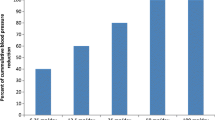
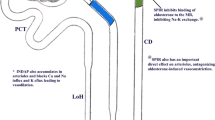
Summary
Indomethacin attenuates the antihypertensive effect of both thiazide diuretics and β-adrenoceptor blocking drugs. The mechanisms of these interactions are poorly understood but sodium and water retention, suppression of plasma renin activity, alterations in adrenoceptor sensitivity and impaired synthesis of vasodilator prostaglandins may all contribute to this effect. Other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may share this property of indomethacin but sulindac, which is a selective inhibitor of extrarenal prostaglandin synthesis, appears not to. This may have important clinical and theoretical implications. Clinicians must beware of this potential interaction in any patient receiving treatment for hypertension.
NSAIDs may also inhibit the natriuretic response to diuretics with resultant adverse effects in patients with heart failure and other forms of oedema. NSAIDs may also have adverse nephrotoxic effects which may be exacerbated by diuretic therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abate, G.; Polimeni, R.M.; Cuccurullo, F.; Puddu, P. and Lenzi, S.: Effects indomethacin on postural hypotension in Parkinsonism. British Medical Journal 2: 1466–1468 (1979).
Armstrong, J.M.; Dusting, G.J.; Moncada, S. and Vane, J.R.: Cardiovascular actions of prostacyclin (PGI2) a metabolite of arachidonic acid which is synthesized by blood vessels. Circulation Research 43(Suppl. 1): 112–119 (1978).
Attallah, A.A.: Interaction of prostaglandins with diuretics. Prostaglandins 18: 369–375 (1979).
Bartter, F.C.; Gill, J.R.; Frolich, J.C.; Bowden, R.E.; Hollifield, J.W. et al.: Prostaglandins are over produced by the kidneys and mediate hyperreninemia in Bartter’s syndrome. Transactions of the Association of American Physicians 89: 77–91 (1976).
Bennett, W.M.; McDonald, W.J.; Kuehnel, E.; Hartnett, M.N. and Porter, G.A.: Do diuretics have antihypertensive properties independent of natriuresis? Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 22: 499–504 (1977).
Birkenhager, W.H.; De Leeuw, P.W.; Wester, A.; Kho, L.T.; Vandongen, R. and Falke, H.E.: Therapeutic effects of β-adrenoceptor blocking agents. Advances in Internal Medicine and Paediatrics 39: 117–134 (1977).
Blair, I.A.; Barrow, S.E.; Waddel, K.A.; Lewis, P.J. and Dollery, C.T.: Prostacyclin is not a circulatory hormone in man. Prostaglandins 23: 579–589 (1982).
Blum, M. and Aviram, A.: Ibuprofen induced hyponatraemia. Rheumatology and Rehabilitation 19: 258–259 (1980).
Brater, D.C.: Analysis of the effect of indomethacin on the response to furosemide in man: Effect of dose of furosemide. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 210: 386–390 (1979).
Buhler, F.R.; Laragh, J.H.; Baer, L.; Vaughan, E.D. and Brunner, H.R.: Propranolol inhibition of renin secretion: A specific approach to diagnosis and treatment of renin-dependent hypertensive diseases. New England Journal of Medicine 287: 1209–1214 (1972).
Chalmers, I.M.; Bell, M.A. and Buchanan, W.W.: Effect of flurbipfrofen on the metabolism of antypyrine in man. Annals of Rheumatic Disease 32: 58–61 (1973).
Chalmers, J.; Ayres, B.; Bune, A.; Graham, J.; West, M. and Wing, L.: Effects of indomethacin, sulindac, naproxen, aspirin and paracetamol in treated hypertensive patients. (Abstract No. 234.) 2nd World Conference on Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics (1983).
Chennavasin, P.; Seiwell, R. and Brater, D.C.: Pharmacokinetic-dynamic analysis of the indomethacin-furosemide interaction in man. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 215: 77–81 (1980).
Ciabattoni, G.; Cinotti, G.A.; Pieruccu, A.; Simonetti, B.M.; Manzi, M. et al.: Effects of sulindac and ibuprofen in patients with chronic glomerular disease. New England Journal of Medicine 310: 279–283 (1984).
