Abstract
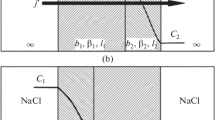
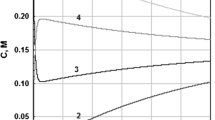
A model of diffusive transport of benzoic acid through a liquid membrane (LM) separating two aqueous solutions, based on diffusion layers and the assumption of a steady state, has been developed and tested using experimental results. It has been found that a model with the apparent partition coefficient dependent on the concentration is able to describe the time dependence of acid concentration in LM with and without a maximum on that dependence. The quality of the model fit with the single apparent diffusion coefficient of benzoic acid is the same as the one which takes into account the diffusion of benzoic acid in different forms (undissociated and dissociated form in aqueous phase, monomer and dimer in organic phase); however, in the second case, the model becomes overparameterized. Assuming that the partition and diffusion coefficients are constant, the diffusion layer model corresponds to the model of reversible consecutive reactions. Analytical solution for such case is given. Apart from the partition equilibrium, also kinetics of partitioning was considered. It was shown that in some basic situations both cases yield identical results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alpoguz, H. K., Memon, S., Ersoz, M., & Yilmaz, M. (2002). Transport of Hg2+ through bulk liquid membrane using a bis-calix[4]arene nitrile derivative as carrier: kinetic analysis. New Journal of Chemistry, 26, 477–480. DOI: 10.1039/B106225P.
Blahušiak, M., Schlosser, Š., & Marták, J. (2010). Simulation of a hybrid fermentation-separation process for production of butyric acid. Chemical Papers, 64, 213–222. DOI: 10.2478/s11696-009-0114-7.
Danesi, P. R., & Cianetti, C. (1984). Multistage separation of metal ions with a series of composite supported liquid membranes. Journal of Membrane Science, 20, 215–226. DOI: 10.1016/S0376-7388(00)81333-2.
Jönsson, J. Å. (2009). Membrane extraction in preconcentration, sampling, and trace analysis. In A. K. Pabby, S. S. H. Rizvi, & A. M. Sastre (Eds.), Handbook of membrane separations. Chemical, pharmaceutical, food, and biotechnological applications. Boca Raton, FL, USA: CRC Press.
Kobya, M., Topçu, N., & Demircioğlu, N. (1997). Kinetic analysis of coupled transport of thiocyanate ions through liquid membranes at different temperatures. Journal of Membrane Science, 130, 7–15. DOI: 10.1016/S0376-7388(96)00348-1.
Koryta, J., Dvořák, J., & Boháčková, V. (1980). Electrochemistry. Warszawa, Poland: PWN. (in Polish)
León, G., de los Santos, R., & Guzmán, M. A. (2004). Reduction of sodium and chloride ion content in aqueous solutions by bulk liquid membranes: a kinetic approach, Desalination, 168, 271–275. DOI: 10.1016/j.desal.2004.07.008.
Long, B., Wang, Y., & Yang, Z. (2008). Partition behaviour of benzoic acid in (water + n-dodecane) solutions at T = (293.15 and 298.15) K. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 40, 1565–1568. DOI: 10.1016/j.jct.2008.06.014.
Ma, M., He, D., Wang, Q., & Xie, Q. (2001). Kinetics of europium( III) transport through a liquid membrane containing HEH(EHP) in kerosene. Talanta, 55, 1109–1117. DOI: 10.1016/S0039-9140(01)00525-2.
Makino, K., Ohshima, H., & Kondo, T. (1990). Kinetic model for membrane transport: 1. Effects of membrane volume and partitioning kinetics. Biophysical Chemistry, 35, 85–95. DOI: 10.1016/0301-4622(90)80063-D.
Marták, J., Schlosser, Š., & Vlčková, S. (2008). Pertraction of lactic acid through supported liquid membranes containing phosphonium ionic liquid. Journal of Membrane Science, 318, 298–310. DOI: 10.1016/j.memsci.2008.02.064.
Saf, A. Ö., Alpaydin, S., & Sirit, A. (2006). Transport kinetics of chromium(VI) ions through a bulk liquid membrane containing p-tert-butyl calix[4]arene 3-morpholino propyl diamide derivative. Journal of Membrane Science, 283, 448–455. DOI: 10.1016/j.memsci.2006.07.023.
Szpakowska, M., & Nagy, O. B. (1991). Membrane material effect on copper coupled transport through liquid membranes. Journal of Membrane Science, 64, 129–143. DOI: 10.1016/0376-7388(91)80084-J.
Tyn, M. T., & Calus, W. F. (1975). Diffusion coefficients in dilute binary liquid mixtures. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 20, 106–109. DOI: 10.1021/je60064a006.
Yang, X.-N., & Matthews, M. A. (2000). Diffusion coefficients of three organic solutes in aqueous sodium dodecyl sulfate solutions. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 229, 53–61. DOI: 10.1006/jcis.2000.7020.
Zhang, W., Liu, J., Ren, Z., Wang, S., Du, C., & Ma, J. (2009). Kinetic study of chromium(VI) facilitated transport through a bulk liquid membrane using tri-n-butyl phosphate as carrier. Chemical Engineering Journal, 150, 83–89. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2008.12.009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koter, S., Szczepański, P. Modeling of diffusive transport of benzoic acid through a liquid membrane. Chem. Pap. 65, 584–595 (2011). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-011-0010-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-011-0010-9