Summary
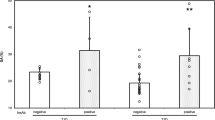
We examined the plasma protein binding of an acidic drug (warfarin bound to albumin) and a basic drug [lidocaine (lignocaine) bound to α1-acid glycoprotein] in 15 patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) and 15 matched controls. We also examined protein binding of warfarin and lidocaine in 30 patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes (NIDDM) and 25 controls. Compared with control, the binding of both warfarin (98.81 ± 0.02 vs 98.57 ± 0.03%, mean ± SEM) and of lidocaine (69 ± 2 vs 58 ± 2%) was significantly reduced in IDDM. This group had lower concentrations of both albumin and α1-acid glycoprotein (AAG), achieving statistical significance vs control for albumin only. In the patients with NIDDM, who had a similar level of glycosylated haemoglobin, while there was no significant difference in the binding of lidocaine there was a significant increase in warfarin binding compared with the control population (99.01 ± 0.03 vs 98.82 ± 0.04%). This study suggests that binding of both acidic and basic drugs is altered in both IDDM and NIDDM.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dengler TJ, Robertz-Vaupel GM, Dengler HJ. Endogenous ligands and structural changes inhibit binding to human serum albumin in chronic renal failure. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 36 (Suppl. 1): A65, 1989
Erill S, Calvo R. Plasma protein carbamylation and decreased acidic drug protein binding in uraemia. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 27: 612–618, 1980
Gatti G, Crema F, Attardo-Partinello G, Fratino P, Aguzzi P, et al. Serum protein binding of Phenytoin and valproic acid in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring 9: 389–391, 1987
Gulyassy PF, Bottini AT, Jarrard EA, Stanfel LA. Isolation of inhibitors of ligand: albumin-binding from uraemic body fluids and normal urine. Kidney International 16 (Suppl.): S238–S242, 1983
Gwilt PR, Nahhas RR, Tracewell WG. The effects of diabetes mellitus on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in humans. Clinical Pharmacokinetics 20: 477–490, 1991
Kemp SF, Kearns GL, Turley CP. Altered Phenytoin binding in children with epilepsy. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 41: 170, 1987
Kremer JMH, Wilting J, Janssen LHM. Drug binding to human alpha-1-acid glycoprotein in health and disease. Pharmacological Reviews 40: 1–47, 1988
Mereish KA, Rosenberg H, Cobby I. Glucosylated albumin and its influence on salicylate binding. Journal of Pharmaceutical Science 71: 235–238, 1982
O’Connor P, Feely J. Clinical pharmacokinetics and endocrine disorders: therapeutic implications. Clinical Pharmacokinetics 13: 345–364, 1987
Ruiz-Cabello F, Erill S. Abnormal serum protein binding of acidic drugs in diabetes mellitus. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 36: 691–695, 1984
Zini R, Riant P, Barré J, Tillement JP. Disease-induced variations in plasma protein levels: implications for drug dosage regimens (Part I). Clinical Pharmacokinetics 19: 147–159, 1990
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
O’Byrne, S., Barry, M.G., Collins, W.C.J. et al. Plasma Protein Binding of Lidocaine and Warfarin in Insulin-Dependent and Non-Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 24, 183–186 (1993). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-199324020-00007
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-199324020-00007