Abstract
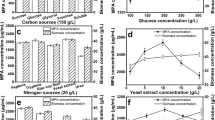
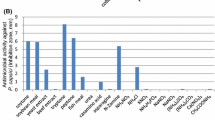
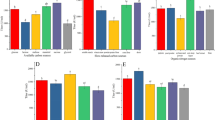
The production of antimicrobial metabolites by Paenibacillus polymyxa RNC-D was assessed. Two process variables, glucose and inoculum concentrations, were evaluated at different levels (5–40 g L−1, and at φ r = 2.5–5.0 %, respectively), and their effects on biomass formation, minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) against Escherichia coli, and surface tension reduction (STR) were studied. When the fermentation process was carried out under non-optimised conditions, the biomass, MIC, and STR achieved the following values: 0.6 g L−1, 1 g L−1, and 18.4 mN m−1, respectively. The optimum glucose (16 g L−1) and inoculum volume ratio (φ r = 5.0 %) were defined in order to maximise the biomass formation, with a low value of MIC and high STR of extract. The experiments carried out under optimal conditions showed the following values for the dependent variables: biomass concentration 2.05 g L−1, MIC 31.2 μg mL−1, and STR 10.7 mN m−1, which represented improvement of 241.7 %, 96.9 %, and 41.9 % for the responses of biomass, MIC, and STR, respectively. This is the first recorded study on the optimisation of culture conditions for the production of antimicrobial metabolites of P. polymyxa RNC-D, and constitutes an important step in the development of strategies to modulate the production of antimicrobial molecules by this microorganism at elevated levels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adinarayana, K., Prabhakar, T., Srinivasulu, V., Anitha Rao, M., Jhansi Lakshmi, P., & Ellaiah, P. (2003). Optimization of process parameters for cephalosporin C production under solid state fermentation from Acremonium chrysogenum. Process Biochemistry, 39, 171–177. DOI: 10.1016/s0032-9592(03)00049-9.
Gogoi, D. K., Mazumder, S., Saikia, R., & Bora, T. C. (2008). Impact of submerged culture conditions on growth and bioactive metabolite produced by endophyte Hypocrea spp. NSF-08 isolated from Dillenia indica Linn. in North-East India. Journal de Mycologie Médicale/Journal of Medical Mycology, 18, 1–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.mycmed.2007.10.006.
Ito, M., & Koyama, Y. (1972a). Jolipeptin, a new peptide antibiotic. I. Isolation, physico-chemical and biological characteristics. The Journal of Antibiotics, 25, 304–308. DOI: 10.7164/antibiotics.25.304.
Ito, M., & Koyama, Y. (1972b). Jolipeptin, a new peptide antibiotic. II. The mode of action of jolipeptin. The Journal of Antibiotics, 25, 309–314. DOI: 10.7164/antibiotics.25.309.
Kajimura, Y., & Kaneda, M. (1996). Fusaricidin A, a new depsipeptide antibiotic produced by Bacillus polymyxa KT-8. Taxonomy, fermentation, isolation, structure elucidation and biological activity. The Journal of Antibiotics, 49, 129–135. DOI: 10.7164/antibiotics.49.129.
Kajimura, Y., & Kaneda, M. (1997). Fusaricidins B, C, and D, new depsipeptide antibiotics produced by Bacillus polymyxa KT-8: Isolation, structure elucidation and biological activity. The Journal of Antibiotics, 50, 220–228. DOI: 10.7164/antibiotics.50.220.
Katz, E., & Demain, A. L. (1977). The peptide antibiotics of Bacillus: chemistry, biogenesis, and possible functions. Bacteriology Reviews, 41, 449–474.
Lam, K. S., Mattei, J., & Forenza, S. (1989). Carbon catabolite regulation of rebeccamycin production in Saccharothrix aerocolonigenes. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 4, 105–108. DOI: 10.1007/bf01569794.
Mussatto, S. I., & Roberto, I. C. (2008). Establishment of the optimum initial xylose concentration and nutritional supplementation of brewer’s spent grain hydrolysate for xylitol production by Candida guilliermondii. Process Biochemistry, 43, 540–546. DOI: 10.1016/j.procbio.2008.01.013.
Nakajima, N., Chihara, S., & Koyama, Y. (1972). A new antibiotic, gatavalin. I. Isolation and characterization. The Journal of Antibiotics, 25, 243–247. DOI: 10.7164/antibiotics.25.243.
National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards (2002). Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing (12th Informational supplement). Wayne, PA, USA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. (M100-S12)
Pichard, B., Larue, J. P., & Thouvenot, D. (1995). Gavaserin and saltavalin, new peptide antibiotics produced by Bacillus polymyxa. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 133, 215–218. DOI: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1995.tb07887.x.
Ratti, R. P., Serrano, N. F. G., Hokka, C. O., & Sousa, C. P. (2008). Antagonistic properties of some microorganisms isolated from Brazilian tropical savannah plants against Staphylococcus coagulase-positive strain. Journal of Venomous Animals and Toxins Including Tropical Diseases, 14, 294–302. DOI: 10.1590/s1678-91992008000200007.
Raza, W., Wu, H. S., & Shen, Q. R. (2010). Use of response surface methodology to evaluate the effect of metal ions (Ca2+, Ni2+, Mn2+, Cu2+) on production of antifungal compounds by Paenibacillus polymyxa. Bioresource Technology, 101, 1904–1912. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2009.10.029.
Rodrigues, L. R., Teixeira, J. A., van der Mei, H. C., & Oliveira, R. (2006). Isolation and partial characterization of a biosurfactant produced by Streptococcus thermophilus A. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 53, 105–112. DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2006.08.009.
Santos, J. C., Mussatto, S. I., Cunha, M. A. A., & Silva, S. S. (2005). Variables that affect xylitol production from sugarcane bagasse hydrolysate in a zeolite fluidized bed reactor. Biotechnology Progress, 21, 1639–1643. DOI: 10.1021/bp050219n.
Schulz, B., Boyle, C., Draeger, S., Römmert, A. K., & Krohn, K. (2002). Endophytic fungi: a source of novel biologically active secondary metabolites. Mycological Research, 106, 996–1004. DOI: 10.1017/s0953756202006342.
Shen, J., Lu, Z.X., Bie, X.M., Lü, F. X., & Huang, X. Q. (2005). Media optimization for the novel antimicrobial peptide by Bacillus sp. fmbJ224. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 21, 609–614. (in Chinese)
Sogn, J. A. (1976). Structure of the peptide antibiotic polypeptin. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 19, 1228–1231. DOI: 10.1021/jm00232a012.
Strobel, G., Daisy, B., Castillo, U., & Harper, J. (2004). Natural products from endophytic microorganisms. Journal of Natural Products, 67, 257–268. DOI: 10.1021/np030397v.
Wang, Z. W., & Liu, X. L. (2008). Medium optimization for antifungal active substances production from a newly isolated Paenibacillus sp. using response surface methodology. Bioresource Technology, 99, 8245–8251. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2008.03.039.
Wang, X., Huang, L., Kang, Z., Buchenauer, H., & Gao, X. (2010). Optimization of the fermentation process of Actinomycete strain Hhs.015T. Journal of Biomedicine and Biotechnology, 2010, 141876. DOI: 10.1155/2010/141876.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Serrano, N.F.G., Rodrigues, L., Hokka, C.O. et al. Optimal glucose and inoculum concentrations for production of bioactive molecules by Paenibacillus polymyxa RNC-D. Chem. Pap. 66, 1111–1117 (2012). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-012-0242-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-012-0242-3