801. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-4455
Hosseini A, Soleimani S, Pezeshgi Modarres H, Hojjati Emami S, Tondar M, Bahlakeh G, Hasani-Sadrabad MM (2016) Exosome-inspired targeting of cancer cells with enhanced affinity. J Mater Chem B 4:768–778. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TB01741F
Hulín I (2009) Hulínová patofyziológia: exkrečné funkcie obličiek a ich poruchy. In: Hulín I (ed) Hulínova patofyziológia, 7th edn. Slovak Academic Press, Bratislava, pp 782–788
Izquierdo-Useros N, Naranjo-Gómez M, Archer J, Hatch SC, Erkizia I, Blanco J, Borràs FE, Puertas MC, Connor JH, Fernández-Figueras MT, Moore L, Clotet B, Gummuluru S, Martinez-Picado J (2009) Capture and transfer of HIV-1 particles by mature dendritic cells converges with the exosome-dissemination pathway. Blood 113:2732–2741. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2008-05-158642
Janowska-Wieczorek A, Wysoczynski M, Kijowski J, Marquez-Curtis L, Machalinski B, Ratajczak J, Ratajczak MZ (2005) Microvesicles derived from activated platelets induce metastasis and angiogenesis in lung cancer. Int J Cancer 113:752–760. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.20657
Jung T, Castellana D, Klingbeil P, Cuesta Hernández I, Vitacolonna M, Orlicky DJ, Roffler SR, Brodt P, Zöller M (2009) CD44v6 dependence of premetastatic niche preparation by exosomes. Neoplasia 11:1093–1105. https://doi.org/10.1593/neo.09822
Kalra H, Simpson RJ, Ji H, Aikawa E, Altevogt P, Askenase P, Bond VC, Borràs FE, Breakefield X, Budnik V, Buzas E, Camussi G, Clayton A, Cocucci E, Falcon-Perez JM, Gabrielsson S, Gho YS, Gupta D, Harsha HC, Hendrix A, Hill AF, Inal JM, Jenster G, Krämer-Albers EM, Lim SK, Llorente A, Lötvall J, Marcilla A, Mincheva-Nilsson L, Nazarenko I, Nieuwland R, Nolte'-t Hoen EN, Pandey A, Patel T, Piper MG, Pluchino S, Prasad TS, Rajendran L, Raposo G, Record M, Reid GE, Sánchez-Madrid F, Schiffelers RM, Siljander P, Stensballe A, Stoorvogel W, Taylor D, Thery C, Valadi H, van Balkom BW, Vázquez J, Vidal M, Wauben MH, Yáñez-Mó M, Zoeller M, Mathivanan S (2012) Vesiclepedia: a compendium for extracellular vesicles with continuous community annotation. PLoS Biol 10:e1001450. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1001450
Keller S, Rupp C, Stoeck A, Runz S, Fogel M, Lugert S, Hager HD, Abdel-Bakky MS, Gutwein P, Altevogt P (2007) CD24 is a marker of exosomes secreted into urine and amniotic fluid. Kidney Int 72:1095–1102. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ki.5002486
Kerr JF, Wyllie AH, Currie AR (1972) Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer 26:239–257. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1972.33
Kleinjan A, Böing AN, Sturk A, Nieuwland R (2012) Microparticles in vascular disorders: how tissue factor-exposing vesicles contribute to pathology and physiology. Thromb Res 130:S71–S73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.thromres.2012.08.281
Klibi J, Niki T, Riedel A, Pioche-Durieu C, Souquere S, Rubinstein E, Le Moulec S, Guigay J, Hirashima M, Guemira F, Adhikary D, Mautner J, Busson P (2009) Blood diffusion and Th1-suppressive effects of galectin-9-containing exosomes released by Epstein-Barr virus-infected nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Blood 113:1957–1966. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2008-02-142596
Kobayashi N, Karisola P, Pena-Cruz V, Dorfman DM, Jinushi M, Umetsu SE, Butte MJ, Nagumo H, Chernova I, Zhu B, Sharpe AH, Ito S, Dranoff G, Kaplan GG, Casasnovas JM, Umetsu DT, Dekruyff RH, Freeman GJ (2007) TIM-1 and TIM-4 glycoproteins bind phosphatidylserine and mediate uptake of apoptotic cells. Immunity 27:927–940. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2007.11.011
Kooijmans SAA, Fliervoet LAL, van der Meel R, Fens MHAM, Heijnen HFG, van Bergen En Henegouwen PMP, Vader P, Schiffelers RM (2016) PEGylated and targeted extracellular vesicles display enhanced cell specificity and circulation time. J Control Release 224:77–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.01.009
