Summary
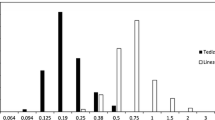
In an open, randomised comparative study, 23 patients with bone, joint or soft tissue infections were treated with ampicillin 2g plus sulbactam 1g 3 times a day or cefotaxime 2g 3 times a day as an initial 2- week therapy. Monoinfections with Staphylococcus aureus were the most common bone or joint infections. Clinical cure or improvement 2 weeks after the end of therapy was observed in all 13 patients treated with sulbactam/ampicillin and in 7 of the 8 patients evaluated for efficacy after treatment with cefotaxime.
Most organisms identified before the onset of therapy were susceptible to the antibiotic randomly selected for therapy, although the majority of infections due to β- lactamase- producing staphylococci could not have been treated with ampicillin without sulbactam. Treatment failed to eradicate S. aureus in 1 patient from each group. In addition, S. aureus infection recurred in 2 patients in the cefotaxime group within 2 weeks after the end of therapy. No serious side effects were observed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Bibliography
English AR, Retsema JA, Girard AE, Lynch JE, Barth WE. CP-43, 899, a β-laclamase inhibitor that extends the antibacterial spectrum of β-lactams: initial bacteriological characterisation. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 14: 414–419. 1978
Loftier L, Bauernfeind A, Keyl WS, Hoffstedt B. Piergies A, et al. An open comparative study of sulbactam plus ampicillin versus cefotaxime as initial therapy for serious soft tissue and bone and joint infections. Reviews of Infectious Diseases 8 (Suppl. 5): S593–S598, 1986
Mackowiak PA, Jones SR, Smith JW. Diagnostic value of sinus tract cultures in chronic osteomyelitis. Journal of the American Medical Association 239: 2772–2775, 1978
Pichichero ME, Friesen HA. Polymicrobial osteomyelitis: report of three cases and review of the literature. Reviews of Infectious Diseases 4: 86–96, 1982
Retsema JA. English AR, Girard AE. CP-45, 899 in combination with penicillin or ampicillin against penicillin-resistant Staphylococcus, Haemophilus influenzae, and Bacteroides. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 17: 615–622, 1980
Templeton WC III, Wawrukiewic A, Melo JC. Schiller MG, Raff MJ. Anaerobic osteomyelitis of long bones. Reviews of Infectious Diseases 5: 692–712, 1983
Waldvogel FA, Medoff G, Schwartz MN. Osteomyelitis: a review of clinical features, therapeutic considerations and unusual aspects. New England Journal of Medicine 282: 198–206, 260-266. 316-322, 1970
Wexler HM, Harris B, Carter WT, Finegold SM. In vitro efficacy of sulbactam combined with ampicillin against anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 27: 876–878, 1985
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Löffler, L., Bauernfeind, A. & Keyl, W. Sulbactam/Ampicillin versus Cefotaxime as Initial Therapy in Serious Soft Tissue, Joint and Bone Infections. Drugs 35 (Suppl 7), 46–52 (1988). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-198800357-00012
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-198800357-00012