Abstract
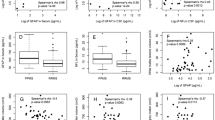
In search of biological marker in multiple sclerosis (MS), total-tau and phospho-tau (Thr181) concentrations were established in CSF and serum of 78 patients with MS, using commercially available kits. Serum and CSF concentrations of IgG, IgM, and albumin were assayed simultaneously to calculate quotients and indices of intrathecal synthesis. Serum t-tau detection was strikingly low (23.1%); therefore, this factor was excluded from further analysis. Serum p-tau levels did not correlate with any of indices or quotients. Unexpectedly, CSF t-tau and p-tau showed an inverse relation with MSSS and EDSS, which has not been published elsewhere. Our results do not support utility of serum t-tau and p-tau as surrogate markers for MS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Stefano N., Matthews P. M., Fu L., Narayanan S., Stanley J., Francis G. S., Antel J. P. et al., Axonal damage correlates with disability in patients with repalsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Results of a longitudinal magnetic resonance spectroscopy study, Brain, 1998; 121, 1469–1477
Roxburgh R. H., Seaman S. R., Masterman T., Hensiek A. E., Sawcer S. J., Vukusic S. et al., Multiple Sclerosis Severity Score: using disability and disease duration to rate disease severity, Neurology, 2005, 64, 1144–1151
Kurtzke J. F., Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: an expanded disability status scale (EDSS), Neurology, 1983, 33, 1444–1452
Pachner A. R., Steiner I., The multiple sclerosis severity score (MSSS) predicts disease severity over time, J. Neurol. Sci., 2009, 278, 66–70
Weingarten M. D., Lockwood A. H., Hwo S-Y., Kirschner M. W., A protein factor essential for microtubule assembly, Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA, 1975, 72, 1858–1862
Trojanowski J. Q., Schuck T., Schmidt M. L., Lee V. M., Distribution of tau proteins in the normal human central and peripheral nervous system, J. Histochem. Cytochem., 1989, 37, 209–215
Avila J., Lucas J. J., Perez M., Hernandez F., Role of tau protein in both physiological and pathological processes. Physiol. Rev., 2004, 84, 361–384
Ibach B., Binder H., Dragon M., Poljansky S., Haen E., Schmitz E., et al., Cerebrospinal fluid tau and β-amyloid in Alzheimer patients, disease controls and an age-matched random sample, Neurobiol. Aging, 2006, 27, 1202–1211
Skinningsrud A., Stenset V., Gundersen A. S., Fladby T., Cerebrospinal fluid markers in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, Cer. Fluid. Res., 2008, 5, 1–8
Süssmuth S. D., Reiber H., Tumani H., Tau protein in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF): a blood-CSF related evaluation in patients with various neurological disease, Neurosci. Lett., 2001, 300, 95–98
Hesse C., Rosengren L., Andreasen N., Davidsson P., Vanderstichele H., Vanmechelen E. et al., Transient increase in total tau but not phospho-tau in human cerebrospinal fluid after acute stroke, Neurosci. Lett., 2001, 297, 187–190
Zelman F. P., Jauch E. C., Mulchahey J. J., Gabbita S. P., Rosenberg W. S., Speciale S. G.et al., C-tau biomarker of neuronal damage is severe brain injured patients: association with elevated intracranial pressure and clinical outocome, Brain Res., 2002, 947, 131–139
Buée L., Bussière T., Buée-Scherrer V., Delacourte A., Hof P. R., Tau protein isoforms, phosphorylation and role in neurodegenerative disorders, Brain Res. Rev., 2000, 33, 95–130
Hernández F., Pérez M., de Barreda E. G., Goñi-Oliver P., Avila J., Tau as a molecular marker of development, aging and neurodegenerative disorders, Curr. Aging Sci., 2008, 1: 56–61
Hein (nee Maier) K., Köhler A., Diem R., Sättler M. B., Demmer I., Lange P. et al., Biological markers for axonal degeneration in CSF and blood of patients with first event indicative for multiple sclerosis, Neurosci. Lett., 2008, 436, 72–76
Reiber H., Proteins in cerebrospinal fluid and blood: barriers, CSF flow rate and source-related dynamics, Rest. Neurol. Neurosci., 2003, 21: 79–96
Polman C. H., Reingold S. C., Edan G., Fillipi M., Hartung H. P., Kappos L. et al., Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2005 revisions to the „McDonald Criteria“, Ann. Neurol., 2005, 58: 840–846
Reiber H., Peter J. B., Cerebrospinal fluid analysis: disease-related data patterns and evaluation programs, J. Neurol. Sci., 2001, 184: 101–122
Jiménez-Jiménez F. J., Zurdo J. M., Hernanz A., Medina-Acebrón S., de Bustos F., Barcenilla B. et al., Tau protein concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with multiple sclerosis, Acta Neurol. Scand., 2002, 106, 351–354