Krämer-Albers EM, Bretz N, Tenzer S, Winterstein C, Möbius W, Berger H, Nave KA, Schild H, Trotter J (2007) Oligodendrocytes secrete exosomes containing major myelin and stress- protective proteins: trophic support for axons? Proteomics Clin Appl 1:1446–1461. https://doi.org/10.1002/prca.200700522
Lachenal G, Pernet-Gallay K, Chivet M, Hemming FJ, Belly A, Bodon G, Blot B, Haase G, Goldberg Y, Sadoul R (2011) Release of exosomes from differentiated neurons and its regulation by synaptic glutamatergic activity. Mol Cell Neurosci 46:409–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcn.2010.11.004
Lakkaraju A, Rodriguez-Boulan E (2008) Itinerant exosomes: emerging roles in cell and tissue polarity. Trends Cell Biol 18:199–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2008.03.002
Laulagnier K, Motta C, Hamdi S, Roy S, Fauvelle F, Pageaux JF, Kobayashi T, Salles JP, Perret B, Bonnerot C, Record M (2004) Mast cell- and dendritic cell-derived exosomes display a specific lipid composition and an unusual membrane organization. Biochem J 380:161–171. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj20031594
Lee SJ, So IS, Park SY, Kim IS (2008) Thymosin beta4 is involved in stabilin-2-mediated apoptotic cell engulfment. FEBS Lett 582:2161–2166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2008.03.058
Lespagnol A, Duflaut D, Beekman C, Blanc L, Fiucci G, Marine JC, Vidal M, Amson R, Telerman A (2008) Exosome secretion, including the DNA damage-induced p53-dependent secretory pathway, is severely compromised in TSAP6/Steap3-null mice. Cell Death Differ 15:1723–1733. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2008.104
Lu J, Li J, Liu S, Wang T, Ianni A, Bober E, Braun T, Xiang R, Yue S (2017) Exosomal tetraspanins mediate cancer metastasis by altering host microenvironment. Oncotarget 8:62803–62815. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.19119
Lugini L, Cecchetti S, Huber V, Luciani F, Macchia G, Spadaro F, Paris L, Abalsamo L, Colone M, Molinari A, Podo F, Rivoltini L, Ramoni C, Fais S (2012) Immune surveillance properties of human NK cell-derived exosomes. J Immunol 189:2833–2842. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1101988
Lv LH, Wan YL, Lin Y, Zhang W, Yang M, Li GL, Lin HM, Shang CZ, Chen YJ, Min J (2012) Anticancer drugs cause release of exosomes with heat shock proteins from human hepatocellular carcinoma cells that elicit effective natural killer cell antitumor responses in vitro. J Biol Chem 287:15874–15885. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.340588
Mallegol J, Van Niel G, Lebreton C, Lepelletier Y, Candalh C, Dugave C, Heath JK, Raposo G, Cerf-Bensussan N, Heyman M (2007) T84-intestinal epithelial exosomes bear MHC class II/peptide complexes potentiating antigen presentation by dendritic cells. Gastroenterology 132:1866–1876. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2007.02.043
Marton A, Vizler C, Kusz E, Temesfoi V, Szathmary Z, Nagy K, Szegletes Z, Varo G, Siklos L, Katona RL, Tubak V, Howard OM, Duda E, Minarovits J, Nagy K, Buzas K (2012) Melanoma cell-derived exosomes alter macrophage and dendritic cell functions in vitro. Immunol Lett 148:34–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imlet.2012.07.006
Mastronardi ML, Mostefai HA, Meziani F, Martinez MC, Asfar P, Andriantsitohaina R (2011) Circulating microparticles from septic shock patients exert differential tissue expression of enzymes related to inflammation and oxidative stress. Crit Care Med 39:1739–1748. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0b013e3182190b4b
Masyuk AI, Huang BQ, Ward CJ, Gradilone SA, Banales JM, Masyuk TV, Radtke B, Splinter PL, LaRusso NF (2010) Biliary exosomes influence cholangiocyte regulatory mechanisms and proliferation through interaction with primary cilia. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 299:G990–G999. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.00093.2010
Mathivanan S, Ji H, Simpson RJ (2010) Exosomes: extracellular organelles important in intercellular communication. J Proteome 73:1907–1920. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2010.06.006
