Abstract
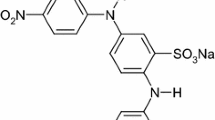
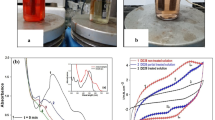
The decolorisation process of a synthetic textile dye, direct violet 51, was investigated in an aqueous solution using an electrochemical method in a batch electrochemical cell. Graphite electrodes were used as the anode and cathode for the decolorisation process. The parameters such as applied current, initial pH, solution conductivity, interfering ions, and effect of electrodes were optimised. It was found that the dye with an initial concentration of 20 mg L−1 could be removed after 50 min using a current of 100 mA with colour removal of up to 94 %. The UV-VIS spectra of the dye were analysed prior to and after treatment and these confirmed that the conjugated systems were decomposed at a current of 100 mA. The optimised method was successfully applied to real wastewater samples.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carneiro, P. A., Boralle, N., Stradiotto, N. R., Furlan, M., & Zanoni, M. V. B. (2004). Decolourization of anthraquinone reactive dye by electrochemical reduction on reticulated glassy carbon electrode, Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society, 15, 587–594. DOI: 10.1590/s0103-50532004000400023.
Cerón-Rivera, M., Dávila-Jiménez, M. M., & Elizalde-González, M. P. (2004). Degradation of the textile dyes Basic yellow 28 and Reactive black 5 using diamond and metal alloys electrodes. Chemosphere, 55, 1–10. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2003.10.060.
Crini, G. (2006). Non-conventional low-cost adsorbents for dye removal: A review. Bioresource Technology, 97, 1061–1085. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2005.05.001.
Daraei, P., Madaeni, S. S., Salehi, E., Ghaemi, N., Ghari, H. S., Khadivi, M. A., & Rostami, E. (2013). Novel thin film composite membrane fabricated by mixed matrix nanoclay/chitosan on PVDF microfiltration support: Preparation, characterization and performance in dye removal. Journal of Membrane Science, 436, 97–108. DOI: 10.1016/j.memsci.2013.02.031.
El-Ashtoukhy, E. S. Z., & Amin, N. K. (2010). Removal of acid green dye 50 from wastewater by anodic oxidation and electrocoagulation—A comparative study. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 179, 113–119. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.02.066.
Forgacs, E., Cserháti, T., & Oros, G. (2004). Removal of synthetic dyes from wastewaters: a review. Environment International, 30, 953–971. DOI: 10.1016/j.envint.2004.02.001.
Kannan, C., Muthuraja, K., & Devi, M. R. (2013). Hazardous dyes removal from aqueous solution over mesoporous aluminophosphate with textural porosity by adsorption. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 244–245, 10–20. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.11.016.
Kong, L. P., Gan, X. J., Ahmad, A. L., Hamed, B. H., Evarts, E. R., Ooi, B. S., & Lim, J. K. (2012). Design and synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles augmented microcapsule with catalytic and magnetic bifunctionalities for dye removal. Chemical Engineering Journal, 197, 350–358. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2012.05.019.
Konicki, W., Sibera, D., Mijowska, E., Lendzion-Bieluń, Z., & Narkiewicz, U. (2013). Equilibrium and kinetic studies on acid dye Acid Red 88 adsorption by magnetic ZnFe2O4 spinel ferrite nanoparticles. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 398, 152–160. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2013.02.021.
Liu, S. T., Huang, J., Ye, Y., Zhang, A. B., Pan, L., & Chen, X. G. (2013). Microwave enhanced Fenton process for the removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution. Chemical Engineering Journal, 215–216, 586–590. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2012.11.003.
Martínez-Huitle, C. A., & Brillas, E. (2009). Decontamination of wastewaters containing synthetic organic dyes by electrochemical methods: A general review. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 87, 105–145. DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2008.09.017.
Martínez-Huitle, C. A., & Ferro, S. (2006). Electrochemical oxidation of organic pollutants for the wastewater treatment: direct and indirect processes. Chemical Society Reviews, 35, 1324–1340. DOI: 10.1039/b517632h.
Méndez-Martínez, A. J., Dávila-Jiménez, M. M., Ornelas-Dávila, O., Elizalde-González, M. P., Arroyo-Abad, U., Sirés, I., & Brillas, E. (2012). Electrochemical reduction and oxidation pathways for Reactive Black 5 dye using nickel electrodes in divided and undivided cells. Electrochimica Acta, 59, 140–149. DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2011.10.047.
Merzouk, B., Gourich, B., Sekki, A., Madani, K., Vial, C., & Barkaoui, M. (2009). Studies on the decolorization of textile dye wastewater by continuous electrocoagulation process. Chemical Engineering Journal, 149, 207–214. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2008.10.018.
Rivera, M., Pazos, M., & Sanromán, M. A. (2011). Development of an electrochemical cell for the removal of Reactive Black 5. Desalination, 274, 39–43. DOI: 10.1016/j.desal.2011.01.074.
Wang, A. M., Qu, J. H., Liu, H. J., & Ge, J. T. (2004). Degradation of azo dye Acid Red 14 in aqueous solution by electrokinetic and electrooxidation process. Chemosphere, 55, 1189–1196. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.01.024.
Wu, F., Deng, N. S., & Hua, H. L. (2000). Degradation mechanism of azo dye C. I. reactive red 2 by iron powder reduction and photooxidation in aqueous solutions. Chemosphere, 41, 1233–1238. DOI: 10.1016/s0045-6535(99)00538-x.
Zodi, S., Merzouk, B., Potier, O., Lapicque, F., & Leclerc, J. P. (2013). Direct red 81 dye removal by a continuous flow electrocoagulation/flotation reactor. Separation and Purification Technology, 108, 215–222. DOI: 10.1016/j.seppur.2013.01.052.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sürme, Y., Demirci, O.B. Determination of direct violet 51 dye in water based on its decolorisation by electrochemical treatment. Chem. Pap. 68, 1491–1497 (2014). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-014-0616-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-014-0616-9