Abstract
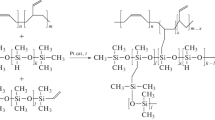
The emissions of hydrocarbons from fossil fuels into atmosphere entail both an economic loss and an environmental pollution. Membrane separations can be used for vapour recovery and/or vapour removal from the permanent gas stream, given that the appropriate membrane is identified. A neat poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) membrane is impermeable to both the representatives of aliphatic hydrocarbons and branched hydrocarbons, namely hexane and isooctane, whereas the permeation flux is enhanced by the presence of 80 mass % of the ionic liquid 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethylsulphonyl)imide in the membrane, as detailed in this work. The permeabilities of hydrocarbon vapours were determined from the binary mixture containing hydrocarbon and nitrogen to simulate the real input of an air stream containing a condensable hydrocarbon. The diffusion coefficient determined from sorption measurements was higher for hexane, as would be expected for a smaller molecule, whereas both the sorption isotherms and permeabilities of the hydrocarbons studied were found to be almost identical. It is possible that the sorption effect predominates in the transport mechanism for VOCs/N2 separations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker, R. W. (2002). Future directions of membrane gas separation technology. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 41, 1393–1411. DOI: 10.1021/ie0108088.
Baker, R. W. (2004). Membrane technology and applications (2nd ed.). Chichester, UK: Wiley.
Bernardo, P., Drioli, E., & Golemme, G. (2009). Membrane gas separation: A review/state of the art. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 48, 4638–4663. DOI: 10.1021/ie8019032.
Bodzek, M. (2000). Membrane techniques in air cleaning. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 9, 1–12.
Crank, J. (1975). The mathematics of diffusion (2nd ed.). Oxford, UK: Clarendon Press.
de los Ríos, A. P., Hernández-Fernández, F. J., Tomás-Alonso, F., Palacios, J. M., & Víllora, G. (2009). Stability studies of supported liquid membranes based on ionic liquids: Effect of surrounding phase nature. Desalination, 245, 776–782. DOI: 10.1016/j.desal.2009.02.051.
Dytrych, P., Kluson, P., Dzik, P., Vesely, M., Morozova, M., Sedlakova, Z., & Solcova, O. (2014). Photo-electrochemical properties of ZnO and TiO2 layers in ionic liquid environment. Catalysis Today, 230, 152–157. DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2013.10.048.
Favre, E., Clément, R., Nguyen, Q. T., Schaetzel, P., & Néel, J. (1993). Sorption of organic solvents into dense silicone membranes. Part 2.—Development of a new approach based on a clustering hypothesis for associated solvents. Journal of the Chemical Society, Faraday Transactions, 89, 4347–4353. DOI: 10.1039/ft9938904347.
Friess, K., Jansen, J. C., Vopička, O., Randová, A., Hynek, V., Šípek, M., Bartovská, L., Izák, P., Dingemans, M., Dewulf, J., Van Langenhove, H., & Drioli, E. (2009). Comparative study of sorption and permeation techniques for the determination of heptane and toluene transport in polyethylene membranes. Journal of Membrane Science, 338, 161–174. DOI: 10.1016/j.memsci.2009.04.030.
Friess, K., Jansen, J. C., Bazzarelli, F., Izák, P., Jarmarová, V., Kačírková, M., Schauer, J., Clarizia, G., & Bernardo, P. (2012). High ionic liquid content polymeric gel membranes: Correlation of membrane structure with gas and vapour transport properties. Journal of Membrane Science, 415–416, 801–809. DOI: 10.1016/j.memsci.2012.05.072.
Funke, H. H., Kovalchick, M. G., Falconer, J. L., & Noble R. D. (1996). Separation of hydrocarbon isomer vapors with silicalite zeolite membranes. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 35, 1575–1582. DOI: 10.1021/ie950495e.
He, X. Z., & Hägg, M. B. (2012). Membranes for environmentally friendly energy processes. Membranes, 2, 706–726. DOI: 10.3390/membranes2040706.
Jansen, J. C., Clarizia, G., Bernardo, P., Bazzarelli, F., Friess, K., Randová, A., Schauer, J., Kubicka, D., Kacirková, M., & Izak, P. (2013). Gas transport properties and pervaporation performance of fluoropolymer gel membranes based on pure and mixed ionic liquids. Separation and Purification Technology, 109, 87–97. DOI: 10.1016/j.seppur.2013.02.034.
Jansen, J. C., Friess, K., Clarizia, G., Schauer, J., & Izák, P. (2011). High ionic liquid content polymeric gel membranes: Preparation and performance. Macromolecules, 44, 39–45. DOI: 10.1021/ma102438k.
Kim, H. J., Nah, S. S., & Min, B. R. (2002). A new technique for preparation of PDMS pervaporation membrane for VOC removal. Advances in Environmental Research, 6, 255–264. DOI: 10.1016/s1093-0191(01)00056-9.
Krull, F. F., Fritzmann, C., & Melin, T. (2008). Liquid membranes for gas/vapor separations. Journal of Membrane Science, 325, 509–519. DOI: 10.1016/j.memsci.2008.09.018.
Lide, D. R. (2003). Handbook of chemistry and physics (84th ed.). Boca Raton, FL, USA: CRC Press.
