Abstract
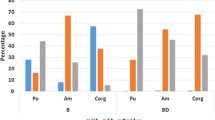
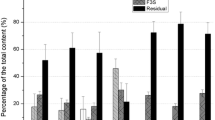
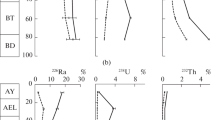
A sequential extraction procedure was used to study the changes in the physicochemical forms of americium (Am), thorium (Th), and uranium (U) in laboratory-contaminated Chernozem soil as a result of sharp variations of the environmental temperature and soil moisture. The influence of freezing and soil drought on the radio-ecological hazard was evaluated three months after radioactive contamination with aqueous solutions of 241Am, 234Th, and U. The subsequent changes in the physicochemical forms of the actinides, caused by sharp increases in the environmental temperature and soil moisture, were examined for one month. The data showed that continuous freezing increased the potentially mobile forms of Am and Th but had the opposite effect on U. Prolonged soil drought did not influence the fractionation of Am and Th but led to the redistribution of U between the carbonates and organic matter and caused its immobilisation. The sharp increase in the temperature of the frozen soil caused the immobilisation of Am and Th and increased the potential mobility of U. The warming and enhanced humidity of the dry soil led to the immobilisation of Am and redistribution of U between the soil phases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ATSDR (1990). Toxicological profile for thorium. Atlanta, GA, USA: Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry, U.S. Public Health Service.
ATSDR (2004). Toxicological profile for americium. Atlanta, GA, USA: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry.
Boyle, R.W. (Ed.) (1982). Geochemical prospecting for thorium and uranium deposits (Series: Developments in economic geology, Vol. 16). Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Elsevier.
Choppin, G. R. (2005). Actinide science: Fundamental and environmental aspects. Journal of Nuclear and Radiochemical Sciences, 6, 1–5.
Degueldre, C., Ulrich, H. J., & Silby, H. (1994). Sorption of 241Am onto montmorillonite, illite and hematite colloids. Radiochimica Acta, 65, 173–179.
Dowdall, M., Standring, W., Shaw, G., & Strand, P. (2008). Will global warming affect soil-to-plant transfer of radionuclides? Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 99, 1736–1745. DOI: 10.1016/j.jenvrad.2008.06.012.
Fedorov, A. A., & Basistyi, V. P. (1974). Winter freezing and chemical properties of meadow brown soils. Sibirski Vestnik Sel'shokhozyaistvennoi Nauki, 4, 8–12.
Glaus, M. A., Hummel, W., & Van Loon, L. R. (1995). Stability of mixed-ligand complexes of metal ions with humic substances and low molecular weight ligands. Environmental Science and Technology, 29, 2150–2153. DOI: 10.1021/es00008a039.
Hallet, B. (1976). Deposits formed by subglacial precipitation of CaCO3. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 87, 1003–1015. DOI: 10.1130/0016-7606(1976)87〈1003:DFBSPO〉2.0.CO;2.
Hlavay, J., Prohaska, T., Weisz, M., Wenzel, W. W., & Stingeder, G. J. (2004). Determination of trace elements bound to soil and sediment fractions (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure and Applied Chemistry, 76, 415–442. DOI: 10.1351/pac200476020415.
Koch-Steindl, H., & Pröhl, G. (2001). Considerations on the behaviour of long-lived radionuclides in the soil. Radiation and Environmental Biophysics, 40, 93–104. DOI: 10.1007/s004110100098.
Lehrsch, G. A., Sojka, R. E., Carter, D. L., & Jolley, P. M. (1991). Freezing effects on aggregate stability affected by texture, mineralogy, and organic matter. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 55, 1401–1406. DOI: 10.2136/sssaj1991.03615995005500050033x.
Marion, G. M. (1995). Freeze-thaw processes and soil chemistry. Special report 95-12. Washington, DC, USA: US Army Corps of Engineers, Cold Regions Research & Engineering Laboratory.
Marquardt, C. M. (Ed.) (2008). Migration of actinides in the system clay, humic substances, aquifer. Wissenschaftliche Berichte, FZKA 7407. Karlsruhe, Germany: Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe GmbH.
Ren, X., Wang, S., Yang, S., & Li, J. (2010). Influence of contact time, pH, soil humic/fulvic acids, ionic strength and temperature on sorption of U(VI) onto MX-80 bentonite. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 283, 253–259. DOI: 10.1007/s10967-009-0323-0.
Schmitt, A., Glaser, B., Borken, W., & Matzner, E. (2008). Repeated freeze-thaw cycles changed organic matter quality in a temperate forest soil. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 171, 707–718. DOI: 10.1002/jpln.200700334.
Schultz, M. K., Burnett, W. C., & Inn, K. G. W. (1998). Evaluation of a sequential extraction method for determining actinide fractionation in soils and sediments. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 40, 155–174. DOI: 10.1016/s0265-931x(97)00075-1.
Ure, A. M., Quevauviller, P., Muntau, H., & Griepink, B. (1993). Speciation of heavy metals in soils and sediments. An account of the improvement and harmonization of extraction techniques undertaken under the auspices of the BCR of the Commission of the European Communities. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 51, 135–151. DOI: 10.1080/03067319308027619.
Wong, S. C., Li, X. D., Zhang, G., Qi, S. H., & Min, Y. S. (2002). Heavy metals in agricultural soils of the Pearl River Delta, South China. Environmental Pollution, 119, 33–44. DOI: 10.1016/s0269-7491(01)00325-6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kovacheva, P., Mitsiev, S. & Djingova, R. Physicochemical fractionation of americium, thorium, and uranium in Chernozem soil after sharp temperature change and soil drought. Chem. Pap. 68, 336–341 (2014). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-013-0457-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-013-0457-y