Abstract
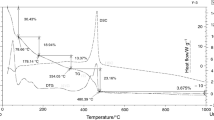
Activated sewage sludge samples obtained from two different waste water treatment plants were investigated by thermogravimetric analysis. Due to a very high content of water in the sludge samples, these had to be dried at 160°C in an electrical oven in order to remove all adsorbed water. To ensure pyrolysis conditions, nitrogen atmosphere was applied. The pyrolysis decomposition process was carried out in the temperature range from ambient temperature to 900°C at three different heating rates: 2 K min−1, 5 K min−1, 10 K min−1. TGA and DTG curves of the decomposition processes were obtained. Temperature of onset decomposition, final temperature of decomposition, maximum decomposition rate, and decomposition temperature were determined by thermogravimetric analysis for both sludge samples used. The main decomposition process takes place at temperatures in the range from 230°C to 500°C. Above this temperature, there are only small changes in the mass loss which are often attributed to the decomposition of carbonates present in the sewage sludge samples. To determine the apparent kinetic parameters such as the activation energy and the preexponential factor, the so called Friedman isoconversional method was used. Because of the requirements of this method, initial and final parts of the decomposition process, where crossings of the decomposition lines occurred, were cut off. Obtained dependencies of the apparent activation energies and preexponential factors as a function of conversion were used backwards to calculate the modeled decomposition process of sewage sludge and the experimental data were in good accordance with the data obtained by simulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biagini, E., Fantei, A., & Tognotti, L. (2008). Effect of the heating rate on the devolatilization of biomass residues. Thermochimica Acta, 472, 55–63. DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2008.03.015.
Bridgwater, A. V. (2004). Biomass fast pyrolysis. Thermal Science, 8(2), 21–49.
Bridgwater, A. V., Toft, A. J., & Brammer, J. G. (2002). A techno-economic comparison of power production by biomass fast pyrolysis with gasification and combustion. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 6, 181–246. DOI: 10.1016/S1364-0321(01)00010-7.
Calvo, L. F., Otero, M., Jenkins, B. M., Garcia, A. I., & Morán, A. (2004). Heating process characteristics and kinetics of sewage sludge in different atmospheres. Thermochimica Acta, 409, 127–135. DOI: 10.1016/S0040-6031(03)00359-9.
Di Blasi, C. (2008). Modeling chemical and physical processes of wood and biomass pyrolysis. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 34, 47–90. DOI: 10.1016/j.pecs.2006.12.001.
Drtil, M., & Hutňan, M. (2007). Technologický projekt: časť procesy a technológie čistenia odpadových vôd (Technological project: processes and waste water cleaning technologies). Bratislava, Slovakia: Vydavatel’stvo NOI. ISBN 978-80-89088-57-7
Folgueras, M. B., Díaz, R. M., Xiberta, J., & Prieto, I. (2003). Thermogravimetric analysis of the co-combustion of coal and sewage sludge. Fuel, 82, 2051–2055. DOI: 10.1016/S0016-2361(03)00161-3.
Fonts, I., Azuara, M., Gea, G., & Murillo, M. B. (2009). Study of the pyrolysis liquids obtained from different sewage sludge. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 85, 184–191. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaap.2008.11.003.
Fytili, D., & Zabaniotou, A. (2008). Utilization of sewage sludge in EU application of old and new methods—A review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 12, 116–140. DOI: 10.1016/j.rser.2006.05.014.
García Barneto, A., Ariza Carmona, J., Martín Alfonso, J. E., & Díaz Blanco, J. (2009). Kinetic models based in biomass components for the combustion and pyrolysis of sewage sludge and its compost. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 86, 108–114. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaap.2009.04.011.
Gašparovič, L., Koreňová, Z., & Jelemenský, Ľ. (2009). Kinetic study of wood chips decomposition by TGA. Chemical Papers, 64, 174–181. DOI: 10.2478/s11696-009-0109-4.
Grønli, M. G., Várhegyi, G., & Di Blasi, C. (2002). Thermogravimetric analysis and devolatilization kinetics of wood. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 41, 4201–4208. DOI: 10.1021/ie0201157.
Ji, A., Zhang, S., Lu, X., & Liu, Y. (2009). A new method for evaluating the sewage sludge pyrolysis kinetics. Waste Management, 30, 1225–1229. DOI: 10.1016/j.wasman.2009.10.003.
Kirch, K., Augenstein, D., Batmale, J. P., Benemann, J., Rutledge, B., & Salour, D. (2005). Biomethane from dairy waste. San Francisco, CA, USA: Sustainable Conservation.
Koreňová, Z., Juma, M., Annus, J., Markoš, J., & Jelemensky, L. (2006). Kinetics of pyrolysis and properties of carbon black from a scrap tire. Chemical Papers, 60, 422–426. DOI: 10.2478/s11696-006-0077-x.
