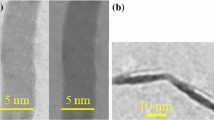
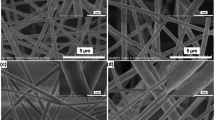
Abstract
Polyaniline (PANI) nanofibres were synthesised by the chemical oxidative polymerisation method using ammonium peroxydisulphate (APS) as an oxidant/initiator. In this work, a surfactant-assisted method without shaking and stirring was used for the synthesis of PANI nanofibres. The effect was investigated of various parameters such as monomer/oxidant ratio, polymerisation temperature, and the presence of surfactant (Triton X-100 as a non-ionic surfactant) on the morphology and electrical conductivity of nanofibres. The morphology of PANI nanofibres was characterised by scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. The results demonstrate that the morphology of PANI nanofibres was significantly influenced by the aniline/APS mole ratio, polymerisation temperature and presence of the surfactant during synthesis. The results showed that more regular and consistent nanofibres were obtained using a monomer/oxidant ratio of 4 at ambient temperature of polymerisation. PANI nanofibres with diameters in the range of 10–100 nm and length up to several μm were obtained. PANI nanofibres were also characterised using FTIR and UV-VIS absorption spectroscopy. The electrochemical behaviour of PANI nanofibres was studied by cyclic voltammetry. It was found that the electrical conductivity of PANI nanofibres increased with the increasing monomer/oxidant ratio and decreasing polymerisation temperature, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ansari, R., & Mosayebzadeh, Z. (2011). Application of polyaniline as an efficient and novel adsorbent for azo dyes removal from textile wastewaters. Chemical Papers, 65, 1–8. DOI: 10.2478/s11696-010-0083-x.
Carswell, A. D. W., O’Rear, E. A., & Grady, B. P. (2003). Adsorbed surfactants as templates for the synthesis of morphologically controlled polyaniline and polypyrrole nanostructures on flat surfaces: From spheres to wires to flat films. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 125, 14793–14800. DOI: 10.1021/ja0365983.
Chiou, N. R., & Epstein, A. J. (2005). Polyaniline nanofibers prepared by dilute polymerization. Advanced Materials, 17, 1679–1683. DOI: 10.1002/adma.200401000.
Du, X. S., Zhou, C. F., & Mai, Y. W. (2008). Facile synthesis of hierarchical polyaniline nanostructures with dendritic nanofibers as scaffolds. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 112, 19836–19840. DOI: 10.1021/jp8069404.
Goel, S., Gupta, A., Singh, K. P., Mehrotra, R., & Kandpal, H. C. (2007). Optical studies of polyaniline nanostructures. Materials Science and Engineering A, 443, 71–76. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2006.08.035.
He, C., Tan, Y., & Li, Y. (2003). Conducting polyaniline nanofiber networks prepared by the doping induction of camphor sulfonic acid. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 87, 1537–1540. DOI: 10.1002/app.11599.
Huang, H. M., Li, Z. Y., & Wang, C. (2007). An electrospinning approach to polyaniline nanofibers by template. Solid State Phenomena, 121–123, 579–582. DOI: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/ssp.121-123.579.
Huang, J., & Kaner, R. B. (2004). A general chemical route to polyaniline nanofibers. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 126, 851–855. DOI: 10.1021/ja0371754.
Jing, X., Wang, Y., Wu, D., & Qiang, J. (2007). Sonochemical synthesis of polyaniline nanofibers. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 14, 75–80. DOI: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2006.02.001.
Konyushenko, E. N., Trchová, M., Stejskal, J., & Sapurina, I. (2010). The role of acidity profile in the nanotubular growth of polyaniline. Chemical Papers, 64, 56–64. DOI: 10.2478/s11696-009-0101-z.
Li, D., & Kaner, R. B. (2006). Shape and aggregation control of nanoparticles: Not shaken, not stirred. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 128, 968–975. DOI: 10.1021/ja056609n.
Li, G., Zhang, C., Li, Y., Peng, H., & Chen, K. (2010). Rapid polymerization initiated by redox initiator for the synthesis of polyaniline nanofibers. Polymer, 51, 1934–1939. DOI: 10.1016/j.polymer.2010.03.004.
Li, G., & Zhang, Z. (2004). Synthesis of dendritic polyaniline nanofibers in a surfactant gel. Macromolecules, 37, 2683–2685. DOI: 10.1021/ma035891k.
Li, X., Zhuang, T., Wang, G., & Zhao, Y. (2008). Stabilizer-free conducting polyaniline nanofiber aqueous colloids and their stability. Materials Letters, 62, 1431–1434. DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2007.08.078.
Liu, J. M., & Yang, S. C. (1991). Novel colloidal polyaniline fibrils made by template guided chemical polymerization. Journal of the Chemical Society, Chemical Communications, 1991, 1529–1531. DOI: 10.1039/c39910001529.
Marjanović, B., Juranić, I., Mentus, S., Ćirić-Marjanović, G., & Holler, P. (2010). Oxidative polymerization of anilinium 5-sulfosalicylate with peroxydisulfate in water. Chemical Papers, 64, 783–790. DOI: 10.2478/s11696-010-0064-0.