Mittelbrunn M, Gutiérrez-Vázquez C, Villarroya-Beltri C, González S, Sánchez-Cabo F, González MÁ, Bernad A, Sánchez-Madrid F (2011) Unidirectional transfer of microRNA-loaded exosomes from T cells to antigen-presenting cells. Nat Commun 2:282. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms1285
Miyanishi M, Tada K, Koike M, Uchiyama Y, Kitamura T, Nagata S (2007) Identification of Tim4 as a phosphatidylserine receptor. Nature 450:435–439. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06307
Möbius W, Ohno-Iwashita Y, van Donselaar EG, Oorschot VM, Shimada Y, Fujimoto T, Heijnen HF, Geuze HJ, Slot JW (2002) Immunoelectron microscopic localization of cholesterol using biotinylated and non-cytolytic perfringolysin O. J Histochem Cytochem 50:43–55. https://doi.org/10.1177/002215540205000105
Monleón I, Martinez-Lorenzo MJ, Monteagudo L, Lasierra P, Taulés M, Iturralde M, Piñeiro A, Larrad L, Alava MA, Naval J, Anel A (2001) Differential secretion of Fas ligand- or APO2 ligand/TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-carrying microvesicles during activation-induced death of human T cells. J Immunol 167:6736–6744. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.167.12.6736
Montecalvo A, Larregina AT, Shufesky WJ, Stolz DB, Sullivan ML, Karlsson JM, Baty CJ, Gibson GA, Erdos G, Wang Z, Milosevic J, Tkacheva OA, Divito SJ, Jordan R, Lyons-Weiler J, Watkins SC, Morelli AE (2012) Mechanism of transfer of functional microRNAs between mouse dendritic cells via exosomes. Blood 119:756–766. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2011-02-338004
Morelli AE (2006) The immune regulatory effect of apoptotic cells and exosomes on dendritic cells: its impact on transplantation. Am J Transplant 6:254–261. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-6143.2005.01197.x
Morelli AE, Larregina AT, Shufesky WJ, Sullivan ML, Stolz DB, Papworth GD, Zahorchak AF, Logar AJ, Wang Z, Watkins SC, Falo LD Jr, Thomson AW (2004) Endocytosis, intracellular sorting, and processing of exosomes by dendritic cells. Blood 104:3257–3266. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2004-03-0824
Mulcahy LA, Pink RC, Carter DR (2014) Routes and mechanisms of extracellular vesicle uptake. J Extracell Vesicles 3. https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v3.24641
Muralidharan-Chari V, Clancy J, Plou C, Romao M, Chavrier P, Raposo G, D'Souza-Schorey C (2009) ARF6-regulated shedding of tumor cell-derived plasma membrane microvesicles. Curr Biol 19:1875–1885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2009.09.059
Nabhan JF, Hu R, Oh RS, Cohen SN, Lu Q (2012) Formation and release of arrestin domain-containing protein 1-mediated microvesicles (ARMMs) at plasma membrane by recruitment of TSG101 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:4146–4151. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1200448109
Nanbo A, Kawanishi E, Yoshida R, Yoshiyama H (2013) Exosomes derived from Epstein-Barr virus-infected cells are internalized via caveola-dependent endocytosis and promote phenotypic modulation in target cells. J Virol 87:10334–10347. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01310-13
Näslund TI, Paquin-Proulx D, Paredes PT, Vallhov H, Sandberg JK, Gabrielsson S (2014) Exosomes from breast milk inhibit HIV-1 infection of dendritic cells and subsequent viral transfer to CD4+ T cells. AIDS 28:171–180. https://doi.org/10.1097/QAD.0000000000000159
Nguyen DG, Booth A, Gould SJ, Hildreth JE (2003) Evidence that HIV budding in primary macrophages occurs through the exosome release pathway. J Biol Chem 278:52347–52354. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M309009200
Nolte-'t Hoen EN, Wauben MH (2012) Immune cell-derived vesicles: modulators and mediators of inflammation. Curr Pharm Des 18:2357–2368. https://doi.org/10.2174/138161212800166013
Nolte-'t Hoen EN, Buschow SI, Anderton SM, Stoorvogel W, Wauben MH (2009) Activated T cells recruit exosomes secreted by dendritic cells via LFA-1. Blood 113:1977–1981. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2008-08-174094
Ogawa Y, Kanai-Azuma M, Akimoto Y, Kawakami H, Yanoshita R (2008) Exosome-like vesicles with dipeptidyl peptidase IV in human saliva. Biol Pharm Bull 31:1059–1062. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.31.1059
