Abstract
Background
Previous studies have proposed the association between pemphigus and several autoimmune diseases, but no large-scale study has been reported.
Objectives
To delineate the association between pemphigus and autoimmune diseases including psoriasis.
Materials & Methods
A total of 1,998 patients with pemphigus and 7,992 control subjects were enrolled from the National Health Insurance Research Database in Taiwan from 1997 to 2010. The odds of comorbidities between these two groups were analysed by multivariate logistic regression.
Results
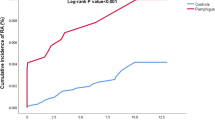
Compared with control subjects, patients with pemphigus were much more likely to have Sjögren’s syndrome (odds ratio [OR]: 15.0; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 3.16-71.5), psoriasis (OR: 7.18; 95% CI: 5.55-9.29), systemic lupus erythematosus (OR: 4.46; 95% CI: 1.88-10.6), and alopecia areata (OR: 2.68; 95% CI: 1.26-5.67). According to gender-stratified analyses, however, the association between pemphigus and Sjögren’s syndrome or alopecia areata was found to be significant only in the female patients.
Conclusion
We confirm the association between pemphigus and some autoimmune diseases, including Sjögren’s syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus, and alopecia areata. In addition, we present the novel finding that patients with pemphigus have an increased risk of psoriasis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Callen JP. Internal disorders associated with bullous disease of the skin. A critical review. J Am Acad Dermatol 1980; 3: 107–19.
Leshem YA, Katzenelson V, Yosipovitch G, David M, Mimouni D. Autoimmune diseases in patients with pemphigus and their first-degree relatives. Int J Dermatol 2011; 50: 827–31.
Parameswaran A, Attwood K, Sato R, Seiffert-Sinha K, Sinha AA. Identification of a new disease cluster of pemphigus vulgaris with autoimmune thyroid disease, rheumatoid arthritis and type I diabetes. Br J Dermatol 2015; 172: 729–38.
Ansar A, Farshchian M, Farahnaki S, Farshchian M. Thyroid autoimmunity in Iranian patients with pemphigus vulgaris. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2009; 23: 719–20.
Daneshpazhooh M, Behjati J, Hashemi P, et al. Thyroid autoimmunity and pemphigus vulgaris: is there a significant association? J Am Acad Dermatol 2010; 62: 349–51.
Chen YT, Chen YJ, Hwang CY, et al. Comorbidity profiles in association with vitiligo: a nationwide population-based study in Taiwan. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2015; 29: 1362–9.
Somers EC, Thomas SL, Smeeth L, Hall AJ. Autoimmune diseases cooccurring within individuals and within families: a systematic review. Epidemiology 2006; 17: 202–17.
Chu SY, Chen YJ, Tseng WC, et al. Comorbidity profiles among patients with alopecia areata: the importance of onset age, a nationwide population-based study. J Am Acad Dermatol 2011; 65: 949–56.
Zhao Y, Li Y, Wang L, et al. Primary Sjogren syndrome in Han Chinese: clinical and immunological characteristics of 483 patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 2015; 94: e667.
Wilczek A, Sticherling M. Concomitant psoriasis and bullous pemphigoid: coincidence or pathogenic relationship? Int J Dermatol 2006; 45: 1353–7.
Ohata C, Ishii N, Koga H, et al. Coexistence of autoimmune bullous diseases (AIBDs) and psoriasis: a series of 145 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol 2015; 73: 50–5.
Tsai TF, Wang TS, Hung ST, et al. Epidemiology and comorbidities of psoriasis patients in a national database in Taiwan. J Dermatol Sci 2011; 63: 40–6.
Morita E, Amagai M, Tanaka T, Horiuchi K, Yamamoto S. A case of herpetiform pemphigus coexisting with psoriasis vulgaris. Br J Dermatol 1999; 141: 754–5.
Daulat S, Detweiler JG, Pandya AG. Development of pemphigus vulgaris in a patient with psoriasis treated with etanercept. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2009; 23: 483–4.
Caldarola G, Carbone A, De Simone C, Pellicano R. Development of pemphigus vulgaris in a patient with psoriasis treated with cyclosporine. J Am Acad Dermatol 2010; 63: 356–7.
Kurtzman DJ, Christopher M, Lian F, Sligh JE. A blistering response: concurrent psoriasis and pemphigus foliaceus. Am J Med 2015; 128: 24–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Chiu, YW., Chen, YD., Hua, TC. et al. Comorbid autoimmune diseases in patients with pemphigus: a nationwide case-control study in Taiwan. Eur J Dermatol 27, 375–381 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1684/ejd.2017.3060
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1684/ejd.2017.3060