Abstract
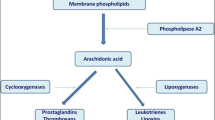
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic, relapsing skin condition that affects over 2% of the population. The pathophysiology of this disease is not completely understood, but immunologic abnormalities and the subsequent release of inflammatory mediators play a central role. Treatment with glucocorticoids has long been the standard of care, but their use is limited by their adverse effect profile. Leukotrienes (LTB4, LTC4, LTD4, and LTE4) are metabolites of arachidonic acid produced through the 5-lipoxygenase pathway. They play an important role in inflammatory and atopic conditions. LT modulating agents have been used with success in asthma. Recently, there has been increased interest in the potential utility of LT antagonists in atopic dermatitis. In vitro and in vivo data have demonstrated that LTs may play a key role in atopic dermatitis. The 2 different types of LT-modulating agents are 5-lipoxygenase inhibitors and LT receptor antagonists. Since the 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor acts at an earlier step in the LT synthetic pathway, it has the ability to alter the production of all the LTs, including LTB4, while the receptor antagonists target only the cysteinyl LTs, LTC4, LTD4, and LTE4. This reduction of LTB4 activity may point to a therapeutic advantage in using LT synthesis inhibitors as opposed to LT receptor antagonists for atopic dermatitis. Clinical evidence of the use of LT agents in atopic dermatitis is limited, but initial results have been promising and these agents may one day serve as corticosteroid-sparing treatments for atopic dermatitis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Champion R.H., Parish W.E. Atopic dermatitis. In: Rook A., Wilkinson D.S., Ebling F.J.G., editors. Textbook of dermatology. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1986: 419–434
Leung D.Y.M., Tharp M., Boguniewicz M. Atopic dermatitis. In: Freedberg I., Eisen A.Z., Wolff K., editors. Fitzpatrick’s dermatology in general medicine. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1999: 1464–1480
Koro O., Furutani K., Hide M., et al. Chemical mediators in atopic dermatitis: involvement of leukotriene B4 released by a type I allergic reaction in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1999 Apr; 103 (4): 663–670
Hanifin J., Chan S.C. Diagnosis and treatment of atopic dermatitis. Dermatol Ther 1996; 1: 9–18
Ikai K., Imamura S. Role of eicosanoids in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 1993 Jun; 48 (6): 409–416
Horwitz R.J., McGill K.A., Busse W.W. The role of leukotriene modifiers in the treatment of asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1998 May; 157 (5 Pt 1): 1363–1371
Busse W.W. Leukotrienes and inflammation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1998 Jun; 157 (6 Pt 2): S210–S213; discussion S247-8
Dahlen S.E. Leukotriene receptors. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 1999 spring–summer; 17 (1–2): 179–191
Songzhu A., Goetzl E.J. Lipid mediators of hypersensitivity and inflammation. In: Middleton E., Ellis E.F., Yunginger J.W., editors. Allergy: principles and practice. St. Louis: Mosby-Year Book, 1998: 168–182 (C14)
Fischer A.R., Drazen J.M. Antileukotriene drugs in the treatment of asthma. In: Middleton E., Ellis E.F., Yunginger J.W., editors. Allergy: principles and practice. St. Louis: Mosby-Year Book, 1998: 678–684 (C49)
McGill K.A., Busse W.W. Zileuton. Lancet 1996 Aug 24; 348 (9026): 519–524
Dahlen B., Zetterstrom O., Bjorck T., et al. The leukotriene-antagonist ICI-204,219 inhibits the early airway reaction to cumulative bronchial challenge with allergen in atopic asthmatics. Eur Respir J 1994 Feb; 7 (2): 324–331
Soter N.A., Lewis R.A., Corey E.J., et al. Local effects of synthetic leukotrienes (LTC4, LTD4, LTE4, and LTB4) in human skin. J Invest Dermatol 1983 Feb; 80 (2): 115–119
Ikai K., Okano H., Sakamoto Y., et al. Leukotriene A4 hydrolase in human skin and peripheral leukocytes. In: Abstracts of 8th International Congress of Immunology, Hungary, 1992: 454
Neuber K., Hilger R.A., Konig W. Interleukin-3, interleukin-8, FMLP and C5a enhance the release of leukotrienes from neutrophils of patients with atopic dermatitis. Immunology 1991; 73: 83–87
Ruzicka T., Ring J. Enhanced releasability of prostaglandin E2 and leukotrienes B4 and C4 from leukocytes of patients with atopic eczema. Acta Dermatovener (Stockholm) 1987; 67: 469–475
Fogh K. Herlin T., Kragballe K. Eicosanoids in skin of patients with atopic dermatitis: prostaglandin E2 and leukotriene B4 are present in biologically active concentrations. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1989 Feb; 83 (2 Pt 1): 450–455
Ruzicka T., Simmet T., Peskar B.A., et al. Skin levels of arachidonic acid-derived inflammatory mediators and histamine in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol 1986 Feb; 86 (2): 105–108
Sansom J.E., Taylor G.W., Dollery C.T., et al. Urinary leukotriene E4 levels in patients with atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol 1997 May; 136 (5): 790–791
Fauler J., Neumann C., Tsikas D., et al. Enhanced synthesis of cysteinyl leukotrienes in atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol 1993 Jun; 128 (6): 627–630
Talbot S.F., Atkins P.C., Goetzl E.J., et al. Accumulation of leukotriene C4 and histamine in human allergic skin reactions. J Clin Invest 1985; 76: 650–656
Nakayama J., Kiryu H., Hori Y. Leukotriene B4 in patients with atopic dermatitis and other skin diseases: changes by an anti-allergic agent, azelastine hydrochloride. In: Proceeding of the 7th Korea-Japan Joint Meeting of Dermatology, Korea, 1991: 388–397
Spector S., Tan R.A. Antileukotrienes in chronic urticaria. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1998 Apr; 101 (4 Pt 1): 572
Carucci J.A., Washenik K., Weinstein A., et al. The leukotriene antagonist zafirlukast as a therapeutic agent for atopic dermatitis. Arch Dermatol 1998 Jul; 134 (7): 785–786
Woodmansee D.P., Simon R.A. A pilot study examining the role of zileuton in atopic dermatitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 1999 Dec; 83 (6 Pt 1): 548–5452
Van Pelt J.P., De Jong E.M., Seijer M.M., et al. Investigation of a novel and specific leukotriene B4 receptor antagonist in the treatment of stable plaque psoriasis. Br J Dermatol 1998 Sep; 139 (3): 396–402
Yanase D.J., David-Bajar K.M. The leukotriene antagonist montelukast as a therapeutic agent for atopic dermatitis. In: 58th Annual Meeting of American Academy of Dermatology: 2000 Mar 10–15. Poster abstract book. San Francisco: American Academy of Dermatology, 2000
Wenzel S.E., Kamada A.K. Zileuton: the first 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor for the treatment of asthma. Ann Pharmacother 1996 Jul–Aug 30 (7–8): 858–864
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chari, S., Clark-Loeser, L., Shupack, J. et al. A Role for Leukotriene Antagonists in Atopic Dermatitis?. Am J Clin Dermatol 2, 1–6 (2001). https://doi.org/10.2165/00128071-200102010-00001
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00128071-200102010-00001