Ciabattoni, G.; Pugliese, F.; Cinotti, G.A.; Stirati, G.; Ronci, R. et al.: Characterization of furosemide-induced activation of the renal prostaglandin system. European Journal of Pharmacology 60: 181–187 (1979).
Ciabottoni, G.; Pugliese, F.; Cinotti, G.A. and Patrono, C.: Renal effects of anti-inflammatory drugs. European Journal of Rheumatology and Inflammation 3: 210–221 (1980).
Clive, D.M. and Stoff, J.S.: Renal syndromes associated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. New England Journal of Medicine 31: 563–572 (1984).
Cohn, J.N.: Haemodynamic effects of β-blockers. Drugs 25(Suppl. 2): 100–102 (1983).
Conway, J. and Lauwers, P.: Haemodynamic and hypotensive effects of long-term therapy with chlorothiazide. Circulation 21: 21–27 (1960).
Data, J.L.; Rane, A.; Gierkens, J.; Wilkinson, G.R.; Nies, A.S. and Branch, R.A.: The influence of indomethacin on the pharmacokinetics, diuretic response and haemodynamics of furosemide in the dog. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 206: 431–438 (1978).
Dollery, C.T.; Patterson, J.W. and Connelly, M.E.: Clinical pharmacology of beta receptor blocking drugs. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 10: 765–799 (1969).
Donoso, E.; Cohn, L.J.; Newman, B.J.; Broome, H.S.; Stein, W.G. and Friedberg, C.K.: Effects of propranolol on patients with complete heart block and implanted pacemaker. Circulation 36: 534–538 (1967).
Durao, V.; Martins-Prata, M. and Pires Gonçalves, L.M.: Modification of antihypertensive effect of β-adrenoceptor blocking agents by inhibition of endogenous prostaglandin synthesis. Lancet 2: 1005–1007 (1977).
Dzau, V.J.; Packer, M.; Lilly, L.S.; Swartz, S.L.; Hollenberg, N.K. and Williams, G.H.: Prostaglandins in severe congestive heart failure in relation to activation of the renin-angiotensin system and hyponatremia. New England Journal of Medicine 310: 347–352 (1984).
Eckstein, J.W.; Abboud, F.M. and Pereda, S.A.: Effects of noradrenaline on cardiac output, blood pressure and heart rate in dogs treated with chlorothiazide. Journal of Clinical Investigation 41: 1578–1583 (1962).
Eckstein, J.W.; Wendling, M.G. and Abboud, F.M.: Circulatory responses to noradrenaline after prolonged treatment with chlorothiazide. Circulation Research 28(Suppl. 1): 48–53 (1966).
Elliott, H.C.: Reduced adrenocortical steroid excretion rates in man following aspirin administration. Metabolism 11: 1015–1018 (1962).
Favre, L.; Glasson, P. and Vallotton, M.B.: Reversible acute renal failure with combined triamterene and indomethacin. A study in healthy subjects. Annals of Internal Medicine 96: 317–320 (1982).
Favre, L.; Glasson, P.H.; Riondel, A. and Vallotton, M.B.: Interaction of diuretics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in man. Clinical Science 64: 407–415 (1983).
Fitzgerald, G.A.; Brash, A.R.; Falardeau, P. and Oates, J.A.: Estimated rate of prostacyclin secretion into the circulation of normal man. Journal of Clinical Investigation 68: 1272–1276 (1981).
Feely, J. and Wood, A.J.J.: Effect of inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis on hepatic drug clearance. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 15: 109–111 (1983).
Fowler, R.W. and Arnold, K.G.: Non-steroidal analgesic and anti-inflammatory agents. British Medical Journal 287: 835 (1983).
Friedman, P.L.; Brown, E.J.; Gunther, S.; Alexander, R.W.; Barry, W.H.; Mudge, G.H. and Grossman, W.: Coronary vasoconstrictor effect of indomethacin in patients with coronary-artery disease. New England Journal of Medicine 305: 1171–1175 (1981).
Fries, E.D.; Wanko, A.; Schnaper, H.W. and Frolich, E.D.: Mechanism of altered blood pressure responsiveness produced by chlorothiazide. Journal of Clinical Investigation 39: 1277–1281 (1960).
