Abstract
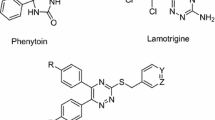
Lamotrigine (LTG) is an antiepileptic drug used for the prevention of convulsions. Except several known side effects, hepatic dysfunction is also reported. Hepatotoxic side effects occur due to the dichlorophenyl moiety which develops an abnormally low level of glutathione. Depletion of glutathione causes oxidative stress and hepatic cell damage. The goal of the present study was to test the action and side effects of the three compounds synthesised and compared to LTG. Three amide prodrugs of LTG were synthesised by its reaction with N-acetylamino acids, viz, glycine, glutamic acid, and methionine. Purified synthesised prodrugs were subjected to thin layer chromatography, melting point, solubility and partition coefficients determination and characterised by UV, FTIR, 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy. The synthesised prodrugs were subjected to in vitro hydrolysis and to anticonvulsant and hepatotoxic activity studies. Significant reduction in hepatotoxicity and comparable anticonvulsant activities were obtained in all synthesised prodrugs as compared to LTG.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Attwell, P. J. E., Singh Kent, N., Jane, D. E., Croucher, M. J., & Bradford, H. F. (1998). Anticonvulsant and glutamate release-inhibiting properties of the highly potent metabotropic glutamate receptor agonist (2S,2′R,3′R)-2-(2′,3′-dicarboxycyclopropyl)glycine (DCG-IV). Brain Research, 805, 138–143. DOI: 10.1016/S0006-8993(98)00698-2.
Barbosa, N. R., & Mídio, A. F. (2000). Validated highperformance liquid chromatographic method for the determination of lamotrigine in human plasma. Journal of Chromatography B, 741, 289–293. DOI: 10.1016/S0378-4347(00)00102-X.
Dakin, H. D. (1929). The condensation of aromatic aldehydes with glycine and acetylglycine. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, LXXXII, 439–446.
du Vigneaud, V., Kilmer, G. W., Rachele, J. R., & Cohn, M. (1944). On the mechanism of the conversion in vivo of methionine to cystine. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 155, 645–651.
Fayad, M., Choueiri, R., & Mikati, M. (2000). Potential hepatotoxicity of lamotrigine. Pediatric Neurology, 22, 49–52. DOI: 10.1016/S0887-8994(99)00106-X.
GraphPad Software, Inc. (2009). GraphPad Prism, Version 5.0 for Windows. La Jolla, CA, USA: GraphPad Software, Inc.
Maggs, J. L., Naisbitt, D. J., Tettey, J. N. A., Pirmohamed, M., & Park, B. K. (2000). Metabolism of lamotrigine to a reactive arene oxide intermediate. Chemical Research in Toxicology, 13, 1075–1081. DOI: 10.1021/tx0000825.
Makin, A. J., Fitt, S., & Williams, R. (1995). Fulminant hepatic failure induced by lamotrigine. British Medical Journal, 311, 292.
May, T. W., Rambeck, B., & Jürgens, U. (1996). Serum concentrations of lamotrigine in epileptic patients: the influence of dose and comedication. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring, 18, 523–531. DOI: 10.1097/00007691-199610000-00001.
Meshkibaf, M. H., Ebrahimi, A., Ghodsi, R., & Ahmadi, A. (2006). Chronic effects of lamotrigine on liver function in adult male rats. Indian Journal of Clinical Biochemistry, 21, 161–164. DOI: 10.1007/BF02913087.
Moeller, K. E., Wei, L., Jewell, A. D., & Carver, L. A. (2008). Acute hepatotoxicity associated with lamotrigine. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 165, 539–540. DOI: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2007.07050728.
Nam, N.-H., Kim, Y., You, Y.-J., Hong, D.-H., Kim, H.-M., & Ahn, B.-Z. (2003). Water soluble prodrugs of the antitumor agent 3-[(3-amino-4-methoxy)phenyl]-2-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)cyclopent-2-ene-1-one. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 11, 1021–1029. DOI: 10.1016/S0968-0896(02)00514-X.
Nedelcheva, V. Gut, I., Souček, P., & Frantík, E. (1998). Cytochrome P450 catalyzed oxidation of monochlorobenzene, 1,2- and 1,4-dichlorobenzene in rat, mouse, and human liver microsomes. Chemico-Biological Interactions, 115, 53–70. DOI: 10.1016/S0009-2797(98)00058-1.
Overstreet, K., Costanza, C., Behling, C., Hassanin, T., & Masliah, E. (2002). Fatal progressive hepatic necrosis associated with lamotrigine treatment: A case report and literature review. Digestive Diseases and Sciences, 47, 1921–1925. DOI: 10.1023/A:1019627618972.
Pugazhendhy, S., Shrivastava, P. K., Sinha, S. K., & Shrivastava, S. K. (2010). Lamotrigine-dextran conjugatessynthesis, characterization, and biological evaluation. Medicinal Chemistry Research, Online First, 24 May 2010. DOI: 10.1007/s00044-010-9355-9.
San-Miguel, B., Alvarez, M., Culebras, J. M., González-Gallego, J., & Tuñón, M. J. (2006). N-acetyl-cysteine protects liver from apoptotic death in an animal model of fulminant hepatic failure. Apoptosis, 11, 1945–1957. DOI: 10.1007/s10495-006-0090-0.
Santos, N. A. G., Medina, W. S. G., Martins, N. M., Carvalho Rodrigues, M. A., Curti, C., & Santos, A. C. (2008). Involvement of oxidative stress in the hepatotoxicity induced by aromatic antiepileptic drugs. Toxicology in Vitro, 22, 1820–1824. DOI: 10.1016/j.tiv.2008.08.004.
Sauvé, G., Bresson-Hadni, S., Prost, P., Le Calvez, S., Becker, M.-C., Galmiche, J., Carbillet, J.-P., & Miguet, J.-P. (2000). Acute hepatitis after lamotrigine administration. Digestive Diseases and Sciences, 45, 1874–1877. DOI: 10.1023/A:1005593119425.
Serwetman, L. R. C., Krikorian, S. A., & Javedan, H. (2008). Rash and liver dysfunction related to lamotrigine therapy. The Journal of Pharmacy Technology, 24, 17–21.
Shorvon, S., & Stefan, H. (1997). Overview of the safety of newer antiepileptic drugs. Epilepsia, 38, S45–S51. DOI: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1997.tb04519.x.
Siritantikorn, A., Johansson, K., Åhlen, K., Rinaldi, R., Suthiphongchai, T., Wilairat, P., & Morgenstern, R. (2007). Protection of cells from oxidative stress by microsomal glutathione transferase 1. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 355, 592–596. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.02.018.
Tanaka, K., & Kawasaki, Y. (1957). A group of compounds possessing anticonvulsant activity In the maximal electroshock seizure test. The Japanese Journal of Pharmacology, 6, 115–121. DOI: 10.1254/jjp.6.115.
Younis, H. S., Hoglen, N. C., Kuester, R. K., Gunawardhana, L., & Sipes, I. G. (2000). 1,2-Dichlorobenzene-mediated hepatocellular oxidative stress in Fischer-344 and Sprague-Dawley rats. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 163, 141–148. DOI: 10.1006/taap.1999.8860.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sinha, S.K., Shrivastava, P.K. & Shrivastava, S.K. Synthesis, characterisation, and biological activity of three new amide prodrugs of lamotrigine with reduced hepatotoxicity. Chem. Pap. 65, 70–76 (2011). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-010-0094-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-010-0094-7