Abstract
Objective
To perform a comparative quantitative evaluation of the prediction accuracy for human hepatic metabolic clearance of 5 different mathematical models: allometric scaling (multiple species and rat only), physiologically based direct scaling, empirical in vitro-in vivo correlation, and supervised artificial neural networks.
Methods
The mathematical prediction models were implemented with a publicly available dataset of 22 extensively metabolised compounds and compared for their prediction accuracy using 3 quality indicators: prediction error sum of squares (PRESS), r2 and the fold-error.
Results
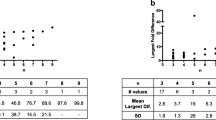
Approaches such as physiologically based direct scaling, empirical in vitro-in vivo correlation and artificial neural networks, which are based on in vitro data only, yielded an average fold-error ranging from 1.64 to 2.03 and r2 values greater than 0.77, as opposed to r2 values smaller than 0.44 when using allometric scaling combining in vivo and in vitro preclinical data. The percentage of successful predictions (less than 2-fold error) ranged from 55% (rat allometric scaling) to between 64 and 68% with the other approaches.
Conclusions
On the basis of a diverse set of 22 metabolised drug molecules, these studies showed that the most cost-effective and accurate approaches, such as physiologically based direct scaling and empirical in vitro-in vivo correlation, are based on in vitro data alone. Inclusion of in vivo preclinical data did not significantly improve prediction accuracy; the prediction accuracy of the allometric approaches was at the lower end of all methods compared.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lavé T, Coassolo P, Reigner B. Prediction of hepatic metabolic clearance based on interspecies allometric scaling techniques and in vitro-in vivo correlations. Clin Pharmacokinet 1999; 36: 211–31
Lavé T, Dupin S, Schmitt C, et al. Integration of in vitro data into allometric scaling to predict hepatic metabolic clearance in man: application to 10 extensively metabolized drugs. J Pharm Sci 1997; 86: 584–90
Lavé T, Dupin S, Schmitt C, et al. The use of human hepatocytes to select compounds based on their expected hepatic extraction ratios in humans. Pharm Res 1997; 14: 152–5
Cross DM, Bayliss MK. A commentary on the use of hepatocytes in drug metabolism studies during drug discovery and development. Drug Metab Rev 2000; 32: 219–40
Bayliss MK, Bell JA, Jenner WN, et al. Utility of hepatocytes to model species differences in the metabolism of loxtidine and to predict pharmacokinetic parameters in rat, dog and man. Xenobiotica 1999; 29: 253–68
Iwatsubo T, Hirota N, Ooie T, et al. Prediction of in vivo drug disposition from in vitro data based on physiological pharmacokinetics. Biopharm Drug Dispos 1996; 17: 273–310
Iwatsubo T. Prediction of in vivo drug metabolism in the human liver from in vitro metabolism data. Pharmacol Ther 1997; 73: 147–71
Ito K, Iwatsubo T, Kanamitsu S, et al. Quantitative prediction of in vivo drug clearance and drug interactions from in vitro data on metabolism, together with binding and transport. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 1998; 38: 461–99
Izumi T, Enomoto S, Hosiyama K, et al. Prediction of the human pharmacokinetics of troglitazone, a new and extensively metabolized antidiabetic agent, after oral administration, with an animal scale-up approach. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1996; 277: 1630–41
Iwatsubo T, Suzuki H, Sugiyama Y. Prediction of species differences (rats, dogs, humans) in the in vivo metabolic clearance of YM796 by the liver from in vitro data. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1997; 283: 462–9
Iwatsubo T. Prediction of in vivo hepatic metabolic clearance of YM796 from in vitro data by use of human liver microsomes and recombinant P-450 isozymes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1997; 282: 909–19
Obach RS, Baxter JG, Liston TE, et al. The prediction of human pharmacokinetic parameters from preclinical and in vitro metabolism data. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1997; 283: 46–58
Houston JB. Utility of in vitro drug metabolism data in predicting in vivo metabolic clearance. Biochem Pharmacol 1994; 47: 1469–79