Pan BT, Johnstone RM (1983) Fate of the transferrin receptor during maturation of sheep reticulocytes in vitro: selective externalization of the receptor. Cell 33:967–978. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(83)90040-5
Park D, Tosello-Trampont AC, Elliott MR, Lu M, Haney LB, Ma Z, Klibanov AL, Mandell JW, Ravichandran KS (2007) BAI1 is an engulfment receptor for apoptotic cells upstream of the ELMO/Dock180/Rac module. Nature 450:430–434. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06329
Parolini I, Federici C, Raggi C, Lugini L, Palleschi S, De Milito A, Coscia C, Iessi E, Logozzi M, Molinari A, Colone M, Tatti M, Sargiacomo M, Fais S (2009) Microenvironmental pH is a key factor for exosome traffic in tumor cells. J Biol Chem 284:34211–34222. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.041152
Patel B, Patel J, Cho JH, Manne S, Bonala S, Henske E, Roegiers F, Markiewski M, Karbowniczek M (2015) Exosomes mediate the acquisition of the disease phenotypes by cells with normal genome in tuberous sclerosis complex. Oncogene 35:3027–3036. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.358
Pisitkun T, Shen RF, Knepper MA (2004) Identification and proteomic profiling of exosomes in human urine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:13368–13373. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0403453101
Poliakov A, Spilman M, Dokland T, Amling CL, Mobley JA (2009) Structural heterogeneity and protein composition of exosome-like vesicles (prostasomes) in human semen. Prostate 69:159–167. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.20860
Qu JL, Qu XJ, Zhao MF, Teng YE, Zhang Y, Hou KZ, Jiang YH, Yang XH, Liu YP (2009a) Gastric cancer exosomes promote tumour cell proliferation through PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK activation. Dig Liver Dis 41:875–880. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dld.2009.04.006
Qu Y, Ramachandra L, Mohr S, Franchi L, Harding CV, Nunez G, Dubyak GR (2009b) P2X7 receptor-stimulated secretion of MHC class II-containing exosomes requires the ASC/NLRP3 inflammasome but is independent of caspase-1. J Immunol 182:5052–5062. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.0802968
Rajendran L, Honsho M, Zahn TR, Keller P, Geiger KD, Verkade P, Simons K (2006) Alzheimer’s disease beta-amyloid peptides are released in association with exosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:11172–11177. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0603838103
Rak J (2010) Microparticles in cancer. Semin Thromb Hemost 36:888–906. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0030-1267043
Ramachandra L, Qu Y, Wang Y, Lewis CJ, Cobb BA, Takatsu K, Boom WH, Dubyak GR, Harding CV (2010) Mycobacterium tuberculosis synergizes with ATP to induce release of microvesicles and exosomes containing major histocompatibility complex class II molecules capable of antigen presentation. Infect Immun 78:5116–5125. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.01089-09
Rana S, Zöller M (2011) Exosome target cell selection and the importance of exosomal tetraspanins: a hypothesis. Biochem Soc Trans 39:559–562. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST0390559
Rana S, Yue S, Stadel D, Zöller M (2012) Toward tailored exosomes: the exosomal tetraspanin web contributes to target cell selection. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 44:1574–1584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2012.06.018
Raposo G, Stoorvogel W (2013) Extracellular vesicles: exosomes, microvesicles and friends. J Cell Biol 200:373–383. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201211138
Raposo G, Nijman HW, Stoorvogel W, Liejendekker R, Harding CV, Melief CJ, Geuze HJ (1996) B lymphocytes secrete antigen-presenting vesicles. J Exp Med 183:1161–1172. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.183.3.1161
Ratajczak J, Wysoczynski M, Hayek F, Janowska-Wieczorek A, Ratajczak MZ (2006) Membrane-derived microvesicles: important and underappreciated mediators of cell-to-cell communication. Leukemia 20:1487–1495. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404296
