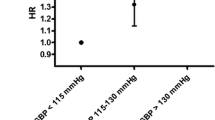
Summary
Intra-arterial ambulatory blood pressure was measured over a 24-hour period in 34 patients with untreated hypertension then randomised to either atenolol, metoprolol, pindolol, or long acting propranolol. A second intra-arterial recording was made after the drugs had been taken once daily for 3 to 8 months and was started 4 hours after the last dose. Atenolol (mean dose 128mg) significantly lowered mean arterial pressure for all 24/24 recorded hours, metoprolol (311mg) for 12/24h, pindolol (33mg) for 15/24h and long acting propranolol (45 7mg) for 22/24h. Atenolol and long acting propranolol reduced the variability of systolic blood pressure. Significant bradycardia was seen with atenolol for 20/24h, metoprolol for 20/24h, pindolol for 10/24h and long-acting propranolol for 24/24h.
Atenolol and long acting propranolol are effective antihypertensive agents when taken once daily; metoprolol and pindolol need to be given more frequently, although pindolol, having partial agonist activity, may raise heart rate and attenuate the fall in blood pressure during sleep.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amery, A.; DePlaen, J.F.; Lijnen, P.; McAinsh, J. and Reybrouck, T.: Relationship between blood level of atenolol and pharmacologic effect. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 21: 691–699 (1977).
Castleden, C.M.; Duthan, J.R.E. and George, C.F.: A comparison of once and twice daily atenolol in hypertension. Postgraduate Medical Journal 53: 679–682 (1977).
Douglas-Jones, A.P.; Baber, N.S. and Lee, A.: Once daily propranolol in the treatment of mild to moderate hypertension. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 14: 163–166 (1978).
Douglas-Jones, A.P. and Cruickshank, J.M.: Once-daily dosing with atenolol in patients with mild or moderate hypertension. British Medical Journal 1: 990–991 (1976).
Erikssen, J.; Nundal, R.; Thaulow, E. and Nitter-Hauge, S.: Dosing intervals in beta-blocking therapy. Lancet 2: 800–801 (1980).
Floras, J.S.; Jones, J.V.; Fox, P.; Hassan, M.O.; Turner, K.L. and Sleight, P.: The effect of long-term, once-daily administration of atenolol on the blood pressure of hypertensive subjects. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 3: 958–964 (1981).
Frithz, G.: Pindolol once daily in the treatment of hypertension. Upsala Journal of Medical Sciences 81: 151–154 (1976).
Gould, B.A.; Mann, S.; Altman, D. and Raftery, E.B.: Can placebo therapy in clinical trials really influence the blood pressure? Clinical Science 61 (Suppl.): 487s–490s (1981).
Gugler, R. and Bodem, G.: Single and multiple dose pharmacokinetics of pindolol. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 13: 13–16 (1978).
Jeffers, T.A.; Webster, J.; Petrie, J.C. and Barker, N.P.: Atenolol once daily in hypertension. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 4: 523–527 (1977).
Karlberg, B.E.; Nilsson, I.; Tolagen, K.; Netelius, E. and Waern, U.: Once daily treatment with metoprolol in primary hypertension. Effects on blood pressure in relation to plasma renin activity, urinary aldosterone excretion and the concentration of metoprolol in plasma. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 25: 399–407 (1979).
Littler, W.A.; Honour, A.J.; Pugsley, D.J. and Sleight, P.: Continuous recording of direct arterial pressure in unrestricted patients; its role in the diagnosis and mangement of high blood pressure. Circulation 51: 1101–1106 (1975).
Littler, W.A.; Honour, A.J.; Sleight, P. and Stott, F.D.: Continuous recording of direct arterial pressure and electrocardiogram in unrestricted man. British Medical Journal 3: 76–78 (1972).
Mann, S.; Millar-Craig, M.W.; Altman, D.; Melville, D. and Raftery, E.B.: The effects of metoprolol on ambulatory blood pressure. Clinical Science 57 (Suppl. 5): 375s–337s (1979).
Mann, S.; Millar-Craig, M.W.; Balasubramanian, V.; Cashman, P.M. and Raftery, E.B.: Ambulant blood pressure: reproducibility and the assessment of interventions. Clinical Science 59: 497–500 (1980).
Mann, S.; Millar-Craig, M.W.; Balasubramanian, V. and Raftery, E.B.: Propranolol LA and ambulatory blood pressure. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 10: 443–447 (1980).
Marshall, A.J.; Barritt, D.W. and Harry, J.D.: Dose response and frequency of administration of atenolol in essential hypertension — once daily treatment with beta-blockade. Postgraduate Medical Journal 53 (Suppl. 3): 168–172 (1977).
Mehta, S.K.; Walsh, J.T.; Moni, K. and Goldberg, A.D.: Single daily dosage of acebutolol in hypertensives; the effect on the circadian rhythms as measured with 24 hour blood pressure monitoring; in Stott et al. (Eds) ISAM 1979, pp. 197–202 (Academic Press, London 1980).
Millar-Craig, M.W.; Mann, S.; Balasubramanian, V.; Altman, D. and Raftery, E.B.: The acute and chronic effects of oxprenolol on ambulatory blood pressure and heart rate in essential hypertension. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 8: 389p (1979).
Petrie, J.C.; Jeffers, T.A.; Robb, O.J.; Scott, A.R. and Webster, J.: Atenolol, sustained-release oxprenolol and long acting propranolol in hypertension. British Medical Journal 2: 1573–1574 (1980).
Reybrouck, T.; Amery, A.; Fagard, R.; Jousten, P.; Ligmen, P. and Meulpas, E.: Beta-blockers: Once or three times a day? British Medical Journal 1: 1386–1388 (1978).
Sleight, P.; Floras, J.S. and Jones, J.V.: Automatic analysis of continuous intra-arterial blood pressure recordings; in Clement (Ed.) Blood Pressure Variability, pp. 61–66 (MTP Pressr Lancaster 1979).
Stott, F.D.: The Oxford portable blood pressure transducer; in Clement (Ed.) Blood Pressure Variability, pp. 55–60 (MTP Press, Lancaster 1979).
Taub, Y.M. and Rosenfeld, J.B.: Once a day pindolol in hypertension. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 21: 588–592 (1977).
Vaughan-Williams, E.M.; Hassan, M.O.; Floras, J.S.; Sleight, P. and Jones, J.V.: Adaption of hypertensives to treatment with cardioselective and non-selective beta-blockers. Absence of correlation between bradycardia and blood pressure control, and reduction in the slope of the Q-T/R-R relation. British Heart Journal 44: 473–487 (1980).
Watson, R.D.S.; Stallard, T.J. and Littler, W.A.: Influence of once-daily administration of beta-adrenoceptor antagonists on arterial pressure and its variability. Lancet 1: 1210–1213 (1979).
West, M.J.; Sleight, P. and Honour, A.J.: Clinical trial of the beta-adrenoceptor blocking agent tolamolol with the use of 24 hour blood pressure recordings. Clinical Science and Molecular Medicine 51 (Suppl.): 545s–547s (1976).
Wilson, M.; Morgan, G. and Morgan, T.: The effect on blood pressure of beta-adrenoceptor blocking drugs administered once daily and their duration of action when therapy is ceased. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 3: 857–861 (1976).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Floras, J.S., Hassan, M.O., Jones, J.V. et al. Ambulatory Blood Pressure and its Variability During Randomised Double-blind Administration of Atenolol, Metoprolol, Pindolol and Long Acting Propranolol in Subjects with Mild to Moderate Hypertension. Drugs 25 (Suppl 2), 19–25 (1983). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-198300252-00005
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-198300252-00005