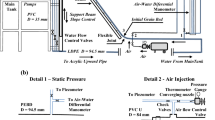
Abstract
Particle horizontal transport and vertical entrainment of widely different materials (silica sand, alumina, ceramsite, dry sludge, and wood shreds) are explored by experimental measurements. Experiments have been performed with two very narrow fractions of solids (0.315–0.50 mm and 1.4–1.6 mm) on a laboratory setup. Simple empirical correlations are proposed in terms of the Reynolds and Archimedes criteria for the commencement of the horizontal conveying as well as the vertical entrainment of particles in pipelines.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ƌ p :
-
mean particle size determined by sieving. m, mm
- g:
-
acceleration due to gravity ( = 9.807 m s−2)
- log:
-
denotes base-ten or Briggsian logarithm
- P:
-
pressure. kPa
- T:
-
thermodynamic temperature. K
- U t :
-
minimum superficial velocity of a gas stream at which particles are entrained upwards. m s−1
- U tr :
-
minimum superficial velocity of a gas stream needed to transport (pickup) solid particles through a horizontal tube m s−1
- µf :
-
fluid (air) viscosity. kg (m s)−1, Pa s
- ρ f :
-
fluid (air) density. kg m−3
- ρ p :
-
particle density kg. m−3
- Ar:
-
Archimedes number ( = ƌ 3p gρ f(ρ p − ρ f)/μ 2f )
- Re t :
-
Reynolds number at gas velocity when particles are just entrained upwards ( = U t ƌ p ρ f/μ f)
- Re tr :
-
Reynolds number at minimum gas velocity needed to transport (pickup) particles through horizontal pipe ( = U tr ƌ p ρ f/μ f)
References
Hartman, M., Svoboda, K., and Trnka, O., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 30, 1855 (1991).
Pohořelý, M., Svoboda, K., and Hartman, M., Powder Technol. 142, 1 (2004).
Pohořelý, M., Svoboda, K., and Hartman, M., Chem. Listy 98, 361 (2004).
Yates, J. G. and Simons, S. J. R., Int. J. Multiphase Flow 20(Suppl.), 297 (1994).
Werther, J., Powder Technol. 102, 15 (1999).
Cabrejos, F. J. and Klincing, G. E., Powder Technol. 72, 51 (1992).
Cabrejos, F. J. and Klincing, G. E., Powder Technol. 79, 173 (1994).
Hayden, K. S., Park, K., and Curtis, J. S., Powder Technol. 131, 7 (2003).
Hubert, M. and Kalman, H., Powder Technol. 134, 156 (2003).
Hartman, M., Trnka, O., and Svoboda, K., Chem. Eng. Sci. 55, 6269 (2000).
Hartman, M., Trnka, O., and Svoboda, K., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 33, 1979 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hartman, M., Phořelý, M. & Trnka, O. Transport velocities of different particulate materials in pneumatic conveying. Chem. Pap. 60, 74–77 (2006). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-006-0015-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-006-0015-y