Summary
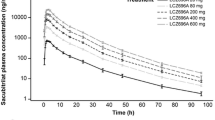
The effect of renal function on the pharmacokinetics of valsartan was investigated in this trial. In order to cover the full spectrum of renal function, a total of 19 subjects with normal renal function and various degrees of renal dysfunction, as determined by creatinine clearance (CLCR), were assigned to four groups: normal renal function (CLCR > 90 ml/min), and mild (CLCR 61 to 90 ml/min), moderate (CLCR 30 to 60 ml/min) and severe (CLCR < 30 ml/min) renal dysfunction. Creatinine clearance was determined following a 24-hour urine collection just prior to drug administration. Each subject received a single oral dose of 80mg of valsartan (capsule) after an overnight fast. Blood samples were collected at frequent intervals up to 48 hours postdose and plasma valsartan concentrations were determined. Pharmacokinetic parameters [area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC), maximum plasma valsartan concentration (Cmax), time to reach Cmax (tmax), and the terminal elimination half-life (t½)] were calculated. Statistical analysis using a cubic polynomial regression function was performed to examine a relationship between renal function and the pharmacokinetic parameters of valsartan.
Scatter plots of pharmacokinetic parameters did not indicate any clear relationship with creatinine clearance. The regression coefficients of linear, quadratic and cubic terms for the AUC and Cmax of valsartan versus renal function were not significantly different from zero. Thus, the pharmacokinetics of valsartan did not correlate with renal function. In addition, no clinically significant adverse experiences were observed in this trial; the 80mg dose of valsartan was well tolerated. Based on these observations, there is no rationale for dosage adjustment of valsartan in patients with impaired renal function.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Criscione L, de Gasparo M, Bühlmayer P, et al. Pharmacological profile of valsartan: a potent, orally active, nonpeptide antagonist of angiotensin II ATI-receptor subtype. Br J Pharmacol 1993; 110: 761–71
Oparil S, Dyke S, Harris F, et al. The efficacy and safety of valsartan compared with placebo in the treatment of patients with essential hypertension. Clin Ther 1996; 18: 797–810
Morice A, Lowry R, Brown M, et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme and cough refelx. Lancet 1987; 2: 1116–8
Singer D, McGregor G. Angioneurotic oedema associated with two angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors. BMJ 1986; 293: 1243
Flesch G, Müller P, Hell F, et al. Absolute bioavailability of valsartan in healthy volunteers. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. In press
Brunner L, Powell M, Degan P, et al. A semi-automated analytical method for the determination of potential antihypertensive agents (CGP 48933 and/or CGP 48369) in human plasma using high performance liquid chromatography. Lab Robot Automat 1994; 6: 171–9
Sioufi A, Marfil F, Jaouen A, et al. The effect of age on the pharmacokinetics of valsartan. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. In press
Waldmeier F, Flesch G, Müller P, et al. Pharmacokinetics, disposition and biotransformation of [14C]-radiolabeled valsartan in healthy male volunteers after a single oral dose. Xenobiotica 1997; 27: 59–71
Acknowledgements
This trial was supported by a grant from Ciba Pharmaceuticals, Summit, New Jersey, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prasad, P., Mangat, S., Choi, L. et al. Effect of Renal Function on the Pharmacokinetics of Valsartan. Clinical Drug Investigation 13, 207–214 (1997). https://doi.org/10.2165/00044011-199713040-00005
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00044011-199713040-00005