Summary
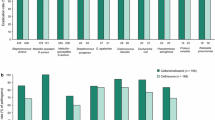
Patients with skin and soft tissue infections were enrolled in a study comparing 2 dosage regimens of orally administered cefpodoxime proxetil; 204 patients with mild to moderate infections received cefpodoxime proxetil 200mg twice daily and 47 patients with severe infections received 400mg twice daily. Both dosage regimens were given for 7 to 14 days. 132 of 142 (93.0%) evaluable patients in the 200mg group and 22 of 29 (75.9%) in the 400mg group were clinically cured post-therapy, the remainder in both groups being classified as improved. The pathogen eradication rate at the end of therapy in the 200mg group was 161 of 165 (97.6%), and 38 of 38 (100%) in the 400mg group. Adverse reactions (drug-related) were reported by 20 (8.0%) patients overall, and there was no apparent relationship between the dosage group and the incidence of adverse reactions. The most commonly reported reactions involved the gastrointestinal tract (diarrhoea) or female genital tract (vaginitis). Cefpodoxime proxetil appears to be a useful and safe agent in the therapy of skin and soft tissue infections.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borin MT, Hughes GS, Spillers CR, Patel RK. Pharmacokinetics of cefpodoxime in plasma and skin blister fluid following oral dosing of cefpodoxime proxetil. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 34: 1094–1099, 1990
Jones RN, Barry AL. Antimicrobial activity and disk diffusion testing of U-76,253A (R-3746), the active metabolite of the new cephalosporin ester, U-76,252 (CS-807). Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 32: 443–449, 1988
Komai T, Kawai K, Tsubaki H, Tokui T, Kinoshita T, et al. Absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of CS-807, a new oral cephem antibiotic, in experimental animals. Chemotherapy (Tokyo) 36: 229–240. 1988
Molthan L. Reidenberg MM, Eichman MF. Positive Coombs’ tests due to cephalothin. New England Journal of Medicine 277: 123. 1967
National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Performance standards for antimicrobial disk susceptibility tests. 4th ed.. NCCLS. Villanova Pennsylvania. 1990
O’Neill P. Nye K. Dounce G. Andrews J. Wise R. Pharmacokinetics and inflammatory fluid penetration of cefpodoxime proxetil in volunteers. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 34: 232–234, 1990
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tack, K.J., Wilks, N.E., Semerdjian, G. et al. Cefpodoxime Proxetil in the Treatment of Skin and Soft Tissue Infections. Drugs 42 (Suppl 3), 51–56 (1991). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-199100423-00010
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-199100423-00010