Record M, Carayon K, Poirot M, Silvente-Poirot S (2014) Exosomes as new vesicular lipid transporters involved in cell-cell communication and various pathophysiologies. Biochim Biophys Acta 1841:108–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2013.10.004
Rhee JS, Black M, Schubert U, Fischer S, Morgenstern E, Hammes HP, Preissner KT (2004) The functional role of blood platelet components in angiogenesis. Thromb Haemost 92:394–402. https://doi.org/10.1160/TH03-04-0213
Roucourt B, Meeussen S, Bao J, Zimmermann P, David G (2015) Heparanase activates the syndecan-syntenin-ALIX exosome pathway. Cell Res 25:412–428. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2015.29
Sadovska L, Santos CB, Kalniņa Z, Linē A (2015) Biodistribution, Uptake and Effects Caused by Cancer-derived Extracellular Vesicles. J Circ Biomark 4:2. https://doi.org/10.5772/60522
Saunderson SC, Dunn AC, Crocker PR, McLellan AD (2014) CD169 mediates the capture of exosomes in spleen and lymph node. Blood 123:208–216. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2013-03-489732
Schnitzer JK, Berzel S, Fajardo-Moser M, Remer KA, Moll H (2010) Fragments of antigen-loaded dendritic cells (DC) and DC-derived exosomes induce protective immunity against Leishmania major. Vaccine 28:5785–5793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2010.06.077
Segura E, Guérin C, Hogg N, Amigorena S, Théry C (2007) CD8+ dendritic cells use LFA-1 to capture MHC-peptide complexes from exosomes in vivo. J Immunol 179:1489–1496. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.179.3.1489
Simons M, Raposo G (2009) Exosomes – vesicular carriers for intracellular communication. Curr Opin Cell Biol 21:575–581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceb.2009.03.007
Skog J, Wurdinger T, van Rijn S, Meijer DH, Gainche L, Sena-Esteves M, Curry WT Jr, Carter BS, Krichevsky AM, Breakefield XO (2008) Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nat Cell Biol 10:1470–1476. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1800
Skokos D, LePanse S, Villa I, Rousselle JC, Peronet R, David B, Namane A, Mécheri S (2001) Mast cell-dependent B and T lymphocyte activation is mediated by the secretion of immunologically active exosomes. J Immunol 166:868–876. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.166.2.868
Skokos D, Botros HG, Demeure C, Morin J, Peronet R, Birkenmeier G, Boudaly S, Mécheri S (2003) Mast cell-derived exosomes induce phenotypic and functional maturation of dendritic cells and elicit specific immune responses in vivo. J Immunol 170:3037–3045. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.170.6.3037
Skriner K, Adolph K, Jungblut PR, Burmester GR (2006) Association of citrullinated proteins with synovial exosomes. Arthritis Rheum 54:3809–3814. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.22276
Smyth TJ, Redzic JS, Graner MW, Anchordoquy TJ (2014) Examination of the specificity of tumor cell derived exosomes with tumor cells in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta 1838:2954–2965. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2014.07.026
Stepanek O, Brdicka T, Angelisova P, Horvath O, Spicka J, Stockbauer P, Man P, Horejsi V (2011) Interaction of late apoptotic and necrotic cells with vitronectin. PLoS One 6:e19243. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0019243
Stoeck A, Keller S, Riedle S, Sanderson MP, Runz S, Le Naour F, Gutwein P, Ludwig A, Rubinstein E, Altevogt P (2006) A role for exosomes in the constitutive and stimulus-induced ectodomain cleavage of L1 and CD44. Biochem J 393:609–618. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20051013
Svensson KJ, Christianson HC, Wittrup A, Bourseau-Guilmain E, Lindqvist E, Svensson LM, Mörgelin M, Belting M (2013) Exosome uptake depends on ERK1/2-heat shock protein 27 signaling and lipid Raft-mediated endocytosis negatively regulated by caveolin-1. J Biol Chem 288:17713–17724. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.445403