Guimarães J., Cardoso M. J., Sá M. J., Tau protein seems not to be a useful routine clinical marker of axonal damage in multiple sclerosis, Mult. Scler., 2006; 12, 354–356
Valis M., Talab R., Stourac P., Andrys C., Masopust J., Tau protein, phosphorylated tau protein and beta-amyloid42 in the cerebrospinal fluid of multiple sclerosis patients, Neuro. Endocrinol. Lett., 2008, 29, 971–976
Kapaki E., Paraskevas G. P., Michalopoulou M., Kilidireas K., Increased cerebrispinal fluid tau protein in multiple sclerosis, Eur. Neurol., 2000, 43, 228–232
Terzi M., Birinci A., Çetinkaya E., Onar M. K., Cerebrospinal fluid total tau protein levels in patients with multiple sclerosis, Acta Neurol. Scand., 2007, 115, 325–330
Brettschneider J., Maier M., Arda S., Claus A., Süssmuth S. D., Kassubek J. et al., Tau protein level in cerebrospinal fluid is increased in patients with early multiple sclerosis, Mult. Scler., 2005, 11, 261–265
Rostazy K., Withhut E., Pohl D., Lange P., Cisielcyk B., Diem R. et al., Tau, phospho-tau and S-100B in cerebrospinal fluid of children with multiple sclerosis, J. Child. Neurol., 2005, 20, 822–825
Teunissen C. E., Dijkstra C., Polman C., Biological markers in CSF and blood for axonal degeneration in multiple sclerosis, Lancet Neurol., 2005, 4, 32–41
Anderson J. M., Patani R., Reynolds R., Nicholas R., Compston A., Spillantini M. G. et al., Evidence for abnormal tau phosphorylation in early aggressive multiple sclerosis, Acta Neuropathol., 2009, 117, 583–589
Anderson J. M., Hampton D. W., Patani R., Pryce G., Crowther R. A., Reynolds R. et al., Abnormally phosphorylated tau is associated with neuronal and axonal loss in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and multiple sclerosis, Brain, 2008, 131, 1736–48
Andersson M., Alvarez-Cermeño J., Bernardi G., Cogato I., Fredman P., Frederiksen J, Fredrikson S. et al., Cerebrospinal fluid in the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: a consensus report, J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry, 1994, 57, 897–902
Zemlan F. P., Rosenberg W. S., Luebbe P. A., Campbell T. A., Dean G. E., Weiner N. E. et al., Quantification od axonal damage in traumatic brain injury: affinity purification and characterization of cerebrospinal fluid tau proteins, J. Neurochem., 1999, 72, 741–750
Ingelson M., Blomberg M., Benedikz E., Wahlund L-O., Karlsson E., Vanmechelen E. et al., Tau immunoreactivity detected in human plasma, but no obvious increase in dementia, Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord, 1999, 10, 442–445
Bakshi R., Dandamudi Venkata S. R., Neema M., De C., Bermel R. A., Measurement of brain and spinal cord atrophy by magnetic resonance imaging as a tool to monitor multiple sclerosis, J Neuroimaging, 2005, 15, 30S–45S
Jasperse B., Jakobs C., Eikelenboom M. J., Dijkstra C. D., Uitdehaag B. M. J., Barkhoff F. et al., N-acetylaspartic acid in cerebrospinal fluid of multiple sclerosis patients determined by gaschromatography-mass spectrometry, J Neurol, 2007, 254, 631–637
Tenissen C. E., Iacobaeus E., Khademi M., Brundin L., Norgren N., Koel-Simmelink M. J. A. et al., Combination of CSF N-acetylaspartate and neurofilaments in multiple sclerosis, Neurology, 2009, 72, 1322–1329
Compston A., Lassmann H., Smith K., Differences between acute, relapsing and progressive multiple sclerosis, In: Compston A., Confavreux C., Lassmann H., McDonald I., Miller D., Noseworthy J. et al., McAlpine’s Multiple Sclerosis, 4th Ed., Churchill Livingstone Elsevier, Oxford, UK, 2005, 594–596
Ott B. R., Cohen R. A., Gongvatana A., Okonkwo O. C., Johanson C. E., Stopa E. G. et al., Brain ventricular volume and cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease, J Alzheimer Dis, 2010, 20, 647–657
Fagan A. M., Head D., Shah A. R., Marcus D., Mintun M., Morris J. C. et al., Decreased CSF Aβ42 correlates with brain atrophy in cognitively normal elderly, Ann Neurol, 2009, 65, 176–183
Tosun D., Schuff N., Truran-Sacrey D., Shaw L. M., Trojanowski J. Q., Aisen P. et al, Relations between brain tissue loss, CSF biomarkers, and the ApoE genetic profile: a longitudinal study, Neurobiol Aging, 2010, 31, 1340–1354
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Jaworski, J., Psujek, M. & Bartosik-Psujek, H. CSF and serum total-tau and phospho-tau(181P) in MS patients. cent.eur.j.med 6, 193–200 (2011). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11536-011-0003-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11536-011-0003-7