Martin, C. R. (1996). Membrane-based synthesis of nanomaterials. Chemistry of Materials, 8, 1739–1746. DOI: 10.1021/cm960166s.
Pillalamarri, S. K., Blum, F. D., Tokuhiro, A. T., Story, J. G., & Bertino, M. F. (2005). Radiolytic synthesis of polyaniline nanofibers: A new templateless pathway. Chemistry of Materials, 17, 227–229. DOI: 10.1021/cm0488478.
Qiang, J., Yu, Z., Wu, H., & Yun, D. (2008). Polyaniline nanofibers synthesized by rapid mixing polymerization. Synthetic Metals, 158, 544–547. DOI: 10.1016/j.synthmet.2008.03.023.
Qiu, H., Qi, S., Wang, D., Wang, J., & Wu, X. (2010). Synthesis of polyaniline nanostructures via soft template of sucrose octaacetate. Synthetic Metals, 160, 1179–1183. DOI: 10.1016/j.synthmet.2010.03.005.
Rahy, A., Sakrout, M., Manohar, S., Cho, S. J., Ferraris, J., & Yang, D. J. (2008). Polyaniline nanofiber synthesis by co-use of ammonium peroxydisulfate and sodium hypochlorite. Chemistry of Materials, 20, 4808–4814. DOI: 10.1021/cm703678m.
Rahy, A., & Yang, D. J. (2008). Synthesis of highly conductive polyaniline nanofibers. Materials Letters, 62, 4311–4314. DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2008.06.057.
Sarno, D. M., Manohar, S. K., & MacDiarmid, A. G. (2005). Controlled interconversion of semiconducting and metallic forms of polyaniline nanofibers. Synthetic Metals, 148, 237–243. DOI: 10.1016/j.synthmet.2004.09.038.
Stejskal, J., Sapurina, I., & Trchová, M. (2010). Polyaniline nanostructures and the role of aniline oligomers in their formation. Progress in Polymer Science, 35, 1420–1481. DOI: 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2010.07.006.
Su, B., Tong, Y., Bai, J., Lei, Z., Wang, K., Mu, H., & Dong, N. (2007). Acid doped polyaniline nanofibers synthesized by interfacial polymerization. Indian Journal of Chemistry, 46A, 595–599.
Subramania, A., & Devi, S. L. (2008). Polyaniline nanofibers by surfactant-assisted dilute polymerization for supercapacitor applications. Polymers for Advanced Technologies, 19, 725–727. DOI: 10.1002/pat.1016.
Wang, J., Wang, J., Yang, Z., Wang, Z., Zhang, F., & Wang, S. (2008). A novel strategy for the synthesis of polyaniline nanostructures with controlled morphology. Reactive and Functional Polymers, 68, 1435–1440. DOI: 10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2008.07.002.
Weng, S., Lin, Z., Chen, L., & Zhou, J. (2010). Electrochemical synthesis and optical properties of helical polyaniline nanofibers. Electrochimica Acta, 55, 2727–2733. DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2009.12.032.
Wu, C. G., & Bein, T. (1994). Conducting polyaniline filaments in a mesoporous channel host. Science, 264, 1757–1759. DOI: 10.1126/science.264.5166.1757.
Xing, S., Zhao, C., Jing, S., & Wang, Z. (2006). Morphology and conductivity of polyaniline nanofibers prepared by ’seeding’ polymerization. Polymer, 47, 2305–2313. DOI: 10.1016/j.polymer.2006.02.008.
Xing, S., Zheng, H., & Zhao, G. (2008). Preparation of polyaniline nanofibers via a novel interfacial polymerization method. Synthetic Metals, 158, 59–63. DOI: 10.1016/j.synthmet.2007.12.004.
Yang, C. H., Chih, Y. K., Cheng, H. E., & Chen, C. H. (2005). Nanofibers of self-doped polyaniline. Polymer, 46, 10688–10698. DOI: 10.1016/j.polymer.2005.09.044.
Zhang, X., Chan-Yu-King, R., Jose, A., & Manohar, S. K. (2004). Nanofibers of polyaniline synthesized by interfacial polymerization. Synthetic Metals, 145, 23–29. DOI: 10.1016/j.synthmet.2004.03.012.
Zhang, C., Li, G., & Pengn, H. (2009). Large-scale synthesis of self-doped polyaniline nanofibers. Materials Letters, 63, 592–594. DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2008.11.041.
Zhang, X., & Manohar, S. K. (2004). Polyaniline nanofibers: chemical synthesis using surfactants. Chemical Communications, 2004, 2360–2361. DOI: 10.1039/b409309g.
Zhao, W., Ma, L., & Lu, K. (2007). Facile synthesis of polyaniline nanofibers in the presence of polyethylene glycol. Journal of Polymer Research, 14, 1–4. DOI: 10.1007/s10965-006-9069-3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Olad, A., Ilghami, F. & Nosrati, R. Surfactant-assisted synthesis of polyaniline nanofibres without shaking and stirring: effect of conditions on morphology and conductivity. Chem. Pap. 66, 757–764 (2012). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-012-0197-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-012-0197-4