Frolich, E.D.; Tarazi, R.C.; Dunstan, H.C. and Page, I.H.: The paradox of beta adrenergic blockade in hypertension. Circulation 37: 417–423 (1968).
Frolich, J.C.; Hollifield, J.W.; Dormois, J.C.; Frolich, B.L.; Seyberth, H.; Michelakis, A.M. and Oates, J.A.: Suppression of plasma renin activity by indomethacin in man. Circulation Research 39: 447–452 (1976).
Glasson, P.; Gaillard, R.; Riondel, A. and Vallotton, M.B.: Role of renal prostaglandins and relationships to renin aldosterone and antidiuretic hormone during salt depletion in man. J. Clin. Endocrin. Metab. 49: 176–181 (1979).
Goldszer, R.C.; Goodley, E.L.; Rosner, M.J.; Simons, W.M. and Schwartz, A.B.: Hyperkalemia associated with indomethacin. Archives of Internal Medicine 141: 802–804 (1981).
Guyton, A.C.; Coleman, T.G.; Cowley, A.W.; Manning, R.O.; Norman, R.A. and Ferguson, J.D.: A system analysis approach to understanding long-range arterial blood pressure control. Circulation Research 35: 159–176 (1974).
Harms, H.H.; Gooren, L.; Spoelstra, A.J.G.; Hesse, C. and Verschoor, L.: Blockade of isoprenaline-induced changes in plasma free fatty acids. immunoreactive insulin levels and plasma renin activity in healthy subjects, by propranolol, pindolol, practolol, atenolol, metoprolol and acebutolol. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 5: 19–26 (1978).
Hollifield, J.W.; Sherman, K.; van der Zwagg, R. and Shand, D.G.: Proposed mechanism of propranolol’s antihypertensive effect in essential hypertension. N. Eng. J. Med. 295: 68–73 (1976).
Jackson, E. and Duff, R.S.: Effect of chlorothiazide on noradrenaline vasoconstriction in man. Clinical Science 24: 24–27 (1963).
Jones, B. and Nanra, R.S.: Double-blind trial of antihypertensive effects of chlorothiazide in severe renal failure. Lancet 2: 1258–1260 (1979).
Koopmans, P.P.; Thien, Th. and Gribnau, F.W.J.: Influence of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on diuretic treatment of mild to moderate essential hypertension. British Medical Journal 289: 1492–1494 (1984).
Kramer, H.G.; Dusing, R.; Stinnesbeck, B.; Prior, W.; Backer, A. et al.: Interactions of conventional and antikaliuretic diuretics with the renal prostaglandin system. Clinical Science 59: 67–70 (1980).
Langer, S.Z.: The role of α and β presynaptic receptors in the regulation of noradrenaline release elicited by nerve stimulation. Clinical Science 51(Suppl. 3): 421–426 (1976).
Lewis, P.J.: Propranolol — an antihypertensive drug with a central action; in Davies and Reid (Eds) Central Actions of Drugs in Blood Pressure Regulation, pp. 206–213 (Pitman Medical, Tunbridge Wells 1975).
Lewis, R.V.; Toner, J.M.; Jackson, P.R. and Ramsey, L.E.: Effects of sulindac and indomethacin on the blood pressure of hypertensive patients. (Abstract C44.) Proceedings of the British Pharmacological Society (1985).
Lopez-Ovejero, J.A.; Weber, M.A.; Drayer, J.I.M.; Sealey, J.E. and Laragh, J.H.: Effects of indomethacin alone and during diuretic or β-adrenoceptor-blockade therapy on blood pressure and the renin system in essential hypertension. Clinical Science and Molecular Medicine 55(Suppl. 4): 203S–205S (1978).
Mackay, G.; Muir, A.L. and Watson, M.L.: Contribution of prostaglandins to the systemic and renal vascular responses to frusemide in normal man. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 17: 513–519 (1984).
Nowak, J. and Wennmalm, A.: Influence of indomethacin and of prostaglandin E, on total and regional blood flow in man. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica 102: 484–491 (1978).
Oliw, E.; Kover, G.; Larsson, C. and Anggard, E.: Reduction by indomethacin of furosemide effects in the rabbit. European Journal of Pharmacology 38: 95–100 (1976).