Tang K, Zhang Y, Zhang H, Xu P, Liu J, Ma J, Lv M, Li D, Katirai F, Shen GX, Zhang G, Feng ZH, Ye D, Huan B (2012) Delivery of chemotherapeutic drugs in tumour cell-derived microparticles. Nat Commun 3:1282. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms2282
Tauro BJ, Greening DW, Mathias RA, Ji H, Mathivanan S, Scott AM, Simpson RJ (2012) Comparison of ultracentrifugation, density gradient separation, and immunoaffinity capture methods for isolating human colon cancer cell line LIM1863-derived exosomes. Methods 56:293–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2012.01.002
Temchura VV, Tenbusch M, Nchinda G, Nabi G, Tippler B, Zelenyuk M, Wildner O, Uberla K, Kuate S (2008) Enhancement of immunostimulatory properties of exosomal vaccines by incorporation of fusion-competent G protein of vesicular stomatitis virus. Vaccine 26:3662–3672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2008.04.069
Thali M (2009) The roles of tetraspanins in HIV-1 replication. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 339:85–102. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-02175-6_5
Théry C, Regnault A, Garin J, Wolfers J, Zitvogel L, Ricciardi-Castagnoli P, Raposo G, Amigorena S (1999) Molecular characterization of dendritic cell-derived exosomes. Selective accumulation of the heat shock protein hsc73. J Cell Biol 147:599–610. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.147.3.599
Théry C, Zitvogel L, Amigorena S (2002) Exosomes: composition, biogenesis and function. Nat Rev Immunol 2:569–579. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri855
Tian T, Wang Y, Wang H, Zhu Z, Xiao Z (2010) Visualizing of the cellular uptake and intracellular trafficking of exosomes by live-cell microscopy. J Cell Biochem 111:488–496. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.22733
Timár CI, Lörincz AM, Ligeti E (2013) Changing world of neutrophils. Pflugers Arch 465:1521–1533. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-013-1285-1
Trajkovic K, Hsu C, Chiantia S, Rajendran L, Wenzel D, Wieland F, Schwille P, Brügger B, Simons M (2008) Ceramide triggers budding of exosome vesicles into multivesicular endosomes. Science 319:1244–1247. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1153124
Turturici G, Tinnirello R, Sconzo G, Geraci F (2014) Extracellular membrane vesicles as a mechanism of cell-to-cell communication: advantages and disadvantages. Am J Phys Cell Physiol 306:C621–C633. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00228.2013
Valadi H, Ekström K, Bossios A, Sjöstrand M, Lee JJ, Lötvall JO (2007) Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol 9:654–659. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1596
van Eijk IC, Tushuizen ME, Sturk A, Dijkmans BA, Boers M, Voskuyl AE, Diamant M, Wolbink GJ, Nieuwland R, Nurmohamed MT (2010) Circulating microparticles remain associated with complement activation despite intensive anti-inflammatory therapy in early rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 69:1378–1382. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2009.118372
Vella LJ, Greenwood DLV, Cappai R, Scheerlinck JPY, Hill AF (2008) Enrichment of prion protein in exosomes derived from bovine cerebral spinal fluid. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 124:385–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetimm.2008.04.002
Véron P, Segura E, Sugano G, Amigorena S, Théry C (2005) Accumulation of MFG-E8/lactadherin on exosomes from immature dendritic cells. Blood Cells Mol Dis 35:81–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcmd.2005.05.001
Wang JG, Williams JC, Davis BK, Jacobson K, Doerschuk CM, Ting JPY, Mackman N (2011a) Monocytic microparticles activate endothelial cells in an IL-1β-dependent manner. Blood 118:2366–2374. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2011-01-330878
Wang S, Cesca F, Loers G, Schweizer M, Buck F, Benfenati F, Schachner M, Kleene R (2011b) Synapsin I is an oligomannose-carrying glycoprotein, acts as an oligomannose-binding lectin, and promotes neurite outgrowth and neuronal survival when released via glia-derived exosomes. J Neurosci 31:7275–7290. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6476-10.2011