Obach RS. Prediction of human clearance of 29 drugs from hepatic microsomal intrinsic clearance data: an examiniation of in vitro half-life approach and nonspecific binding to microsomes. Drug Metab Dispos 1999; 27: 1350–9
Boxenbaum H, Fertig JB. Scaling of antipyrine intrinsic clearance of unbound drug in 15 mammalian species. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 1984; 9: 177–83
Campbell DB. Can allometric interspecies scaling be used to predict human kinetics. Drug Inf J 1994; 28: 235–45
Mordenti J. Man versus beast: pharmacokinetic scaling in mammals. J Pharm Sci 1986; 75: 1028–40
Lavé T, Coassolo P, Ubeaud G, et al. Interspecies scaling of bosentan, a new endothelin receptor antagonist and integration of in vitro data into allometric scaling. Pharm Res 1996; 13: 97–101
Lavé T, Dupin S, Schmitt M, et al. Interspecies scaling of tolcapone, a new inhibitor of catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT): use of in vitro data from hepatocytes to predict metabolic clearance in animals and humans. Xenobiotica 1996; 26: 839–51
Schneider G, Coassolo P, Lavé T. Combining in vitro and in vivo pharmacokinetic data for prediction of hepatic drug clearance in humans by artificial neural networks and multivariate statistical techniques. J Med Chem 1999; 42: 5072–6
Kachigan SK. Multivariate statistical analysis: a conceptual introduction. New York: Radius Press, 1991
Mathews JH. Numerical methods for mathematics, science, and engineering. Englewood Cliffs (NJ): Prentice Hall, 1992
Hussain AS, Johnson RD, Vachharajani NN, et al. Feasibility of developing a neural network for prediction of human pharmacokinetic parameters from animal data. Pharm Res 1993; 10: 466–9
Erb RJ. The backpropagation neural network — a Bayesian classifier: introduction and applicability to pharmacokinetics. Clin Pharmacokinet 1995; 29: 69–79
Gobburu JV, Chen EP. Artificial neural networks as a novel approach to integrated pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic analysis. J Pharm Sci 1996; 85: 505–10
Schneider G, Wrede P. Artificial neural networks in computer-based molecular design. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 1998; 70: 175–222
Rosenblatt F. Principles of neurodynamics. New York: Spartan, 1962
Minsky ML. Perceptrons. Cambridge: MIT Press, 1969
Hertz J, Krogh A, Palmer RG, eds. Introduction to the theory of neural computation. Redwood City (CA): Addison-Wesley, 1991
Bishop M. Neural networks for pattern recognition. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1995
Ripley BD. Pattern recognition and neural networks. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1996
Brown PJ. Measurement, regression, and calibration. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1993
Höskuldsson A. PLS regression models. J Chemother 1988; 2: 211–28
Helland IS. Partial least squares regression and statistical methods. Scand J Stat 1990; 17: 97–114
Garthwaite PH. An interpretation of partial least squares. J Am Stat Assoc 1994; 89: 122–7
Boxenbaum H. Interspecies pharmacokinetic scaling and the evolutionary-comparative paradigm. Drug Metab Rev 1984; 15: 1071–121
Boxenbaum H, Dilea C. First-time-in-human dose selection: allometric thoughts and perspectives. J Clin Pharmacol 1995; 35: 957–66
Rowland M, Tozer T. Clinical pharmacokinetics: concepts and applications. Philadelphia (PA): Lea and Febiger, 1989
Houston JB, Carlile DJ. Prediction of hepatic clearance from microsomes, hepatocytes, and liver slices. Drug Metab Rev 1997; 29: 891–922
Houston JB, Kenworthy KE. In vitro-in vivo scaling of CYP kinetic data not consistent with the classical Michaelis-Menten model. Drug Metab Dispos 2000; 28: 246–54
Reibnegger G, Weiss G, Werner-Felmayer G, et al. Neural networks as a tool for utilizing laboratory information: comparison with linear discriminant analysis and with classification and regression trees. Proc Natl Acad Sci 1991; 88: 11426–30
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zuegge, J., Schneider, G., Coassolo, P. et al. Prediction of Hepatic Metabolic Clearance. Clin Pharmacokinet 40, 553–563 (2001). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-200140070-00006
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-200140070-00006