Abstract
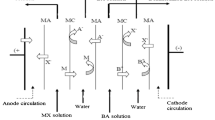
Batch electrodialysis of aqueous solutions of oxalic acid was investigated using a laboratory electrodialyzer ED-Z mini equipped with ion-exchange membranes Ralex-AMH-PES and Ralex-CMHPES (Mega, Stráž pod Ralskem, Czech Republic). The paper presents a mathematical model which enables to predict changes in the oxalic acid concentrations in the diluate and concentrate compartments during the electrodialysis process under various conditions specified by combinations of the initial acid concentrations with current densities. The calculation proved a good agreement between the developed model and the experimental results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buck, R. P. (1984). Kinetics of bulk and interfacial ionic motion: microscopic bases and limits of the Nernst-Planck equation applied to membrane systems. Journal of Membrane Science, 17, 1–62. DOI: 10.1016/s0376-7388(00)81386-1.
Cwirko, E. H., & Carbonell, R. G. (1992). Ionic equilibria in ion-exchange membranes: a comparison of pore model predictions with experimental results. Journal of Membrane Science, 67, 211–226. DOI: 10.1016/0376-7388(92)80026-g.
Dube, S. K., Vasudevan, P., & Khandelwal, B. (1982). Oxalic acid manufacture. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 32, 909–919.
Kirk, R. E., & Othmer, D. F. (1984). Encyclopaedia of chemical technology (3rd ed.). New York, NY, USA: Wiley.
Kraaijeveld, G., Sumberova, V., Kuindersma, S., & Wesselingh, H. (1995). Modelling electrodialysis using the Maxwell-Stefan description. The Chemical Engineering Journal and the Biochemical Engineering Journal, 57, 163–176. DOI: 10.1016/0923-0467(94)02940-7.
Michaeli, L., Kedem, O. (1961). Description of the transport of solvent and ions through membranes in terms of differential coefficients. Part I. Phenomenological characterization of flows. Transactions of the Faraday Society, 57, 1185–1190. DOI: 10.1039/tf9615701185.
Nikonenko, V., Zabolotsky, V., Larchet, C., Auclair, B., & Pourcelly, G. (2002). Mathematical description of ion transport in membrane systems. Desalination, 147, 369–374. DOI: 10.1016/s0011-9164(02)00611-2.
Perry, R. H., & Green, D. W. (1999). Perry’s Chemical engineers’ handbook. New York, NY, USA: McGraw-Hill.
Strathmann, H. (2004). Ion exchange membrane separation processes (Membrane science and technology series, Vol. 9). Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Elsevier.
Tanaka, Y. (2007). Ion exchange membranes: Fundamentals and applications (Membrane science and technology series, Vol. 12). Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Elsevier.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaláb, J., Palatý, Z. Electrodialysis of oxalic acid: batch process modeling. Chem. Pap. 66, 1118–1123 (2012). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-012-0232-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-012-0232-5