Kumar, A., Wang, L., Dzenis, Y. A., Jones, D. D., & Hanna, M. A. (2008). Thermogravimetric characterization of corn stover as gasification and pyrolysis feedstock. Biomass and Bioenergy, 32, 460–467. DOI: 10.1016/j.biombioe.2007.11.004.
Li, Z., Liu, C., Chen, Z., Qian, J., Zhao, W., & Zhu, Q. (2009). Analysis of coals and biomass pyrolysis using the distributed activation energy model. Bioresource Technology, 100, 948–952. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2008.07.032.
Mohan, D., Pittman, C. U., Jr., & Steele, P. H. (2006). Pyrolysis of wood/biomass for bio-oil: A critical review. Energy & Fuels, 20, 848–889. DOI: 10.1021/ef0502397.
Müller-Hagedorn, M., Bockhorn, H., Krebs, L., & Müller, U. (2003). A comparative kinetic study on the pyrolysis of three different wood species. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 68–69, 231–249. DOI: 10.1016/S0165-2370(03)00065-2.
Munir, S., Daood, S. S., Nimmo, W., Cunliffe, A. M., & Gibbs, B. M. (2009). Thermal analysis and devolatilization kinetics of cotton stalk, sugar cane bagasse and shea meal under nitrogen and air atmospheres. Bioresource Technology, 100, 1413–1418. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2008.07.065.
Nowicki, L., Stolarek, P., Olewski, T., Bedyk, T., & Ledakowicz, S. (2008). Mechanism and kinetics of sewage sludge pyrolysis by thermogravimetry and mass spectrometry analysis. Chemical and Process Engineering, 29, 813–825.
Otero, M., Calvo, L. F., Gil, M. V., García, A. I., & Morán, A. (2008). Co-combustion of different sewage sludge and coal: A non-isothermal thermogravimetric kinetic analysis. Bioresource Technology, 99, 6311–6319. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2007.12.011.
Otero, M., Gómez, X., García, A. I., & Morán, A. (2007). Effects of sewage sludge blending on the coal combustion: A thermogravimetric assessment. Chemosphere, 69, 1740–1750. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.05.077.
Paik, P., & Kar, K. K. (2009). Thermal degradation kinetics and estimation of lifetime of polyethylene particles: Effects of particle size. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 113, 953–961. DOI: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2008.08.075.
Quan, C., Li, A., & Gao, N. (2009). Thermogravimetric analysis and kinetic study on large particles of printed circuit board wastes. Waste Management, 29, 2353–2360. DOI: 10.1016/j.wasman.2009.03.020.
Samtani, M., Dollimore, D., & Alexander, K. S. (2002). Comparison of dolomite decomposition kinetics with related carbonates and the effect of procedural variables on its kinetic parameters. Thermochimica Acta, 392.393, 135–145. DOI: 10.1016/S0040-6031(02)00094-1.
Scott, S. A., Dennis, J. S., Davidson, J. F., & Hayhurst, A. N. (2006). Thermogravimetric measurements of the kinetics of pyrolysis of dried sewage sludge. Fuel, 85, 1248–1253. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2005.11.003.
Šimon, P. (2004). Isoconversional methods: Fundamentals, meaning and application. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 76, 123–132. DOI: 10.1023/B:JTAN.0000027811.80036.6c.
Thipkhunthod, P., Meeyoo, V., Rangsunvigit, P., & Rirksomboon, T. (2007). Describing sewage sludge pyrolysis kinetics by a combination of biomass fractions decomposition. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 79, 78–85 DOI: 10.1016/j.jaap.2006.10.005.
Tsai, W.-T., Chang, J.-H., Hsien, K.-J., & Chang, Y.-M. (2009). Production of pyrolytic liquids from industrial sewage sludges in an induction-heating reactor. Bioresource Technology, 100, 406–412. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2008.06.013.
Wang, G., Li, W., Li, B., & Chen, H. (2008). TG study on pyrolysis of biomass and its three components under syngas. Fuel, 87, 552–558. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2007.02.032.
Xiao, H.-M., Ma, X.-Q., & Lai, Z.-Y. (2009). Isoconversional kinetic analysis of co-combustion of sewage sludge with straw and coal. Applied Energy, 86, 1741–1745. DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2008.11.016.
Yang, H., Yan, R., Chen, H., Lee, D. H., & Zheng, C. (2007). Characteristics of hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin pyrolysis. Fuel, 86, 1781–1788. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2006.12.013.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Presented at the 37th International Conference of the Slovak Society of Chemical Engineering, Tatranské Matliare, 24–28 May 2010.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gašparovič, L., Hrablay, I., Vojteková, Z. et al. Kinetic study of pyrolysis of waste water treatment plant sludge. Chem. Pap. 65, 139–146 (2011). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-010-0081-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-010-0081-z