Patak, R.V.; Mookerjee, B.K.; Bentzel, C.J.; Hysert, P.E.; Babej, M. and Lee, J.B.: Antagonism of the effects of furosemide by indomethacin in normal and hypertensive man. Prostaglandins 10: 649–658 (1975).
Ramsay, L.E.; Harrison, I.R.; Shelton, J.R. and Vose, C.W.: Influence of acetylsalicylic acid on the renal handling of a spironolactoine metabolite in healthy subjects. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 10: 43–48 (1976).
Rolf Smith, S.; Gibson, R.; Bradley, D. and Kendall, M.J.: Failure of indomethacin to modify adrenoceptor blockade. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 15: 267–268 (1983).
Rubin, P.; Jackson, G., and Blaschke, T.: Studies on the clinical pharmacology of prazosin II: The influence of indomethacin and of prazoson on the action and disposition of prazosin. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 10: 33–39 (1980).
Salvetti, A.; Arzilli, F.; Pedrinelli, R.; Beggi, P. and Motolese, M.: Interaction between oxprenolol and indomethacin on blood pressure in essential hypertension patients. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 22: 197–201 (1982a).
Salvetti, A.; Pedrinelli, R.; Magagna, A. and Abdel-Haq, B.: The influence of indomethacin on some pharmacological actions of atenolol; in Dunn et al. (Eds). Prostaglandins and the Kidney, pp. 287–295, (Plenum, New York, 1982b).
Salvetti, A.; Pedrinelli, R.; Magagna, A. and Ugenti, P.: Differential effects of selective and non-selective prostaglandin synthesis inhibition on the pharmacological responses to captopril in patients with essential hypertension. Clinical Science 63: 261S–263S (1982c).
Salvetti, A.; Pedrinelli, R.; Alberici, P.; Magagna, A. and Abdel-Haq, B.: The influence of indomethacin and sulindac on some pharmacological actions of atenolol in hypertensive patients. Brit. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 17(Suppl. 1): 108S–111S (1984).
Scherer, B. and Weber, P.C.: Time dependent changes in prostaglandin excretion in response to frusemide in man. Clinical Science 56: 77–81 (1979).
Steiness, E. and Waldorff, S.: Different interactions of indomethacin and sulindac with thiazides in hypertension. British Medical Journal 285: 1702–1703 (1982).
Tarazi, R.C. and Dunstan, H.P.: Beta adrenergic blockade in hypertension. Practical and theoretical implications of long term haemodynamic variations. American Journal of Cardiology 29: 633–640 (1972).
Tweeddale, M.G. and Ogilvie, R.I.: Antagonism of spironolactone-induced natriuresis by aspirin in man. New England Journal of Medicine 289: 198–200 (1973).
Yeung, Laiwah, A.C. and Mactier, R.A.: Antagonistic effect of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on frusemide-induced diuresis in cardiac failure. Brit. Med. J. 283: 714A (1981).
Walker, R.M.; Brown, R.S. and Stoff, J.S.: Role of renal prostaglandins during antidiuresis and water diuresis in man. Kidney International 21: 365–370 (1981).
Watkins, J.; Carl Abbott, E.; Hensby, C.N.; Webster, J. and Dollery, C.T.: Attenuation of hypotensive effect of propranolol and thiazide diuretics by indomethacin. British Medical Journal 281: 702–705 (1980).
Webster, J.; Hawksworth, G.M.; McLean, I. and Petrie, J.C.: Flurbiprofen interaction with single doses of atenolol and propranolol. Brit. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 18: 861–866 (1984).
Webster, J.; Hensby, C.N.; Dollery, C.T. and Friedman, L.A.: The antihypertensive action of bendroflumethiazide-increased prostacyclin production. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 28: 751–758 (1980).
Weinberger, M.H.; Ramsdell, J.W.; Rosner, D.R. and Geddes, J.J.L.: Effect of chlorothiazide and sodium on vascular responsiveness to angiotensin II. American Journal of Physiology 223: 1049–1052 (1972).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Webster, J. Interactions of NSAIDs with Diuretics and β-Blockers. Drugs 30, 32–41 (1985). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-198530010-00004
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-198530010-00004