Liu, Y. J., Feng, X., & Lawless, D. (2006). Separation of gasoline vapor from nitrogen by hollow fiber composite membranes for VOC emission control. Journal of Membrane Science, 271, 114–124. DOI: 10.1016/j.memsci.2005.07.012.
Liu, L., Chakma, A., Feng, X. S., & Lawless, D. (2009). Separation of VOCs from N2 using poly(ether block amide) membranes. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 87, 456–465. DOI: 10.1002/cjce.20181.
Lozano, L. J., Godínez, C., de los Ríos, A. P., Hernández-Fernández, F. J., Sánchez-Segado, S., & Alguacil, F. J. (2011). Recent advances in supported ionic liquid membrane technology. Journal of Membrane Science, 376, 1–14. DOI: 10.1016/j.memsci.2011.03.036.
Majumdar, S., Bhaumik, D., & Sirkar, K. K. (2003). Performance of commercial-size plasmapolymerized PDMS-coated hollow fiber modules in removing VOCs from N2/air. Journal of Membrane Science, 214, 323–330. DOI: 10.1016/s0376-7388(02)00545-8.
Matsumoto, M., Ueba, K., & Kondo, K. (2009). Vapor permeation of hydrocarbons through supported liquid membranes based on ionic liquids. Desalination, 241, 365–371. DOI: 10.1016/j.desal.2007.11.090.
Nosrati, S., Jayakumar, N. S., & Hashim, M. A. (2011). Performance evaluation of supported ionic liquid membrane for removal of phenol. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 192, 1283–1290. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.06.037.
Pereiro, A. B., Araújo, J. M. M., Esperança, J. M. S. S., Marrucho, I. M., & Rebelo, L. P. N. (2012). Ionic liquids in separations of azeotropic systems - A review. Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 46, 2–28. DOI: 10.1016/j.jct.2011.05.026.
Rebollar-Perez, G., Carretier, E., Lesage, N., & Moulin, P. (2011). Volatile organic compound (VOC) removal by vapor permeation at low VOC concentrations: Laboratory scale results and modeling for scale up. Membranes, 1, 80–90. 10.3390/membranes1010080.
Seber, G. A. F., & Wild, C. J. (2003). Nonlinear regression. Hoboken, NJ, USA: Wiley.
Sedláková, Z., & Wagner, Z. (2012). High-pressure phase equilibria in systems containing CO2 and ionic liquid of the [Cnmim][Tf2N] type. Chemical & Biochemical Engineering Quarterly, 26, 55–60.
Sedláková, Z., Clarizia, G., Bernardo, P., Jansen, J. C., Slobodian, P., Svoboda, P., Kárászová, M., Friess, K., & Izák, P. (2014). Carbon nanotube- and carbon fiber-reinforcement of ethylene-octene copolymer membranes for gas and vapor separation. Membranes, 4, 20–39. DOI: 10.3390/membranes4010020.
Semenova, S. I. (2004). Polymer membranes for hydrocarbon separation and removal. Journal of Membrane Science, 231, 189–207. DOI: 10.1016/j.memsci.2003.11.022.
Sohn, W. I., Ryu, D. H., Oh, S. J., & Koo, J. K. (2000). A study on the development of composite membranes for the separation of organic vapors. Journal of Membrane Science, 175, 163–170. DOI: 10.1016/s0376-7388(00)00417-8.
Vopička, O., Hynek, V., Zgažar, M., Friess, K., & Šípek, M. (2009a). A new sorption model with a dynamic correction for the determination of diffusion coefficients. Journal of Membrane Science, 330, 51–56. DOI: 10.1016/j.memsci.2008.12.037.
Vopička, O., Hynek, V., Friess, K., Šípek, M., & Sysel, P. (2009b). A device for determination of vapor sorption in polymers. Chemické Listy, 103, 310–314.
Vopička, O., Hynek, V., & Rabová, V. (2010a). Measuring the transient diffusion of vapor mixtures through dense membranes. Journal of Membrane Science, 350, 217–225. DOI: 10.1016/j.memsci.2009.12.031.
Vopička, O., Hynek, V., Friess, K., & Izák, P. (2010b). Blended silicone-ionic liquid membranes: Transport properties of butan-1-ol vapor. European Polymer Journal, 46, 123–128. DOI: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2009.10.011.
Vopička, O., Friess, K., Hynek, V., Sysel, P., Zgažar, M., Šípek, M., Pilnáček, K., Lanč, M., Jansen, J. C., Mason, C. R., & Budd, P. M. (2013). Equilibrium and transient sorption of vapours and gases in the polymer of intrinsic microporosity PIM-1. Journal of Membrane Science, 434, 148–160 DOI: 10.1016/j.memsci.2013.01.040.
Zhao, K., Xiu, G. L., Xu, L. H., Zhang, D., Zhang, X. F., & Deshusses, M. A. (2011). Biological treatment of mixtures of toluene and n-hexane vapours in a hollow fibre membrane bioreactor. Environmental Technology, 32, 617–623. DOI: 10.1080/09593330.2010.507634.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dedicated to the memory of professor Elemír Kossaczký
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morávková, L., Vopička, O., Vejražka, J. et al. Vapour permeation and sorption in fluoropolymer gel membrane based on ionic liquid 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethylsulphonyl)imide. Chem. Pap. 68, 1739–1746 (2014). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-014-0623-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-014-0623-x