Wang J, Wu Y, Guo J, Fei X, Yu L, Ma S (2017) Adipocyte-derived exosomes promote lung cancer metastasis by increasing MMP9 activity via transferring MMP3 to lung cancer cells. Oncotarget 8:81880–81891. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.18737
Wood MJ, O’Loughlin AJ, Samira L (2011) Exosomes and the blood-brain barrier: implications for neurological diseases. Ther Deliv 2:1095–1099. https://doi.org/10.4155/TDE.11.83
Wu Y, Singh S, Georgescu MM, Birge RB (2005) A role for Mer tyrosine kinase in alphavbeta5 integrin-mediated phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. J Cell Sci 118:539–553. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.01632
Wu G, Yang G, Zhang R, Xu G, Zhang L, Wen W, Lu J, Liu J, Yu Y (2015) Altered microRNA expression profiles of extracellular vesicles in nasal mucus from patients with allergic rhinitis. Allergy, Asthma Immunol Res 7:449–457. https://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2015.7.5.449
Xitong D, Xiaorong Z (2016) Targeted therapeutic delivery using engineered exosomes and its applications in cardiovascular diseases. Gene 575:377–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2015.08.067
Yáñez-Mó M, Siljander PR, Andreu Z, Zavec AB, Borràs FE, Buzas EI, Buzas K, Casal E, Cappello F, Carvalho J, Colás E, Cordeiro-da Silva A, Fais S, Falcon-Perez JM, Ghobrial IM, Giebel B, Gimona M, Graner M, Gursel I, Gursel M, Heegaard NH, Hendrix A, Kierulf P, Kokubun K, Kosanovic M, Kralj-Iglic V, Krämer-Albers EM, Laitinen S, Lässer C, Lener T, Ligeti E, Linē A, Lipps G, Llorente A, Lötvall J, Manček-Keber M, Marcilla A, Mittelbrunn M, Nazarenko I, Nolte-'t Hoen EN, Nyman TA, O'Driscoll L, Olivan M, Oliveira C, Pállinger É, Del Portillo HA, Reventós J, Rigau M, Rohde E, Sammar M, Sánchez-Madrid F, Santarém N, Schallmoser K, Ostenfeld MS Stoorvogel W, Stukelj R, Van der Grein SG, Vasconcelos MH, Wauben MH, De Wever O (2015) Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J Extracell Vesicles 4:27066. https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v4.27066
Yin W, Ghebrehiwet B, Peerschke EIB (2008) Expression of complement components and inhibitors on platelet microparticles. Platelets 19:225–233. https://doi.org/10.1080/09537100701777311
Yoshioka Y, Konishi Y, Kosaka N, Katsuda T, Kato T, Ochiya T (2013) Comparative marker analysis of extracellular vesicles in different human cancer types. J Extracell Vesicles 2. https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v2i0.20424
You Y, Shan Y, Chen J, Yue H, You B, Shi S, Li X, Cao X (2015) Matrix metalloproteinase 13-containing exosomes promote nasopharyngeal carcinoma metastasis. Cancer Sci 106:1669–1677. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.12818
Zaborowski MP, Balaj L, Breakefield XO, Lai CP (2015) Extracellular Vesicles: Composition, Biological Relevance, and Methods of Study. Bioscience 65:783–797. https://doi.org/10.1093/biosci/biv084
Zech D, Rana S, Büchler MW, Zöller M (2012) Tumor-exosomes and leukocyte activation: an ambivalent crosstalk. Cell Commun Signal 10:37. https://doi.org/10.1186/1478-811X-10-37
Zhou H, Pisitkun T, Aponte A, Yuen PS, Hoffert JD, Yasuda H, Hu X, Chawla L, Shen RF, Knepper MA, Star RA (2006) Exosomal fetuin-A identified by proteomics: a novel urinary biomarker for detecting acute kidney injury. Kidney Int 70:1847–1857. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ki.5001874
Zitvogel L, Regnault A, Lozier A, Wolfers J, Flament C, Tenza D, Ricciardi-Castagnoli P, Raposo G, Amigorena S (1998) Eradication of established murine tumors using a novel cell-free vaccine: dendritic cell-derived exosomes. Nat Med 4:594–600. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0598-594
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by the FWF (P22908), VEGA (2/0063/14 and 2/0020/17) and APVV-16-0452 grants.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Petrovčíková, E., Vičíková, K. & Leksa, V. Extracellular vesicles – biogenesis, composition, function, uptake and therapeutic applications. Biologia 73, 437–448 (2018). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-018-0047-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-018-0047-0